Anatomy Of The Respiratory System Labster Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 8 min read
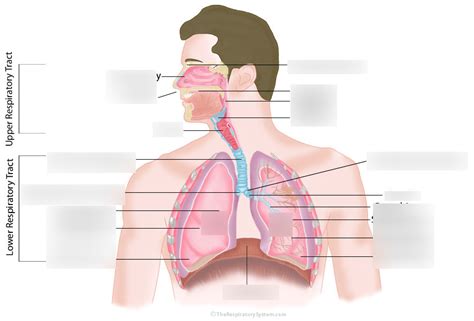
Table of Contents
- Anatomy Of The Respiratory System Labster Quizlet
- Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Respiratory System: A Deep Dive with Labster and Quizlet
- 1. The Upper Respiratory Tract: Your Body's Air Filter
- 2. The Lower Respiratory Tract: Where Gas Exchange Happens
- 3. Muscles of Respiration: The Mechanics of Breathing
- 4. Gas Exchange: The Heart of Respiration
- 5. Control of Breathing: A Complex Regulatory System
- Leveraging Labster and Quizlet for Optimal Learning:
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Anatomy of the Respiratory System: A Deep Dive with Labster and Quizlet
Understanding the respiratory system is crucial for anyone studying biology, medicine, or related fields. This complex system, responsible for the essential process of gas exchange, involves a fascinating interplay of organs and structures. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the respiratory system's anatomy, leveraging the interactive learning experiences offered by Labster and the practice opportunities provided by Quizlet to enhance your understanding. We'll explore each component, from the nasal cavity to the alveoli, highlighting key features and their functions.
1. The Upper Respiratory Tract: Your Body's Air Filter
The upper respiratory tract is the initial gateway for air entering your body. It's responsible for filtering, warming, and humidifying the air before it reaches the delicate lower respiratory tract. Let's break down its key components:
-
Nose and Nasal Cavity: The journey begins here! The nasal cavity is lined with mucous membranes that trap dust, pollen, and other airborne particles. The nasal conchae, bony projections within the nasal cavity, increase the surface area for air to contact the mucous membranes, maximizing their filtering efficiency. Labster simulations effectively visualize these structures and their intricate roles.
-
Pharynx (Throat): This muscular tube acts as a common passageway for both air and food. It's divided into three parts: the nasopharynx (behind the nasal cavity), the oropharynx (behind the oral cavity), and the laryngopharynx (connected to the larynx). The location of the epiglottis, a crucial flap of cartilage that prevents food from entering the trachea, is clearly depicted in Labster's interactive models. Using Quizlet flashcards on this area can help you solidify your understanding of the pharynx's structure and function.
-
Larynx (Voice Box): This cartilaginous structure houses the vocal cords. The vibrations of the vocal cords as air passes over them produce sound. The larynx also plays a vital role in protecting the lower airways by preventing food and other foreign objects from entering the trachea. Think of the epiglottis's critical role here, a concept easily grasped through Labster's animations. Quizlet's spaced repetition system can help you retain this information long-term.
2. The Lower Respiratory Tract: Where Gas Exchange Happens
The lower respiratory tract is where the actual gas exchange—the uptake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide—occurs. This section is equally important and necessitates thorough understanding.
-
Trachea (Windpipe): This flexible tube, reinforced by C-shaped cartilage rings, conducts air from the larynx to the bronchi. The C-shaped rings prevent the trachea from collapsing while allowing it to expand during swallowing. Labster's 3D models allow you to explore the trachea's structure in detail, visualizing the cartilage rings and the smooth muscle between them. Use Quizlet to test your knowledge of the trachea's histology and function.
-
Bronchi: The trachea branches into two main bronchi, one for each lung. These bronchi further subdivide into smaller and smaller branches, forming the bronchial tree. The branching pattern, a key element in maximizing surface area for gas exchange, is perfectly illustrated in Labster's interactive simulations. Review this complex branching using Quizlet's image flashcards.
-
Bronchioles: These are the smallest branches of the bronchial tree. The bronchioles lead to the alveoli, the tiny air sacs where gas exchange takes place. The smooth muscle surrounding the bronchioles allows them to constrict or dilate, regulating airflow. Labster can help you understand the differences between bronchi and bronchioles, and the role of smooth muscle in regulating airflow. Use Quizlet to practice identifying different parts of the bronchial tree.
-
Alveoli: These tiny air sacs are the functional units of the respiratory system. Their thin walls and extensive surface area are perfectly adapted for efficient gas exchange. Surfactant, a lipoprotein secreted by alveolar cells, helps to reduce surface tension and prevent alveolar collapse. Labster provides detailed visualizations of the alveoli, highlighting their structure and the process of gas exchange. Create Quizlet flashcards focusing on the specific cell types within the alveoli and their functions.
