An Increase In The Money Supply Will Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
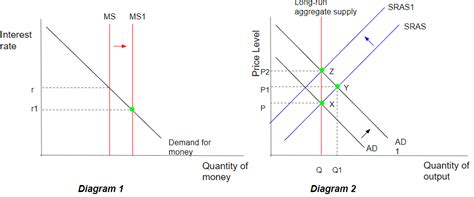
Table of Contents
An Increase in the Money Supply: A Comprehensive Guide
An increase in the money supply, a cornerstone concept in macroeconomics, refers to a rise in the total amount of money circulating within an economy. This seemingly simple phenomenon has profound and multifaceted effects, influencing everything from inflation and interest rates to employment and economic growth. Understanding the mechanics, implications, and potential consequences of an expanding money supply is crucial for anyone seeking a deeper grasp of monetary policy and its impact on the overall health of an economy.
Understanding the Money Supply
Before delving into the effects of an increased money supply, it's essential to define what constitutes the money supply itself. Economists typically categorize money into different measures, primarily M1 and M2, though further classifications like M3 exist depending on the country's central bank's definition.
M1 Money Supply: The Most Liquid Assets
M1 represents the most liquid forms of money, readily available for immediate transactions. This includes:
- Currency in circulation: Physical cash held by individuals and businesses.
- Demand deposits: Funds held in checking accounts, readily accessible via checks, debit cards, or electronic transfers.
- Traveler's checks: Pre-printed checks designed for use by travelers. These are less prevalent today due to the rise of credit and debit cards.
M2 Money Supply: A Broader Measure
M2 encompasses M1 plus less liquid assets that are easily convertible into cash. This includes:
- Savings deposits: Funds deposited in savings accounts that earn interest.
- Money market accounts: Accounts that offer higher interest rates than traditional savings accounts, often with limited check-writing capabilities.
- Small-denomination time deposits: Certificates of deposit (CDs) with relatively short maturities.
- Money market mutual funds: Funds that invest in short-term debt instruments.
Mechanisms of Increasing the Money Supply
Central banks, the regulatory bodies responsible for managing a country's monetary policy, employ various tools to influence the money supply. Key mechanisms include:
1. Open Market Operations: The Primary Tool
This involves the buying and selling of government securities (like Treasury bonds) in the open market. When a central bank buys securities, it injects money into the banking system, increasing the money supply. Conversely, selling securities withdraws money, decreasing the money supply. This is the most frequently used tool due to its precision and immediate impact.
2. Reserve Requirements: Influencing Bank Lending
Commercial banks are required to hold a certain percentage of their deposits as reserves, known as the reserve requirement. Lowering this requirement allows banks to lend out a larger portion of their deposits, expanding the money supply through the process of fractional reserve banking. Raising the requirement has the opposite effect.
3. The Discount Rate: The Lender of Last Resort
The discount rate is the interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow money directly from the central bank. Lowering the discount rate encourages banks to borrow more, increasing their reserves and lending capacity, thus expanding the money supply. A higher discount rate has a contractionary effect.
4. Inflation Targeting: A Modern Approach
Many central banks employ inflation targeting as a primary policy objective. This involves setting a target inflation rate and adjusting monetary policy tools, including the money supply, to achieve this goal. If inflation falls below the target, the central bank may increase the money supply to stimulate economic activity and inflation.
Effects of an Increased Money Supply: A Ripple Effect
An increase in the money supply, while seemingly beneficial in stimulating economic growth, has a complex array of consequences, both positive and negative.
Positive Effects: Stimulating Economic Growth
- Increased investment and consumption: More money in circulation typically leads to lower interest rates, making borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers. This encourages increased investment in capital goods and increased consumer spending, boosting aggregate demand.
- Reduced unemployment: As businesses expand due to increased investment and consumer demand, they require more workers, leading to a decrease in unemployment. This effect is particularly pronounced during periods of recession or economic stagnation.
- Increased economic output: The combination of increased investment and consumption fuels economic growth, resulting in a larger overall production of goods and services. This increased output can lead to improved living standards.
Negative Effects: The Downside of Expansion
- Inflation: Perhaps the most significant negative consequence is inflation. When the money supply grows faster than the economy's capacity to produce goods and services, the value of money declines, leading to a general rise in prices. This erodes purchasing power and can lead to economic instability.
- Asset bubbles: Excess money in the system can lead to speculative bubbles in asset markets, such as real estate or stocks. This can lead to unsustainable price increases, followed by sharp corrections and potential financial crises.
- Currency devaluation: In open economies, an increase in the money supply can lead to a devaluation of the currency relative to other currencies. This makes imports more expensive and exports cheaper, affecting the balance of trade.
- Increased interest rates (in the long run): While initially interest rates may fall, persistent increases in the money supply can lead to higher inflation expectations. This prompts central banks to raise interest rates to curb inflation, ultimately negating the initial stimulative effects.
The Role of Velocity of Money
The velocity of money, representing the rate at which money changes hands within an economy, plays a crucial role in determining the impact of an increased money supply. The equation of exchange, MV = PQ (where M is the money supply, V is velocity, P is the price level, and Q is the quantity of goods and services), illustrates this relationship. An increase in the money supply can lead to inflation if velocity remains stable or increases, but if velocity decreases significantly, the inflationary pressure might be lessened.
The Importance of Monetary Policy
Central banks carefully manage the money supply through monetary policy to achieve macroeconomic stability. The goal is to find a balance between stimulating economic growth and controlling inflation. This involves a delicate balancing act, as policies aimed at boosting economic growth can inadvertently lead to inflation, while measures to control inflation can dampen economic activity. The effectiveness of monetary policy is also influenced by factors such as the responsiveness of businesses and consumers to changes in interest rates, the state of the global economy, and expectations about future inflation.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities
An increase in the money supply is a complex economic phenomenon with far-reaching consequences. While it can stimulate economic growth and reduce unemployment in the short-term, the potential for inflation and asset bubbles necessitates careful management by central banks. Understanding the mechanisms behind money supply changes, their effects on various economic variables, and the role of monetary policy is essential for anyone seeking to comprehend the dynamics of the modern economy. Furthermore, recognizing the interplay between money supply, velocity, and inflation allows for a more nuanced understanding of economic fluctuations and the challenges faced by policymakers in maintaining economic stability. The continued study and analysis of these factors remain crucial for navigating the complexities of the global financial landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Multiple Choice Neuroscience Questions On The Amygdala
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Are The Components Of A Nucleotide
Mar 25, 2025
-
Mas Vale Que Nunca Temprano Rico Tarde Mejor
Mar 25, 2025
-
Select All The Statements About Haydns Early Career
Mar 25, 2025
-
Bar Exam Family Law Multiple Choice Questions
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about An Increase In The Money Supply Will Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
