A Pyrogen Is A Substance That Causes Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
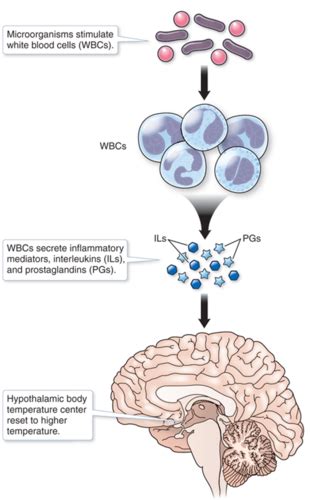
Table of Contents
A Pyrogen Is a Substance That Causes… Fever, and More: A Deep Dive into Pyrogens and Their Effects
Pyrogens. The word itself sounds ominous, conjuring images of laboratory settings and dangerous substances. But what exactly is a pyrogen? Simply put, a pyrogen is a substance that causes fever, but its impact extends far beyond a simple temperature increase. Understanding pyrogens, their sources, and their effects is crucial in various fields, from medicine and pharmaceuticals to environmental health and food safety. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of pyrogens, exploring their nature, detection, and the importance of pyrogen control.
What is a Pyrogen? A Definition and Classification
A pyrogen is any substance that causes fever (pyrexia) when introduced into the body. This feverish response is a systemic reaction, meaning it affects the entire body rather than a localized area. Importantly, the fever isn't a direct effect of the pyrogen itself, but rather an indirect consequence of the body's immune response to the pyrogen's presence.
Pyrogens are broadly classified into two main categories:
1. Exogenous Pyrogens: External Threats
Exogenous pyrogens originate from outside the body. These are the most commonly understood pyrogens, and they include:
-
Bacterial Pyrogens (Endotoxins): These are lipopolysaccharides (LPS) found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Endotoxins are potent pyrogens, even in minute amounts, and are responsible for many of the severe symptoms associated with bacterial infections. They are remarkably heat-stable, surviving temperatures that kill the bacteria themselves. This resilience makes them a significant challenge in sterilization and manufacturing processes.
-
Viral Pyrogens: While not as potent as bacterial endotoxins, certain viruses can also induce fever as part of the body's immune response. Viral pyrogens trigger a cascade of inflammatory mediators, leading to fever and other symptoms.
-
Fungal Pyrogens: Similar to bacteria, certain fungi produce pyrogens that can induce a febrile response.
-
Other Exogenous Sources: Various other substances, including certain plant toxins and some chemical compounds, can also act as exogenous pyrogens.
2. Endogenous Pyrogens: Internal Mediators
Endogenous pyrogens are produced within the body itself as part of the immune response. These substances are not the initial triggers of fever but are critical mediators in the process. Key examples include:
-
Interleukin-1 (IL-1): A cytokine produced by various immune cells, IL-1 plays a significant role in inflammation and fever generation. It acts on the hypothalamus, the brain's temperature control center, to raise the body's set point for temperature.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α): Another crucial cytokine, TNF-α, contributes to fever, inflammation, and other immune responses. It also acts on the hypothalamus, similar to IL-1.
-
Interleukin-6 (IL-6): IL-6, another cytokine, is also involved in the inflammatory response and contributes to fever production.
The interplay between exogenous and endogenous pyrogens is complex. An exogenous pyrogen, such as a bacterial endotoxin, triggers the immune system, leading to the production and release of endogenous pyrogens like IL-1, TNF-α, and IL-6. These endogenous pyrogens then act on the hypothalamus, ultimately resulting in fever.
The Mechanism of Fever Induction: A Cascade of Events
The process of fever induction is a complex interplay of immune signaling and physiological responses. When an exogenous pyrogen enters the body, several steps occur:
-
Recognition: Immune cells, such as macrophages, recognize the pyrogen through specific receptors.
-
Cytokine Release: The recognition of the pyrogen triggers the release of endogenous pyrogens (IL-1, TNF-α, IL-6, etc.).
-
Hypothalamic Action: These cytokines travel to the hypothalamus, the brain region responsible for regulating body temperature.
-
Prostaglandin Synthesis: In the hypothalamus, the cytokines stimulate the production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). PGE2 is a crucial mediator in resetting the body's temperature set point.
