Allocating Common Fixed Expenses To Business Segments
Breaking News Today
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
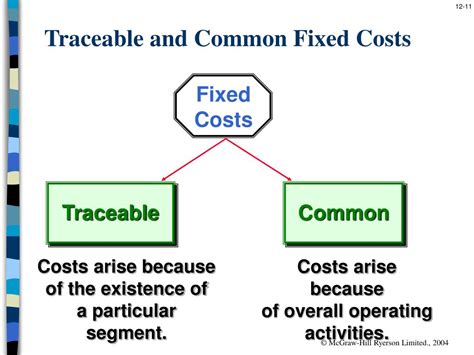
Table of Contents
- Allocating Common Fixed Expenses To Business Segments
- Table of Contents
- Allocating Common Fixed Expenses to Business Segments: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Common Fixed Expenses
- Methods for Allocating Common Fixed Expenses
- 1. Sales Revenue Method
- 2. Number of Employees Method
- 3. Space Occupied Method (Square Footage Method)
- 4. Activity-Based Costing (ABC) Method
- 5. Weighted Average Method
- Choosing the Right Method
- Beyond Allocation: Improving Accuracy and Transparency
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Allocating Common Fixed Expenses to Business Segments: A Comprehensive Guide
Allocating common fixed expenses across different business segments is a crucial yet often complex task for multi-segment organizations. These shared costs, unlike direct expenses easily traceable to specific segments, require careful consideration and a consistent methodology to ensure accurate financial reporting, performance evaluation, and strategic decision-making. This comprehensive guide delves into the various methods used for allocating common fixed expenses, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses to help you choose the most appropriate approach for your business.
Understanding Common Fixed Expenses
Before diving into allocation methods, it's crucial to understand what constitutes common fixed expenses. These are costs that benefit multiple segments of a business but cannot be directly traced to a single segment. Examples include:
- Rent: If your company occupies a single building housing multiple business units, rent is a common fixed expense.
- Salaries of Shared Staff: The salaries of executives, human resources personnel, or IT staff supporting multiple segments are common costs.
- Depreciation of Shared Assets: Depreciation on equipment or facilities used across multiple segments falls under this category.
- Utilities (Electricity, Water, Gas): These expenses often serve multiple segments within a shared facility.
- Insurance Premiums: General liability or property insurance policies covering the entire organization.
- Marketing and Advertising (General): Broad marketing campaigns not specifically targeted at individual segments.
The accurate allocation of these costs is vital because inaccurate allocation can distort segment profitability, leading to flawed strategic decisions. For example, over-allocating common expenses to a high-performing segment can make it appear less profitable than it actually is, potentially leading to underinvestment.
Methods for Allocating Common Fixed Expenses
Several methods exist for allocating common fixed expenses. The choice depends on factors like the nature of the business, the complexity of its structure, and the level of accuracy desired. Here are some of the most widely used approaches:
1. Sales Revenue Method
This is the simplest method, allocating common fixed expenses based on the proportion of each segment's sales revenue to total sales revenue. The formula is:
(Segment Sales Revenue / Total Sales Revenue) * Total Common Fixed Expenses = Allocated Expenses
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and implement.
- Easy Data Availability: Sales revenue data is readily available.
Disadvantages:
- Inaccuracy: Doesn't reflect the actual consumption of resources by each segment. A segment with high sales but low resource usage might be unfairly burdened.
- Ignores Other Factors: Fails to consider factors like the number of employees, operational complexity, or square footage occupied by each segment.
2. Number of Employees Method
This method allocates expenses based on the number of employees in each segment. The formula is:
(Number of Employees in Segment / Total Number of Employees) * Total Common Fixed Expenses = Allocated Expenses
Advantages:
- Relatively Simple: Easier to implement than some more complex methods.
- Relates to Resource Consumption: Reflects the approximate consumption of resources like administrative support and IT services.
Disadvantages:
- Oversimplification: Doesn't consider differences in employee roles or productivity levels. A segment with highly productive employees might be unfairly penalized.
- Ignores Other Factors: Ignores other relevant factors such as sales revenue, space occupied, or the intensity of shared resource usage.
