A Three Phase Induction Motor May Have
Breaking News Today
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
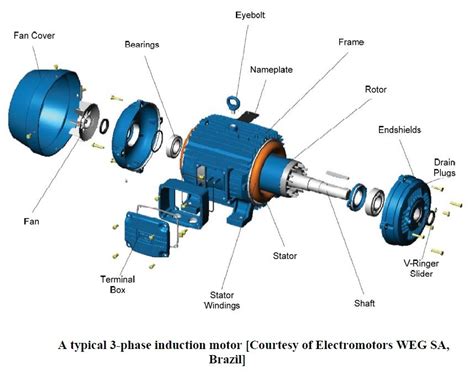
Table of Contents
A Three-Phase Induction Motor May Have: A Deep Dive into Design, Components, and Potential Issues
Three-phase induction motors are workhorses of industrial applications, known for their robustness, reliability, and relatively simple construction. Understanding their intricacies, however, goes beyond simply knowing they convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. This comprehensive guide delves into the various aspects of a three-phase induction motor, exploring its potential configurations, key components, and common issues that may arise.
The Anatomy of a Three-Phase Induction Motor: Key Components and Their Functions
A three-phase induction motor, unlike its single-phase counterpart, doesn't require a starting capacitor. Its inherent design facilitates self-starting capabilities. Let's examine the core components:
1. Stator: The Foundation of Power
The stator forms the stationary outer part of the motor. It houses:
-
Stator Windings: These three-phase windings are arranged strategically around the stator core. They're the conduits for the incoming three-phase AC power. The precise arrangement and configuration of these windings (e.g., star or delta connection) determine the motor's operating characteristics and voltage requirements. Careful design ensures a rotating magnetic field is generated when energized.
-
Stator Core: Constructed from laminated steel sheets, the stator core minimizes eddy current losses. Lamination, a crucial design aspect, reduces energy loss due to heat generation during operation. The core is meticulously engineered to concentrate the magnetic flux produced by the windings.
2. Rotor: The Heart of Mechanical Power
The rotor, the rotating inner part, comes in two primary types:
-
Squirrel-Cage Rotor: This is the most common type. It consists of a cylindrical core with conductive bars embedded in slots, connected at both ends by end rings. This simple, robust design offers high efficiency and reliability, making it ideal for numerous industrial applications. The name derives from its resemblance to a squirrel cage.
-
Wound Rotor: Unlike the squirrel-cage rotor, the wound rotor features independently wound coils connected to slip rings. These slip rings allow external access to the rotor windings, enabling variable speed control through external resistors. While offering more control flexibility, wound rotors are generally more complex and expensive.
3. End Shields and Bearings: Ensuring Smooth Operation
-
End Shields: These protective covers house the bearings, providing mechanical support and protection to the rotor shaft and internal components.
-
Bearings: Ball bearings or sleeve bearings support the rotor shaft, allowing for smooth rotation with minimal friction. Proper lubrication is crucial for bearing longevity and efficient motor operation. The type of bearing chosen significantly impacts the motor's lifespan and operational efficiency.
4. Terminal Box and Connections: Power In, Power Out
-
Terminal Box: This enclosure houses the motor's connection terminals, allowing for convenient wiring to the power supply. Proper labeling and connection are paramount for safe and reliable operation.
-
Wiring Diagram: Each motor comes with a wiring diagram, specifying the correct terminal connections for different voltage configurations (star or delta). Understanding and adhering to this diagram is vital to avoid motor damage.
Types and Variations of Three-Phase Induction Motors: Tailored for Specific Needs
The design of a three-phase induction motor can be further refined based on its intended application. Some key variations include:
1. Design Variations Based on Operating Characteristics
-
High-Slip Motors: These motors operate with a higher slip than standard motors, providing high starting torque, making them suitable for applications requiring significant initial force (e.g., conveyors, crushers).
-
Low-Slip Motors: These motors operate with low slip, offering high efficiency and consistent speed under varying loads, suitable for applications demanding precise speed control (e.g., pumps, fans).
