Abraham Maslow Is Best Known For Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
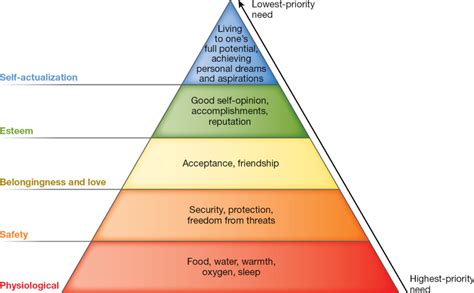
Table of Contents
Abraham Maslow is Best Known For: A Deep Dive into His Hierarchy of Needs
Abraham Maslow, a towering figure in psychology, is best known for his Hierarchy of Needs. This isn't just a simple list; it's a comprehensive theory explaining human motivation and the stages individuals progress through to achieve self-actualization. While often simplified in popular culture, understanding the nuances of Maslow's work reveals a far richer and more complex model than many initially grasp. This article will delve deep into Maslow's hierarchy, exploring its components, criticisms, and lasting impact on various fields. We'll also examine why it remains a cornerstone of understanding human behavior, even amidst ongoing debate and refinement.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: The Foundation
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs is a motivational theory in psychology comprising a five-tier model of human needs, often depicted as a pyramid. Each level represents a different category of needs, with the most basic needs at the bottom and the most advanced at the top. Individuals must fulfill the lower-level needs before progressing to higher levels. Let's break down each level:
1. Physiological Needs: The Base of the Pyramid
These are the most fundamental needs, essential for survival. They include:
- Air: The very breath we take, crucial for sustaining life.
- Water: Hydration, vital for bodily functions.
- Food: Providing the necessary energy and nutrients for survival.
- Shelter: Protection from the elements and a safe place to rest.
- Sleep: Restorative sleep, essential for physical and mental well-being.
- Homeostasis: Maintaining a stable internal environment.
Without these basic needs met, individuals cannot effectively address higher-level needs. Think of a starving person; their primary focus is obtaining food, not pursuing self-esteem or creativity.
2. Safety and Security Needs: Finding Stability
Once physiological needs are met, the focus shifts to safety and security. This level encompasses:
- Personal Security: Feeling safe from violence and harm.
- Financial Security: Having enough resources to meet basic needs consistently.
- Health and Well-being: Maintaining good physical and mental health.
- Property: Owning possessions and having a stable living situation.
This level is about establishing a sense of order and predictability in one's life. A safe environment allows individuals to relax and focus on higher aspirations. Without a sense of security, anxiety and fear can dominate, making it difficult to progress.
3. Love and Belonging Needs: Connection and Relationships
With basic physical and security needs fulfilled, the drive for social connection emerges. This level includes:
- Friendship: Developing meaningful relationships with others.
- Intimacy: Experiencing close, personal relationships, including romantic love.
- Family: Belonging to a supportive family unit.
- Community: Feeling a sense of connection to a larger group or community.
The need for love and belonging is deeply ingrained in human nature. Humans are inherently social creatures, and a lack of connection can lead to feelings of loneliness, isolation, and depression. Strong social bonds are crucial for mental and emotional well-being.
4. Esteem Needs: Self-Respect and Recognition
Once a sense of belonging is established, individuals strive for esteem, encompassing both self-esteem and the esteem of others. This level includes:
- Self-Esteem: Feeling confident, capable, and worthy.
- Confidence: Believing in one's abilities and potential.
- Achievement: Setting and achieving goals, gaining recognition for accomplishments.
- Respect from Others: Gaining the admiration and respect of peers and society.
Achieving esteem fosters feelings of self-worth and accomplishment. However, an overemphasis on external validation can lead to insecurity and dependence on others' approval. A healthy sense of self-esteem is crucial for navigating life's challenges and pursuing personal growth.
5. Self-Actualization: Reaching One's Full Potential
This is the pinnacle of Maslow's hierarchy, representing the realization of one's full potential. Self-actualized individuals are characterized by:
- Creativity: Expressing oneself through artistic endeavors or innovative thinking.
