A 45 Year Old Man Had Coronary Artery Stents
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
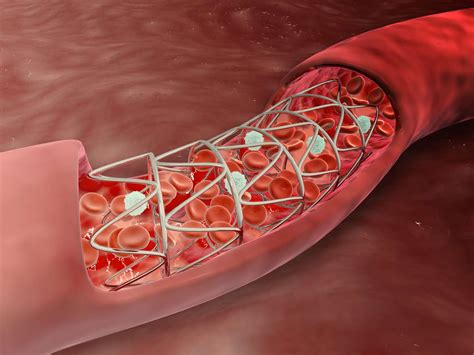
Table of Contents
A 45-Year-Old Man and Coronary Artery Stents: Understanding the Procedure, Recovery, and Long-Term Outlook
For a 45-year-old man, a coronary artery stent procedure can feel like a life-altering event. This article delves deep into the experience, addressing the procedure itself, the recovery process, long-term lifestyle adjustments, and the emotional impact of such a diagnosis and treatment. We'll explore the common causes leading to this situation in younger individuals, and highlight the importance of proactive heart health.
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) in Younger Men
Coronary artery disease (CAD), often associated with older individuals, is increasingly affecting younger populations. While risk factors like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and family history play significant roles, other contributing factors may be at play in younger men. These can include:
- Metabolic Syndrome: A cluster of conditions – increased waist circumference, high triglycerides, low HDL cholesterol, high blood pressure, and elevated fasting blood sugar – significantly elevates the risk of CAD.
- Obesity and Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle coupled with excessive weight contributes to various cardiovascular risks.
- Stress and Anxiety: Chronic stress can negatively impact cardiovascular health, potentially accelerating the development of CAD.
- Poor Diet: A diet lacking in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while rich in saturated and trans fats, contributes significantly to poor heart health.
- Substance Abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, and smoking dramatically increase the risk of CAD.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of premature heart disease can be a significant risk factor.
The symptoms of CAD can vary, and often go unnoticed in early stages. Chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, and discomfort in the jaw, neck, or back are common indicators. However, some individuals, especially younger men, might experience atypical symptoms or no symptoms at all (silent ischemia). This highlights the importance of regular check-ups and proactive health monitoring.
The Coronary Artery Stent Procedure: A Detailed Overview
A coronary artery stent is a small, metal mesh tube placed inside a narrowed or blocked coronary artery to improve blood flow to the heart. The procedure, known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is minimally invasive and typically involves the following steps:
1. Catheterization: Accessing the Coronary Arteries
A thin, flexible tube (catheter) is inserted into an artery in the groin or wrist and guided to the coronary arteries using X-ray guidance.
2. Angiography: Visualizing the Blockage
A contrast dye is injected through the catheter, allowing the doctor to visualize the coronary arteries and identify the location and extent of the blockage.
3. Stent Deployment: Restoring Blood Flow
A balloon-tipped catheter is advanced to the narrowed artery. The balloon is inflated, compressing the plaque against the artery wall, widening the passage. A stent, pre-mounted on the catheter, is then deployed to keep the artery open.
4. Post-Procedure Monitoring: Ensuring Success
Following stent placement, the catheter is removed, and the puncture site is carefully closed. The patient is monitored closely for any complications.
Recovery After Stent Placement: A Gradual Return to Normalcy
Recovery after a stent procedure varies depending on individual factors, but generally involves:
1. Hospital Stay: Short and Focused
The hospital stay is typically short, ranging from a few hours to a day or two.
2. Medication Management: Preventing Future Blockages
A regimen of medications, including antiplatelet agents (to prevent blood clot formation), statins (to lower cholesterol), and potentially other medications like beta-blockers or ACE inhibitors, is crucial for long-term health. Strict adherence to the prescribed medication schedule is vital.
3. Gradual Return to Activity: Listen to Your Body
Physical activity should be resumed gradually. A cardiac rehabilitation program is highly recommended to help patients safely regain strength and stamina.
4. Dietary Changes: Fueling Heart Health
Adopting a heart-healthy diet is essential. This includes reducing saturated and trans fats, increasing fiber intake, and consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
5. Stress Management: A Holistic Approach
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or counseling can significantly contribute to recovery and long-term heart health.
Long-Term Outlook and Lifestyle Adjustments: Living with a Stent
Living with a stent requires ongoing commitment to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This includes:
- Regular Follow-Up Appointments: Consistent check-ups with the cardiologist are crucial for monitoring stent patency and overall heart health.
- Medication Adherence: Maintaining the prescribed medication regimen is critical in preventing future complications.
- Healthy Diet and Exercise: A balanced diet and regular physical activity are non-negotiable for sustained cardiovascular health.
- Stress Management Techniques: Employing effective stress management techniques promotes overall well-being and heart health.
- Smoking Cessation: If the patient smokes, quitting immediately is paramount.
- Regular Blood Tests: Monitoring cholesterol and blood sugar levels regularly is vital.
The Emotional Impact: Coping with a Major Health Event
Receiving a diagnosis of CAD and undergoing a stent procedure can be emotionally challenging. Dealing with the fear, anxiety, and uncertainty requires support and understanding. Here are some strategies:
- Seeking Emotional Support: Talking to family, friends, a therapist, or a support group can provide valuable emotional support.
- Addressing Fear and Anxiety: Open communication with the medical team can help alleviate anxieties and uncertainty.
- Focusing on Positive Changes: Embracing the opportunity to make positive lifestyle changes can empower the patient and enhance emotional well-being.
- Acceptance and Adjustment: Accepting the diagnosis and adapting to the necessary lifestyle changes is crucial for long-term well-being.
Preventing Future Cardiovascular Events: Proactive Heart Health
Preventing future cardiovascular events is a top priority. Strategies include:
- Adopting a Heart-Healthy Diet: Emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, while minimizing saturated and trans fats, sodium, and added sugars.
- Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Managing Stress: Employing effective stress-management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking cessation is crucial for reducing the risk of future cardiovascular events.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Attending regular check-ups with the physician for monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
Conclusion: A Journey Towards Heart Health
A coronary artery stent procedure is a significant medical intervention, but it doesn't mark the end of the journey towards heart health. For a 45-year-old man, this diagnosis serves as a wake-up call to prioritize lifestyle changes and proactive heart health management. With consistent effort, adherence to medical advice, and a supportive network, a positive long-term outlook is achievable. Remember, open communication with the healthcare team and actively participating in one's recovery are integral to achieving optimal heart health and quality of life. This detailed guide aims to empower individuals to navigate this journey with confidence and make informed decisions regarding their health. The information provided here should not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider for any concerns or specific medical questions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Symptoms Of Both Inhaled And Ingested Ricin Include Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
Free Cna Practice Test Quizlet Multiple Choice
Mar 24, 2025
-
Signs And Symptoms Of Major Depressive Disorder Include Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Do Nutritional Needs Change Over Time Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
The Purpose Of A Jump Kit Is To Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A 45 Year Old Man Had Coronary Artery Stents . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