-
Double-Cage Rotors: This design incorporates two layers of rotor bars with different resistances, combining high starting torque with good running efficiency.
2. Mounting Configurations: Adapting to Diverse Environments
Three-phase induction motors come in various mounting configurations, including:
-
Foot-Mounted: Common in industrial settings, these motors are directly mounted to a base or foundation.
-
Flange-Mounted: These motors are mounted directly to a machine via a flange, providing a compact and stable setup.
-
C-Face Mounted: A specific flange mounting style popular for its versatility and easy integration into various machinery.
Potential Issues and Troubleshooting: Identifying and Resolving Problems
Despite their robustness, three-phase induction motors can experience various issues. Early identification and proper troubleshooting are critical to prevent downtime and ensure longevity.
1. Overheating: A Sign of Underlying Problems
Overheating is a common indicator of problems, which could stem from:
-
Overloading: Exceeding the motor's rated capacity leads to excessive current and heat generation.
-
Insufficient Ventilation: Poor ventilation can trap heat, leading to overheating.
-
Bearing Failure: Worn bearings increase friction, generating excessive heat.
-
Windings Faults: Faulty windings increase resistance, causing heat buildup.
2. Vibration and Noise: Indicators of Mechanical Issues
Excessive vibration or noise points towards potential problems such as:
-
Unbalanced Rotor: An unbalanced rotor creates centrifugal forces, resulting in vibration.
-
Bearing Wear: Worn bearings contribute to increased noise and vibration.
-
Loose Mountings: Poorly secured motor mountings can amplify vibrations.
3. Reduced Torque and Efficiency: Performance Degradation
Decreased torque or efficiency could be caused by:
-
Winding Degradation: Ageing or damage to windings reduces motor efficiency and torque.
-
Rotor Problems: Issues with the rotor bars or windings can significantly impact performance.
-
Power Supply Issues: Voltage imbalances or other power supply problems can affect motor performance.
4. Failure to Start: Investigating Starting Issues
If the motor fails to start, the causes could be:
-
Lack of Power: Verify the power supply and connections.
-
Overload Protection: Check if the overload protection device has tripped.
-
Faulty Windings: Damaged windings may prevent the motor from starting.
-
Blocked Rotor: A mechanically obstructed rotor will prevent it from rotating.
Maintenance and Longevity: Ensuring Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance is vital for extending the lifespan and ensuring optimal performance of three-phase induction motors. This includes:
-
Regular Inspection: Visually inspecting the motor for signs of wear, damage, or overheating.
-
Bearing Lubrication: Regularly lubricating bearings according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
-
Cleaning: Keeping the motor clean and free of debris.
-
Vibration Analysis: Periodic vibration analysis to detect early signs of bearing wear or other mechanical issues.
-
Thermal Imaging: Using thermal imaging to identify hotspots indicating overheating problems.
Conclusion: The Versatility and Importance of Three-Phase Induction Motors
Three-phase induction motors are indispensable components in countless industrial and commercial applications, providing reliable and efficient power conversion. Understanding their design, components, potential problems, and maintenance procedures is essential for maximizing their lifespan, ensuring safe operation, and avoiding costly downtime. This detailed guide provides a foundation for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of these crucial industrial workhorses. By addressing potential issues proactively and implementing regular maintenance practices, the long-term efficiency and reliability of these motors can be significantly enhanced. The detailed understanding of the various aspects of a three-phase induction motor discussed in this article is key to successful operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting in any industrial or commercial setting.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Industry Did The Interstate Commerce Act Primarily Affect
Mar 29, 2025
-
Ap Chem Unit 5 Progress Check Mcq
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Of These Are True Of Tests For Online Courses
Mar 29, 2025
-
Drug Addiction Is A Clinical Diagnosis That Everfi
Mar 29, 2025
-
El Nacimiento Es El Fin De La Vida
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Three Phase Induction Motor May Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
