American Heart Association Acls Precourse Self Assessment Answers
Breaking News Today
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
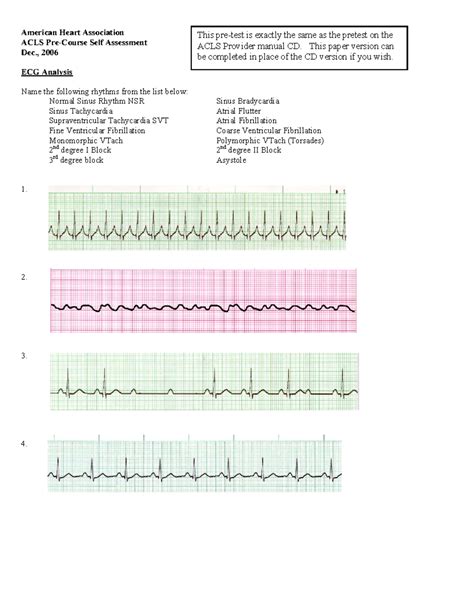
Table of Contents
American Heart Association ACLS Pre-Course Self-Assessment Answers: A Comprehensive Guide
The American Heart Association (AHA) Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) course is a cornerstone of emergency medical training. Before embarking on this crucial certification, the AHA provides a pre-course self-assessment to gauge your existing knowledge and identify areas needing more focus. This comprehensive guide will delve into the key concepts covered in the ACLS pre-course self-assessment, providing insights into the correct answers and explaining the underlying principles. Please note: This article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for the official AHA ACLS course. Always refer to the latest AHA guidelines and materials for accurate and up-to-date information.
Understanding the ACLS Pre-Course Self-Assessment
The self-assessment is designed to be a diagnostic tool, helping you pinpoint your strengths and weaknesses before committing to the full ACLS course. It covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Basic Life Support (BLS) skills: This includes chest compressions, airway management, and ventilation. A strong foundation in BLS is essential for ACLS proficiency.
- ECG interpretation: Understanding different rhythm strips and identifying critical arrhythmias is a significant component of ACLS.
- Pharmacology: ACLS heavily relies on the appropriate and timely administration of medications. Knowing the indications, contraindications, doses, and routes of administration for various drugs is crucial.
- Advanced airway management: Beyond basic airway techniques, ACLS involves more advanced procedures like endotracheal intubation and other airway adjuncts.
- Team dynamics and communication: Effective teamwork and clear communication are vital in high-pressure emergency situations.
- Defibrillation and synchronized cardioversion: Understanding when and how to use these life-saving techniques is a central theme in the ACLS curriculum.
- Post-resuscitation care: Managing patients after a cardiac arrest requires a comprehensive approach to stabilization and monitoring.
Key Concepts and Sample Questions with Explanations
While the exact questions on the pre-course self-assessment can vary, the core concepts remain consistent. Let's explore some example questions and their detailed answers:
Section 1: Basic Life Support (BLS)
Question: What is the correct compression-to-ventilation ratio for adult single-rescuer CPR?
Answer: 30:2
Explanation: The AHA guidelines recommend a 30:2 ratio for adult single-rescuer CPR. This means 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths. This ratio ensures adequate chest compressions while maintaining oxygenation.
Question: What is the proper depth of chest compressions for an adult?
Answer: At least 2 inches (5 cm)
Explanation: Compressions must be deep enough to effectively circulate blood. Insufficient depth can lead to inadequate blood flow and reduce the chances of survival.
Section 2: ECG Interpretation
Question: Identify the rhythm shown in the following ECG strip (example of a strip showing Ventricular Tachycardia).
Answer: Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
Explanation: Accurate identification of VT is critical. The characteristics of VT include a wide QRS complex, absence of P waves, and a rapid ventricular rate. Understanding the treatment algorithm for VT is essential.
Question: What is the first-line treatment for pulseless ventricular tachycardia?
Answer: Defibrillation
Explanation: Pulseless VT is a life-threatening rhythm requiring immediate defibrillation. Defibrillation aims to depolarize the myocardium and allow the heart to resume a normal rhythm.
Section 3: Pharmacology
Question: What is the dose of epinephrine in cardiac arrest?
Answer: 1 mg IV or IO every 3-5 minutes
Explanation: The correct dose and administration route of epinephrine are critical in managing cardiac arrest. The frequency of administration is also important.