-
Temperature Increase: The raised set point in the hypothalamus signals the body to increase its temperature, resulting in fever. This is achieved through shivering, vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels), and reduced heat loss.
The Impact of Pyrogens Beyond Fever: A Broader Perspective
While fever is the most prominent symptom associated with pyrogens, their effects extend far beyond a simple temperature elevation. The inflammatory cascade triggered by pyrogens can lead to a wide range of symptoms and complications, including:
-
Inflammation: Pyrogens trigger widespread inflammation, leading to redness, swelling, pain, and loss of function in affected tissues.
-
Chills and Sweats: The body's attempt to regulate its temperature can cause alternating chills and sweats as it tries to reach and maintain the new, higher set point.
-
Headache: Inflammation in the brain and surrounding tissues can contribute to headaches.
-
Muscle Aches: The inflammatory process can cause muscle pain and fatigue.
-
Nausea and Vomiting: These gastrointestinal symptoms are common during febrile illnesses.
-
Septic Shock: In severe cases, an overwhelming response to pyrogens, particularly bacterial endotoxins, can lead to septic shock, a life-threatening condition characterized by dangerously low blood pressure and organ failure.
Pyrogen Detection and Control: Essential Measures in Various Fields
The presence of pyrogens, especially in medical and pharmaceutical products, can have severe consequences. Therefore, the detection and control of pyrogens are paramount. Several methods are used for pyrogen detection:
1. The Rabbit Pyrogen Test (RPT): The Gold Standard
Historically, the rabbit pyrogen test was the gold standard. This test involves injecting the sample into rabbits and monitoring their temperature for a febrile response. While effective, the RPT is time-consuming, expensive, and raises ethical concerns regarding animal welfare.
2. The Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) Test: A Modern Alternative
The LAL test is a more modern and widely accepted method. It utilizes a lysate from the blood cells of the horseshoe crab (Limulus polyphemus). This lysate contains a clotting enzyme that reacts specifically with bacterial endotoxins, providing a rapid and sensitive detection method. The LAL test is preferred due to its speed, sensitivity, and avoidance of animal testing.
3. Other Detection Methods: Complementing the LAL Test
Other methods, such as the Monocyte Activation Test (MAT), are also used in some cases. These methods offer different sensitivities and specificities, allowing for a comprehensive approach to pyrogen detection.
Pyrogen Control Strategies: Prevention is Key
Controlling pyrogens involves implementing stringent measures throughout the manufacturing and handling processes. Key strategies include:
-
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): GMP guidelines emphasize strict hygiene and cleanliness during manufacturing to minimize the risk of pyrogen contamination.
-
Sterilization Techniques: Effective sterilization methods, such as autoclaving and gamma irradiation, are crucial to eliminate pyrogens. However, it's important to note that some pyrogens are extremely heat-stable, requiring more robust methods for complete elimination.
-
Filtration: Using filters with appropriate pore sizes can remove particulate matter, including pyrogens, from solutions.
-
Depyrogenation Processes: Specialized processes, such as dry heat depyrogenation, are designed to eliminate pyrogens from materials that cannot withstand steam sterilization.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Importance of Pyrogen Awareness
Pyrogens represent a significant challenge across various industries. From the pharmaceutical sector, where contamination can have devastating consequences, to food safety and environmental health, understanding and controlling pyrogens is crucial. The development of sensitive and reliable detection methods, along with the implementation of robust control strategies, continues to be a focal point in ensuring product safety and public health. The ongoing research and advancements in this field underscore the ever-present importance of pyrogen awareness and effective mitigation strategies. The information presented here serves as a foundational understanding, highlighting the complex interactions and the imperative for ongoing vigilance in managing pyrogenic contamination.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Plasterers Scaffolds Horse Scaffolds And Window Jacks
Apr 01, 2025
-
Motor Vehicle Crashes Cost American Taxpayers Over
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between A Load And A Control
Apr 01, 2025
-
Paper Based Pii Is Involved In Data Breaches More Often
Apr 01, 2025
-
Breaking Down Information For Quick Repetition And Memorization Means Using
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Pyrogen Is A Substance That Causes Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