3. Space Occupied Method (Square Footage Method)
This method allocates common fixed expenses based on the proportional amount of space occupied by each segment. The formula is:
(Square Footage of Segment / Total Square Footage) * Total Common Fixed Expenses = Allocated Expenses
Advantages:
- Direct Relationship to Resource Consumption: For expenses like rent, utilities, and maintenance, this method offers a more direct link to consumption.
- Fairer Allocation for Certain Expenses: Particularly suitable for allocating expenses like rent and utilities.
Disadvantages:
- Inapplicable to All Expenses: Doesn't work well for allocating expenses like administrative support or marketing costs.
- Inaccurate for Uneven Resource Usage: A segment occupying a large space but using shared resources sparingly might be unfairly burdened.
4. Activity-Based Costing (ABC) Method
This is a more sophisticated method that traces costs to the activities that consume resources, then allocates those costs to segments based on their consumption of those activities. This requires identifying cost drivers for each activity and tracking their usage by each segment.
Advantages:
- Greater Accuracy: Provides a much more accurate allocation of costs compared to simpler methods.
- Improved Understanding of Costs: Provides valuable insights into cost drivers and resource consumption patterns.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: More complex and time-consuming to implement than simpler methods.
- High Data Requirements: Requires detailed data on activities, cost drivers, and segment usage.
- Costly Implementation: Requires significant upfront investment in data collection and analysis.
5. Weighted Average Method
This method combines multiple factors (e.g., sales revenue, number of employees, space occupied) to determine the allocation weight for each segment. Each factor is assigned a weight reflecting its relative importance, and the weighted average is used to allocate the common fixed expenses.
Advantages:
- Improved Accuracy: Offers a better allocation than using a single factor by incorporating multiple relevant factors.
- Flexibility: Allows for customization based on the specific characteristics of the business and its segments.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Requires careful consideration of weighting factors.
- Subjectivity: Assigning weights can be subjective and may require managerial judgment.
Choosing the Right Method
The optimal method for allocating common fixed expenses depends on various factors specific to your business:
- Industry: The nature of your industry and the type of resources used will influence the most suitable method.
- Business Structure: The complexity and organization of your business segments will affect the feasibility of different methods.
- Data Availability: The availability of accurate and reliable data is crucial for implementing certain methods (especially ABC costing).
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Consider the cost of implementing each method against the potential benefits of improved accuracy.
For smaller businesses with simpler structures, the sales revenue or number of employees method might suffice. Larger, more complex organizations may find ABC costing or the weighted average method more appropriate, despite the increased complexity.
Beyond Allocation: Improving Accuracy and Transparency
While choosing the right allocation method is critical, it's equally important to ensure transparency and accuracy in the process. Consider these additional points:
- Regular Review and Refinement: The chosen allocation method should be reviewed and refined periodically to ensure it remains relevant and accurate.
- Internal Controls: Implement strong internal controls to ensure the accuracy and reliability of data used in the allocation process.
- Communication and Training: Communicate the chosen method and its rationale clearly to all stakeholders. Provide adequate training to personnel involved in the allocation process.
- Consideration of Qualitative Factors: While quantitative methods are essential, qualitative factors influencing resource consumption should also be considered when making strategic decisions.
Conclusion
Allocating common fixed expenses is a vital aspect of accurate financial reporting and strategic decision-making for multi-segment organizations. Selecting the appropriate method, coupled with a commitment to accuracy and transparency, ensures that each segment is fairly assessed, facilitating informed decisions about resource allocation, investment, and overall business strategy. Remember that the most suitable approach will vary depending on the specific circumstances of your business. Therefore, a careful analysis of your business structure, available data, and cost-benefit trade-offs is crucial in making the right choice. Through meticulous planning and consistent implementation, you can unlock the power of accurate cost allocation, leading to improved operational efficiency and enhanced profitability.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Light Dependent Reactions Occur In The Stroma Of The Chloroplast
Apr 09, 2025
-
How Many Chapters In Book Of Mormon
Apr 09, 2025
-
Supply And Demand Coordinate To Determine Prices By Working
Apr 09, 2025
-
As Altitude Increases What Happens To Air Pressure
Apr 09, 2025
-
The Regularity Of El Nino Weather Events Is Determined By
Apr 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Allocating Common Fixed Expenses To Business Segments . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.