Question: What is the primary mechanism of action of amiodarone in treating ventricular fibrillation?
Answer: Reduces myocardial excitability and suppresses ventricular arrhythmias
Explanation: Amiodarone affects various ion channels in the heart, reducing the risk of further arrhythmias. Understanding its role in the ACLS algorithm is essential.
Section 4: Advanced Airway Management
Question: What is the most common complication associated with endotracheal intubation?
Answer: Esophageal intubation
Explanation: Accidental placement of the endotracheal tube into the esophagus instead of the trachea is a serious complication that can lead to hypoxia. Confirmation of proper tube placement is paramount.
Question: Describe the steps involved in confirming proper endotracheal tube placement.
Answer: Chest rise and fall, auscultation of breath sounds over both lung fields, capnography (end-tidal CO2), and confirmation via chest x-ray.
Explanation: Multiple methods should be used to verify proper placement and avoid complications.
Section 5: Team Dynamics and Communication
Question: Describe the importance of effective communication during a cardiac arrest.
Answer: Clear and concise communication is essential for efficient teamwork. Using standardized terminology and a structured approach improves coordination and reduces errors.
Explanation: Effective communication is a crucial aspect of ACLS. Using a clear, concise, and structured approach ensures all team members are on the same page and can effectively contribute to patient care.
Section 6: Defibrillation and Synchronized Cardioversion
Question: When is synchronized cardioversion used?
Answer: For hemodynamically unstable tachydysrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter with rapid ventricular response, or supraventricular tachycardia.
Explanation: Synchronized cardioversion delivers a shock synchronized with the QRS complex to avoid disrupting the heart during a vulnerable part of the cardiac cycle.
Question: What is the difference between defibrillation and cardioversion?
Answer: Defibrillation delivers an unsynchronized shock to treat life-threatening arrhythmias such as ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, while cardioversion delivers a synchronized shock to treat hemodynamically unstable tachydysrhythmias.
Explanation: This key difference highlights the importance of choosing the appropriate treatment based on the patient’s rhythm and hemodynamic status.
Section 7: Post-Resuscitation Care
Question: What are the key aspects of post-resuscitation care?
Answer: Maintaining airway, breathing, and circulation, monitoring vital signs, addressing possible causes of arrest, assessing neurological status, and providing supportive care.
Explanation: Post-resuscitation care is critical for patient survival and recovery. This includes addressing underlying causes, managing complications, and supporting organ function.
Question: What is the importance of targeted temperature management (TTM) in post-cardiac arrest care?
Answer: TTM helps reduce neurological damage and improves chances of survival in patients who have experienced cardiac arrest.
Explanation: Cooling the body to a specific temperature range after cardiac arrest has shown to improve neurologic outcomes.
Beyond the Self-Assessment: Preparing for the ACLS Course
The ACLS pre-course self-assessment is only the first step. Thorough preparation for the full ACLS course involves:
- Reviewing BLS skills: Ensure a solid understanding of basic life support techniques.
- Practicing ECG interpretation: Regular practice interpreting different ECG strips is essential for proficiency.
- Studying ACLS pharmacology: Learn the indications, contraindications, doses, and routes of administration for key medications.
- Familiarizing yourself with ACLS algorithms: Understand the systematic approach to managing different arrhythmias and cardiac arrest scenarios.
- Participating in practice scenarios: Simulations provide invaluable experience in applying your knowledge in a realistic setting.
By dedicating sufficient time and effort to comprehensive review and practice, you’ll be well-prepared to excel in the ACLS course and ultimately provide the best possible care for your patients. Remember, the goal is not just to pass the exam, but to gain the knowledge and skills to confidently manage life-threatening cardiac emergencies. Always prioritize patient safety and follow the latest AHA guidelines. This guide serves as a valuable resource for your learning journey, but it is not a replacement for the complete ACLS course and its comprehensive training. Remember to consult the official AHA materials for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Does A Nursing Assistant Reporting Affect The Mds
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Joint Force Engineer Manages Several Engineering Functions Which Include
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Sentence Describes A Characteristic Of A Poetry Slam
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Idea Was Supported By Both Plato And Aristotle
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Involved In Translation
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about American Heart Association Acls Precourse Self Assessment Answers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
