A Balanced Scorecard For Measuring Company Performance
Breaking News Today
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
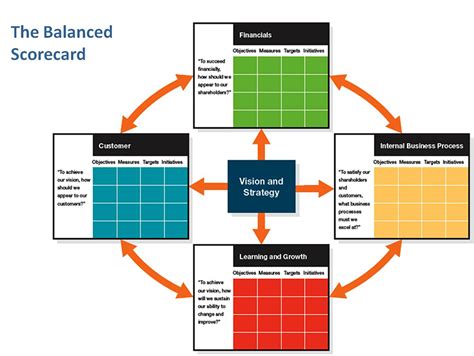
Table of Contents
A Balanced Scorecard for Measuring Company Performance
A balanced scorecard is a strategic planning and management system used to align business activities to the vision and strategy of the organization, improve internal and external communications, and monitor organization performance against strategic goals. It's a powerful tool that moves beyond traditional financial metrics to encompass a broader perspective of organizational success. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of a balanced scorecard, detailing its components, benefits, implementation process, and potential limitations.
Understanding the Four Perspectives of a Balanced Scorecard
The balanced scorecard framework typically incorporates four perspectives, each offering a unique lens through which to assess performance:
1. Financial Perspective: The Bottom Line
This perspective focuses on the hard numbers – the traditional metrics used to measure financial performance. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in this area might include:
- Revenue Growth: Tracking the increase in sales revenue over time.
- Profitability: Measuring net profit margins, return on investment (ROI), and other profitability ratios.
- Cost Reduction: Monitoring expenses and identifying areas for efficiency improvements.
- Cash Flow: Assessing the organization's ability to generate and manage cash.
- Return on Assets (ROA): Measuring how efficiently the company uses its assets to generate profits.
Importance: This perspective remains crucial as it directly reflects the financial health and sustainability of the organization. However, solely relying on financial metrics can be short-sighted, neglecting the drivers of future financial success.
2. Customer Perspective: Meeting Customer Needs
This perspective shifts the focus to customer satisfaction and loyalty. KPIs here might include:
- Customer Satisfaction: Measuring customer satisfaction through surveys, feedback forms, and reviews.
- Customer Retention: Tracking the percentage of customers who continue to do business with the company.
- Market Share: Assessing the company's proportion of the total market.
- Customer Acquisition Cost: Measuring the cost of acquiring new customers.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Gauging customer loyalty and willingness to recommend the company.
Importance: Understanding customer needs and expectations is paramount for long-term growth and sustainability. This perspective helps companies ensure they are delivering value and meeting customer expectations.
3. Internal Processes Perspective: Operational Excellence
This perspective examines the internal processes that drive operational efficiency and effectiveness. KPIs here could include:
- Process Efficiency: Measuring the speed and efficiency of key business processes.
- Product Quality: Tracking the number of defects or errors in products or services.
- Cycle Time: Measuring the time it takes to complete a specific process.
- Employee Productivity: Assessing the output per employee.
- Innovation Rate: Measuring the number of new products or services developed.
Importance: Streamlining internal processes leads to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced quality, ultimately contributing to better financial performance and increased customer satisfaction.
4. Learning and Growth Perspective: Building Capabilities
This perspective focuses on the capabilities and skills of the workforce, the information systems available, and the organizational climate. KPIs here might include:
- Employee Satisfaction: Measuring employee morale and job satisfaction.
- Employee Turnover: Tracking the rate at which employees leave the company.
- Training and Development: Measuring investment in employee training and development.
- Information System Effectiveness: Assessing the effectiveness of information systems in supporting business processes.
- Innovation Capacity: Evaluating the organization's ability to generate new ideas and adapt to change.
Importance: Investing in employees and fostering a culture of learning and growth is essential for long-term competitiveness and adaptability. This perspective ensures that the organization has the right people with the right skills to execute its strategy.
Implementing a Balanced Scorecard: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing a balanced scorecard requires careful planning and execution. Here's a step-by-step guide:
-
Define the Vision and Strategy: Clearly articulate the organization's long-term vision and strategic goals. This forms the foundation upon which the balanced scorecard will be built.
-
Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Select relevant KPIs for each of the four perspectives that align with the strategic goals. Ensure KPIs are measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
-
Develop Strategic Initiatives: Identify the initiatives needed to achieve the desired outcomes for each KPI. These initiatives represent the actions the organization will take to improve performance.
-
Set Targets and Benchmarks: Establish realistic and challenging targets for each KPI. Benchmarking against competitors or industry best practices can help set appropriate targets.
-
Implement Monitoring and Reporting Systems: Establish systems to track progress towards targets and report performance regularly. This might involve using dashboards, spreadsheets, or specialized software.
-
Regular Review and Adjustment: The balanced scorecard is not a static document. It should be reviewed and adjusted regularly to reflect changing circumstances and strategic priorities. This iterative process ensures the scorecard remains relevant and effective.
Benefits of Using a Balanced Scorecard
The balanced scorecard offers numerous benefits to organizations:
- Improved Strategic Alignment: Aligns all levels of the organization with the overall strategic goals.
- Enhanced Communication: Improves communication and understanding of strategic goals across the organization.
- Better Performance Monitoring: Provides a comprehensive view of performance across multiple perspectives.
- Increased Accountability: Increases accountability for achieving strategic goals.
- Improved Decision-Making: Provides data-driven insights to inform better decision-making.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Identifies areas for improvement in operational processes.
- Greater Customer Focus: Enhances the organization's focus on customer needs and satisfaction.
- Improved Employee Engagement: Increases employee engagement and motivation by aligning their work with the organization's strategic goals.
Limitations of a Balanced Scorecard
While the balanced scorecard is a valuable tool, it's crucial to acknowledge its limitations:
- Complexity: Developing and implementing a balanced scorecard can be complex and time-consuming.
- Subjectivity: Some KPIs may be subjective and difficult to measure accurately.
- Data Availability: The effectiveness of the balanced scorecard relies on the availability of accurate and reliable data.
- Resistance to Change: Implementing a balanced scorecard may encounter resistance from employees who are accustomed to traditional performance measurement systems.
- Overemphasis on Metrics: Focusing solely on metrics can lead to neglecting other important aspects of organizational performance.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Strategic Success
The balanced scorecard remains a powerful tool for organizations seeking to improve their strategic planning and performance management. By incorporating financial, customer, internal process, and learning & growth perspectives, organizations gain a holistic understanding of their performance and can make data-driven decisions to achieve their strategic goals. While challenges exist in implementation and interpretation, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks for organizations committed to long-term success and sustainable growth. Remember that the key to success lies in careful planning, consistent monitoring, and a commitment to adapting the scorecard to the organization's evolving needs.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Florida Real Estate 45 Hour Post License Course Exam Answers
Mar 27, 2025
-
Asi Se Dice Level 3 Workbook Answers
Mar 27, 2025
-
Carmella Espinoza Underwent For The Treatment Of Spider Veins
Mar 27, 2025
-
Online Users Posting On A Class Discussion Board Should
Mar 27, 2025
-
In What Way Is A Communication Climate Unlike The Weather
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Balanced Scorecard For Measuring Company Performance . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
