A Recording Of The Heart And Great Vessels
Breaking News Today
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
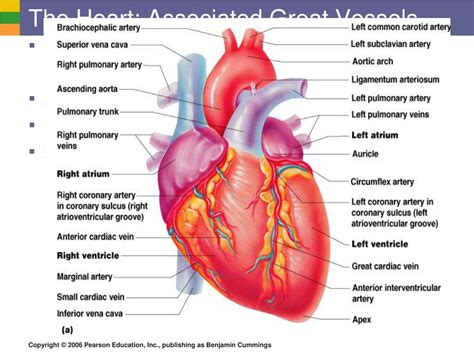
Table of Contents
A Recording of the Heart and Great Vessels: A Comprehensive Guide to Cardiac Imaging
Understanding the intricacies of the heart and its major blood vessels is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of cardiovascular diseases. A recording of the heart and great vessels, encompassing various imaging techniques, provides invaluable insights into the structure and function of this vital organ system. This comprehensive guide will delve into the different methods used, their applications, advantages, and limitations.
Understanding the Cardiovascular System
Before exploring the imaging techniques, let's briefly review the anatomy and physiology of the heart and great vessels. The heart, a muscular organ, acts as a pump, propelling oxygenated blood to the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs. The great vessels – the aorta, pulmonary artery, superior and inferior vena cava – facilitate this circulation. The heart's electrical conduction system ensures coordinated contractions, while its valves regulate blood flow direction.
Key Structures and Their Function:
- Heart Chambers: The four chambers – two atria (receiving chambers) and two ventricles (pumping chambers) – work in synchrony to maintain continuous blood flow.
- Heart Valves: Four valves (tricuspid, mitral, pulmonary, and aortic) prevent backflow of blood, ensuring unidirectional circulation.
- Aorta: The largest artery, carrying oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to the body.
- Pulmonary Artery: Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation.
- Vena Cava (Superior and Inferior): Return deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium.
Imaging Modalities for Recording the Heart and Great Vessels
Several advanced imaging techniques provide detailed recordings of the heart and great vessels, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. The choice of method depends on the specific clinical question and patient factors.
1. Echocardiography (ECHO)
Echocardiography uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to create real-time images of the heart's structure and function. It's a non-invasive, widely available, and relatively inexpensive procedure.
Types of Echocardiography:
- Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE): The most common type, using a transducer placed on the chest wall.
- Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE): A more invasive approach, involving a transducer placed in the esophagus, providing clearer images, particularly of the posterior heart structures.
- Stress Echocardiography: Combines echocardiography with exercise or pharmacological stress to assess heart function under increased workload.
Advantages of Echocardiography:
- Non-invasive: Generally safe and well-tolerated.
- Real-time imaging: Allows assessment of heart function dynamically.
- Widely available and cost-effective: Makes it accessible for a broad patient population.
Limitations of Echocardiography:
- Image quality can be affected by: Body habitus (obesity), lung disease, and bowel gas.
- Limited visualization: May not provide detailed views of certain structures.
2. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (CMR)
CMR uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the heart and great vessels. It's a non-invasive technique offering superior anatomical detail and functional information.
Advantages of CMR:
- Excellent image resolution: Provides detailed anatomical and functional information.
- Non-invasive: Safe for most patients, including those with pacemakers or metallic implants (with certain precautions).
- Versatile: Can assess various cardiac parameters, including blood flow, myocardial viability, and tissue characterization.
Limitations of CMR:
- Costly and time-consuming: Compared to other imaging modalities.
- Claustrophobia: Can be challenging for patients with claustrophobia.
- Contraindications: Patients with certain metallic implants or devices may not be suitable candidates.
3. Cardiac Computed Tomography (CT)
Cardiac CT uses X-rays and computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the heart and great vessels. It is particularly useful for evaluating coronary artery disease.
Types of Cardiac CT:
- Electron-beam CT (EBCT): Rapid acquisition allows for imaging during a single heartbeat. Mostly outdated now.
- Multislice CT (MSCT): Allows for rapid acquisition of high-resolution images, minimizing motion artifacts.
Advantages of Cardiac CT:
- Excellent spatial resolution: Provides detailed images of coronary arteries and other cardiac structures.
- Fast acquisition time: Minimizes motion artifacts.
- Useful for coronary artery disease assessment: Allows for accurate visualization of plaque buildup and stenosis.
Limitations of Cardiac CT:
- Radiation exposure: Involves ionizing radiation.
- Contrast agent: Requires intravenous contrast material, which may have side effects.
- Costly: More expensive than echocardiography.
4. Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is an invasive procedure involving the insertion of a thin, flexible tube (catheter) into a blood vessel, typically in the groin or arm, and advanced to the heart chambers. It allows for direct visualization of the heart chambers and coronary arteries.
Types of Cardiac Catheterization:
- Coronary angiography: Visualizes the coronary arteries to assess for blockages.
- Left and right heart catheterization: Measures pressures and oxygen saturation in different heart chambers.
Advantages of Cardiac Catheterization:
- Direct visualization: Allows for precise assessment of coronary arteries and heart chambers.
- Therapeutic interventions: Can be combined with procedures like angioplasty and stent placement.
Limitations of Cardiac Catheterization:
- Invasive procedure: Carries risks of bleeding, infection, and other complications.
- Requires specialized personnel and facilities: Not widely available in all settings.
5. Nuclear Cardiology
Nuclear cardiology uses radioactive tracers to assess blood flow and myocardial perfusion. It's useful in evaluating coronary artery disease and myocardial viability.
Techniques in Nuclear Cardiology:
- Myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI): Assesses blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT): Creates 3D images of the heart.
- Positron emission tomography (PET): Offers higher resolution images than SPECT.
Advantages of Nuclear Cardiology:
- Sensitive for detecting ischemia: Detects areas of reduced blood flow even in the absence of significant coronary artery stenosis.
- Assesses myocardial viability: Identifies areas of heart muscle that are still salvageable.
Limitations of Nuclear Cardiology:
- Radiation exposure: Involves exposure to ionizing radiation.
- Requires specialized equipment and personnel: Not readily available in all settings.
Choosing the Appropriate Imaging Modality
The selection of the appropriate imaging modality for recording the heart and great vessels depends on several factors, including the clinical question, patient factors, and available resources. For example:
- Suspected coronary artery disease: Cardiac CT or cardiac catheterization are often preferred.
- Valvular heart disease: Echocardiography is usually the initial investigation.
- Assessment of global and regional myocardial function: CMR or nuclear cardiology are excellent choices.
- Evaluation of congenital heart disease: Echocardiography and CMR are commonly used.
Conclusion
A recording of the heart and great vessels, through various imaging techniques, plays an essential role in the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular diseases. Each modality offers unique strengths and limitations, making careful consideration crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for a given clinical scenario. The information provided by these imaging techniques is invaluable for guiding treatment strategies, improving patient outcomes, and ultimately saving lives. Advances in technology continue to enhance the capabilities of these imaging modalities, leading to more accurate diagnoses and improved patient care. Understanding the advantages and limitations of each method is vital for clinicians and healthcare professionals involved in the management of cardiovascular health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Post Test The Early And Mid Nineteenth Century Romanticism
Mar 21, 2025
-
According To Evolutionary Psychology Natural Selection Favors Behaviors That
Mar 21, 2025
-
Every Motor Vehicle Must Be Equipped With
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Generalization About Business Writing Should You Follow
Mar 21, 2025
-
The More Alcohol Concentrated A Beverage Is The
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Recording Of The Heart And Great Vessels . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