- Problem-Solving: Approaching challenges with a proactive and resourceful mindset.
- Acceptance of Facts: Maintaining objectivity and realism.
- Spontaneity: Acting authentically and without inhibition.
- Peak Experiences: Experiencing moments of intense joy and fulfillment.
- Morality: Adhering to a strong moral compass.
- Lack of Prejudice: Embracing diversity and understanding.
Self-actualization is not a destination but a continuous process of growth and self-discovery. It's about living authentically, pursuing one's passions, and contributing meaningfully to the world. It's important to note that Maslow believed only a small percentage of people ever fully reach this stage.
Criticisms and Refinements of Maslow's Hierarchy
Despite its widespread influence, Maslow's Hierarchy has faced valid criticisms:
-
Cultural Bias: The hierarchy is often criticized for being culturally biased, reflecting Western values. Different cultures may prioritize needs differently. For example, collectivist cultures may prioritize belonging over individual achievement.
-
Lack of Empirical Evidence: While Maslow's observations were insightful, the initial hierarchy lacked rigorous empirical evidence. Subsequent research has attempted to validate and refine the model.
-
Rigid Structure: The strictly hierarchical structure has been challenged. Individuals may experience multiple needs simultaneously, and the order of needs may vary based on individual circumstances and cultural context.
-
Oversimplification: The five-tier model simplifies the complexities of human motivation. Some researchers suggest more nuanced models are needed to capture the multifaceted nature of human needs.
Despite these criticisms, Maslow's work remains influential. Later research and revisions have offered improvements, emphasizing the flexibility and interconnectedness of human needs.
Maslow's Hierarchy in Different Contexts
Maslow's Hierarchy has found applications in various fields beyond psychology:
-
Business and Management: Understanding employee motivation. By fulfilling employees' needs, businesses can foster a more productive and engaged workforce.
-
Education: Designing effective learning environments. Addressing students' basic needs creates a supportive atmosphere for learning and growth.
-
Healthcare: Prioritizing patient needs. Addressing physical and psychological needs is essential for effective healthcare.
-
Social Work: Understanding individual and community needs. Maslow's framework helps social workers assess and address various levels of needs within communities.
The Enduring Legacy of Abraham Maslow
Despite the criticisms, Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs remains a cornerstone of understanding human motivation. Its enduring influence stems from its intuitive appeal and its ability to provide a framework for understanding the complex interplay of human needs. While the rigid, pyramidal structure may require adjustments to reflect cultural diversity and individual variations, the core principles – the progression of needs from basic survival to self-actualization – offer valuable insights into human behavior.
The ongoing refinement and expansion of Maslow's theory highlight its adaptability and enduring relevance. Researchers continue to investigate the nuances of human needs and their interplay, incorporating diverse cultural perspectives and rigorous empirical methods. While the original hierarchy may be viewed as a starting point rather than a definitive model, its legacy continues to shape our understanding of human motivation and the pursuit of fulfillment. Ultimately, Maslow's work serves as a powerful reminder that understanding our needs, at all levels, is crucial for personal growth and societal well-being. The quest for self-actualization, though challenging, remains a compelling aspiration, inspiring individuals to strive for their full potential and contribute meaningfully to the world around them. The continued exploration and evolution of Maslow’s ideas underscore the dynamism of human psychology and the ongoing quest for a comprehensive understanding of human motivation. The ongoing dialogue surrounding Maslow’s work ensures its continuing relevance and influence in diverse fields, guaranteeing its position as a crucial element within the broader field of psychology and human understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Tensor Fascia Latae Is Involved In Hip
Apr 01, 2025
-
John B Watson Considered Himself To Be A
Apr 01, 2025
-
Plasterers Scaffolds Horse Scaffolds And Window Jacks
Apr 01, 2025
-
Motor Vehicle Crashes Cost American Taxpayers Over
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between A Load And A Control
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Abraham Maslow Is Best Known For Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