-
Lungs: The lungs are the primary organs of respiration. They are paired, cone-shaped organs located in the thoracic cavity. Each lung is surrounded by a double-layered membrane called the pleura. The pleural fluid between the layers reduces friction during breathing. The lobes of the lungs (three in the right lung and two in the left) are clearly shown in Labster's 3D models, and you can test your knowledge of their locations using Quizlet.
3. Muscles of Respiration: The Mechanics of Breathing
Breathing, or pulmonary ventilation, is an active process involving several key muscles:
-
Diaphragm: This dome-shaped muscle is the primary muscle of inspiration (inhalation). When it contracts, it flattens, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity and drawing air into the lungs. Labster's simulations provide a dynamic view of diaphragm movement during breathing. Use Quizlet to memorize the key actions and results of diaphragm contractions.
-
Intercostal Muscles: These muscles are located between the ribs. External intercostal muscles aid in inspiration by raising the ribs and further increasing the thoracic cavity's volume. Internal intercostal muscles are primarily involved in expiration (exhalation), though their role is less significant during normal quiet breathing. Labster's interactive exercises allow you to visualize how the intercostal muscles contribute to breathing mechanics. Quizlet's matching games can help you associate the muscles with their respective actions.
-
Accessory Muscles: During strenuous exercise or when breathing is compromised, accessory muscles such as the sternocleidomastoid and scalene muscles may be recruited to aid in inspiration. Labster’s simulations may show these muscles in action, offering a practical comparison to normal breathing. Using Quizlet, you can create flashcards focusing on when and why these muscles become involved.
4. Gas Exchange: The Heart of Respiration
The entire process culminates in the crucial step of gas exchange—the movement of oxygen from the alveoli into the blood and the movement of carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveoli. This happens due to the difference in partial pressures of these gases.
-
Partial Pressures: Oxygen has a higher partial pressure in the alveoli than in the pulmonary capillaries, leading to its diffusion into the blood. Carbon dioxide has a higher partial pressure in the blood than in the alveoli, resulting in its diffusion into the alveolar space to be exhaled. Labster’s visualizations make this abstract concept concrete, showing the flow of gases based on partial pressures. Quizlet can help you solidify this concept by testing your knowledge of the partial pressures of different gases in various locations.
-
Hemoglobin: Oxygen binds to hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, increasing the blood's oxygen-carrying capacity. Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood in various forms, including dissolved in plasma, bound to hemoglobin, and as bicarbonate ions. Labster simulations can help you visualize the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin and the different ways carbon dioxide is transported. Use Quizlet's flashcards to review the different forms of carbon dioxide transport.
-
Respiratory Membrane: The respiratory membrane is the thin barrier between the alveoli and the pulmonary capillaries, facilitating efficient gas exchange. Its components – alveolar epithelium, basement membrane, and capillary endothelium – work harmoniously. Labster's detailed models allow you to explore the components of the respiratory membrane and appreciate its role in gas exchange efficiency. Create detailed Quizlet flashcards covering the layers and their structure, and test yourself on the pathway oxygen and carbon dioxide take.
5. Control of Breathing: A Complex Regulatory System
Breathing is not simply a mechanical process; it's tightly regulated by the nervous and endocrine systems.
-
Respiratory Center: This region in the brainstem controls the basic rhythm of breathing. Chemoreceptors detect changes in blood pH, carbon dioxide levels, and oxygen levels, signaling the respiratory center to adjust breathing rate and depth accordingly. Labster's simulations can demonstrate the location of the respiratory center and the feedback loop involved in breathing regulation. Create a Quizlet set comparing and contrasting the roles of central and peripheral chemoreceptors.
-
Feedback Loops: Negative feedback mechanisms ensure that breathing is adjusted to maintain appropriate blood gas levels and pH. For instance, increased carbon dioxide levels lead to increased breathing rate and depth, reducing carbon dioxide levels. Labster's interactive exercises allow you to test your understanding of these feedback loops. Use Quizlet to practice explaining the mechanisms of negative feedback in breathing control.
Leveraging Labster and Quizlet for Optimal Learning:
Labster's interactive simulations and 3D models offer an unparalleled way to visualize the intricate structures and processes of the respiratory system. Its gamified approach makes learning engaging and effective. Quizlet, with its various learning modes like flashcards, matching games, and practice tests, provides a powerful tool to reinforce your understanding and track your progress.
By combining the immersive learning experience of Labster with the focused practice of Quizlet, you can achieve a profound understanding of the respiratory system's anatomy and physiology. Remember to regularly review your Quizlet sets and actively engage with Labster's simulations to ensure long-term retention and mastery of this complex subject. Consistent effort and use of these tools will prepare you for any assessment and help you truly understand this critical body system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Origin Of The External Obliques Includes Ribs
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True About Emergency Contraceptive Pills
Apr 03, 2025
-
An Area Of Hollowness Between Areas Of Volume Is Called
Apr 03, 2025
-
Classify Each Description As True Of Introns Only
Apr 03, 2025
-
Inspiration Sources Such As A Surface Design System Called
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Anatomy Of The Respiratory System Labster Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
