Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Answer Key Cell Transport
Breaking News Today
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
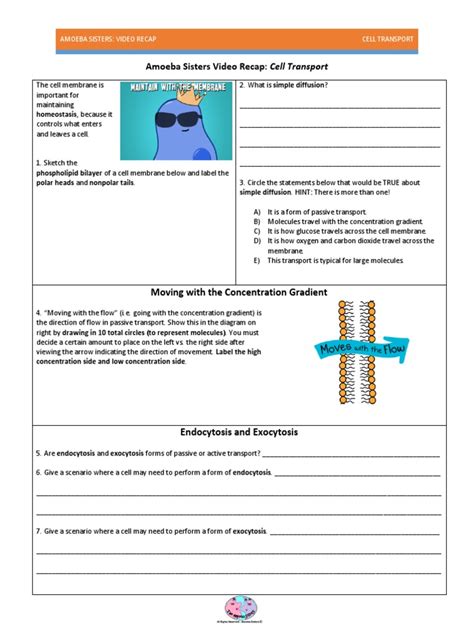
Table of Contents
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Answer Key: Cell Transport – A Comprehensive Guide
The Amoeba Sisters have made learning biology, particularly cell transport, significantly easier and more engaging. Their videos provide a clear, concise, and often humorous approach to complex biological concepts. This article serves as a comprehensive answer key and recap of their cell transport videos, covering key terms, processes, and mechanisms. We will delve deep into passive and active transport, exploring the nuances of each process and providing examples relevant to understanding cellular function.
Understanding Cell Transport: The Basics
Before diving into the specifics, let's establish a foundational understanding of why cell transport is crucial. Cells, the fundamental units of life, constantly exchange materials with their surroundings. This exchange is vital for maintaining homeostasis – a stable internal environment essential for survival. This exchange relies on various transport mechanisms categorized broadly into passive and active transport. The Amoeba Sisters beautifully illustrate these mechanisms, using relatable analogies that stick with the viewer.
Passive Transport: No Energy Required
Passive transport mechanisms don't require energy expenditure by the cell. This is because they rely on the natural movement of substances down their concentration gradient – from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Think of it like rolling a ball downhill; it requires no extra push. The Amoeba Sisters’ videos cleverly utilize this analogy to solidify this fundamental concept.
1. Simple Diffusion: This is the simplest form of passive transport. Small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) can easily pass through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. The Amoeba Sisters highlight how this process is crucial for gas exchange in respiration and photosynthesis.
2. Facilitated Diffusion: Larger or polar molecules require assistance to cross the membrane. This is where membrane proteins come into play. These proteins act as channels or carriers, facilitating the movement of specific molecules down their concentration gradient. The Amoeba Sisters illustrate this with clear visuals, emphasizing the specificity of these protein channels. Glucose transport is a classic example highlighted in their videos.
3. Osmosis: This is a special case of passive transport involving the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Water moves from an area of high water concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of low water concentration (high solute concentration). The Amoeba Sisters effectively use examples of red blood cells in different solutions (hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic) to demonstrate the effects of osmosis. Understanding tonicity (the relative concentration of solutes in two solutions) is critical here.
Active Transport: Energy is Key
Unlike passive transport, active transport requires energy input, usually in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This energy is necessary because active transport moves substances against their concentration gradient – from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This is akin to pushing a ball uphill; it demands extra effort.
1. Sodium-Potassium Pump: This is a prime example of active transport, extensively covered by the Amoeba Sisters. This pump maintains a specific concentration gradient of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions across the cell membrane. This gradient is essential for nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction. The pump's mechanism, involving conformational changes and ATP hydrolysis, is explained with clarity in their videos.
2. Endocytosis and Exocytosis: These processes involve the movement of larger molecules or even whole cells across the membrane. Endocytosis is the process of bringing materials into the cell, while exocytosis is the process of releasing materials from the cell. The Amoeba Sisters use engaging animations to depict the formation of vesicles and their fusion with the membrane in these processes.
* **Phagocytosis ("cell eating"):** The cell engulfs large particles, like bacteria.
* **Pinocytosis ("cell drinking"):** The cell takes in fluids and dissolved substances.
* **Receptor-mediated endocytosis:** Specific molecules bind to receptors on the cell surface, triggering their uptake into the cell.
These processes are crucial for various cellular functions, including nutrient uptake, waste removal, and intercellular communication. The Amoeba Sisters explain the intricacies of these processes, making complex mechanisms easy to grasp.
Deeper Dive into Specific Concepts from the Amoeba Sisters' Videos
The Amoeba Sisters’ videos often focus on specific aspects of cell transport, providing detailed explanations and memorable examples. Let's explore some of these key areas:
The Cell Membrane: The Gatekeeper
The cell membrane is the selectively permeable barrier that controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell. The Amoeba Sisters emphasize the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane, explaining the arrangement of phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol. They highlight how the membrane's structure directly influences its permeability to different substances. Understanding the membrane's composition is fundamental to grasping the mechanisms of transport.
Concentration Gradients and Equilibrium
The concept of concentration gradients is central to understanding both passive and active transport. The Amoeba Sisters visually represent concentration gradients, illustrating how substances move down or against these gradients. They also explain the concept of dynamic equilibrium, where the net movement of substances ceases, though movement still occurs.
The Role of Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins play crucial roles in facilitated diffusion and active transport. The Amoeba Sisters' videos illustrate the different types of membrane proteins, including channel proteins, carrier proteins, and pumps. They explain how these proteins' structures and functions contribute to the specificity and efficiency of transport.
Applications and Real-World Connections
The Amoeba Sisters frequently connect cell transport concepts to real-world applications and biological processes. For instance, they may discuss the role of cell transport in:
- Nutrient absorption in the digestive system: How cells lining the intestines absorb nutrients from digested food.
- Kidney function: How cells in the kidneys filter blood and regulate water balance.
- Nerve impulse transmission: How the sodium-potassium pump contributes to nerve signals.
- Muscle contraction: The role of ion gradients in muscle fiber contraction.
- Plant water uptake: Osmosis and water movement in plants.
These real-world connections help solidify understanding and make the concepts more relatable.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts
While the Amoeba Sisters primarily focus on the fundamentals, understanding more advanced concepts can further enhance knowledge. These might include:
- Cotransport: The coupling of the movement of one substance down its concentration gradient to drive the movement of another substance against its gradient.
- Electrogenic pumps: Pumps that generate a membrane potential, contributing to the overall electrical charge across the membrane.
- The impact of various environmental factors on cell transport: Temperature, pH, and the presence of inhibitors can influence the rate and efficiency of transport processes.
Conclusion: Mastering Cell Transport with the Amoeba Sisters
The Amoeba Sisters’ videos provide a valuable resource for learning cell transport. Their clear explanations, engaging animations, and relatable analogies make complex concepts accessible to a wide audience. This comprehensive recap and answer key aim to further solidify your understanding, providing a deeper dive into the fundamental mechanisms and their broader biological implications. By incorporating the information presented here, you'll not only master the intricacies of cell transport but also appreciate its central role in maintaining the life of cells and organisms. Remember that consistent review and application are key to truly grasping these biological concepts. Happy learning!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Large Vehicles Have Smaller Blind Spots Than Passenger Vehicles
Apr 03, 2025
-
Most Reveals A Sense Of Loss
Apr 03, 2025
-
Michigan Basic Driver Improvement Course Test Questions
Apr 03, 2025
-
Grasping A Toy Writing With A Pencil
Apr 03, 2025
-
Conversion Factors And Problem Solving Lab 2
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Answer Key Cell Transport . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
