Apoptosis Refers To Cell Death And Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
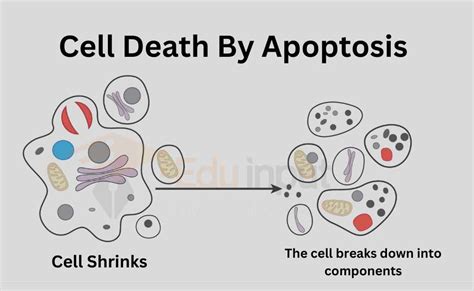
Table of Contents
Apoptosis: Programmed Cell Death and its Relevance (A Deep Dive)
Apoptosis, often referred to as programmed cell death, is a fundamental biological process crucial for the development, maintenance, and health of multicellular organisms. Unlike necrosis, which is a form of accidental cell death due to injury or infection, apoptosis is an active, genetically regulated process that eliminates unwanted or damaged cells in a controlled manner. Understanding apoptosis is critical across various fields, from developmental biology and immunology to cancer research and neurobiology. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of apoptosis, its mechanisms, regulation, significance, and its relationship with the popular study tool, Quizlet.
What is Apoptosis? A Closer Look
Apoptosis is a highly orchestrated process characterized by specific morphological and biochemical changes within the cell. These changes include:
- Cell shrinkage: The cell becomes smaller and more compact.
- Chromatin condensation: The DNA within the nucleus condenses and fragments.
- Formation of apoptotic bodies: The cell breaks down into membrane-bound vesicles containing cellular components.
- Phagocytosis: These apoptotic bodies are efficiently engulfed by neighboring cells or phagocytes, preventing inflammation.
This orderly dismantling prevents the release of harmful cellular contents into the surrounding tissue, unlike the inflammatory response seen in necrosis. This controlled demolition is vital for maintaining tissue homeostasis and preventing damage to surrounding cells.
The Molecular Machinery of Apoptosis: Key Players
The execution of apoptosis involves a complex interplay of various molecules and signaling pathways. Two primary pathways contribute to the initiation and execution of apoptosis:
1. The Intrinsic (Mitochondrial) Pathway:
This pathway is primarily triggered by intracellular stress, such as DNA damage, oxidative stress, or growth factor deprivation. The process begins in the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell. When a cell senses internal stress, it activates pro-apoptotic proteins like Bax and Bak. These proteins permeabilize the mitochondrial outer membrane, leading to the release of cytochrome c and other apoptotic factors into the cytoplasm.
Cytochrome c then binds to Apaf-1 (apoptotic protease activating factor 1), forming the apoptosome, a multi-protein complex. The apoptosome activates caspase-9, an initiator caspase, initiating a cascade of caspase activation. Caspases are a family of proteases, enzymes that break down proteins, crucial for executing the apoptotic program.
2. The Extrinsic (Death Receptor) Pathway:
This pathway is initiated by extracellular signals binding to death receptors on the cell surface. These receptors, members of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily, include Fas (CD95) and TRAIL-R1/R2. Upon ligand binding (e.g., Fas ligand), these receptors trimerize, recruiting adaptor proteins like FADD (Fas-associated death domain protein).
FADD, in turn, recruits and activates caspase-8, another initiator caspase. Caspase-8 then activates downstream executioner caspases, such as caspase-3 and caspase-7, leading to the dismantling of the cell.
The Convergence Point: Executioner Caspases
Regardless of the initiating pathway (intrinsic or extrinsic), both ultimately converge on the activation of executioner caspases, such as caspase-3 and caspase-7. These caspases cleave numerous cellular substrates, leading to the characteristic morphological and biochemical changes of apoptosis. They target key structural proteins, DNA repair enzymes, and inhibitors of DNases, ensuring the complete and controlled demise of the cell.
Regulation of Apoptosis: A Delicate Balance
The process of apoptosis is tightly regulated to prevent unwanted cell death or insufficient removal of damaged cells. A delicate balance exists between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins. The Bcl-2 family of proteins plays a crucial role in this regulation.
Pro-apoptotic proteins, like Bax and Bak, promote apoptosis by permeabilizing the mitochondrial outer membrane. Anti-apoptotic proteins, like Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, inhibit apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial permeabilization and inhibiting caspase activation. The balance between these proteins determines the cell's fate—to live or die.
Other regulatory mechanisms include:
- Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs): These proteins directly inhibit caspases, preventing apoptosis.
- Growth factors and survival signals: These signals can activate anti-apoptotic pathways, promoting cell survival.
- Tumor suppressor genes: Genes like p53 play a crucial role in initiating apoptosis in response to DNA damage.
The Significance of Apoptosis: Why it Matters
Apoptosis is essential for a wide range of biological processes:
- Development: Apoptosis plays a critical role in shaping organs and tissues during embryonic development. For example, it removes interdigital webbing in the developing hand and foot.
- Immune system homeostasis: Apoptosis eliminates self-reactive lymphocytes, preventing autoimmune diseases. It also removes immune cells after an immune response has subsided.
- Neurogenesis: Apoptosis is involved in regulating the number of neurons during brain development.
- Cancer prevention: Apoptosis eliminates damaged or pre-cancerous cells, preventing tumor formation. Dysregulation of apoptosis is a hallmark of cancer.
- Tissue homeostasis: Apoptosis maintains the balance between cell proliferation and cell death, ensuring healthy tissue function.
Dysregulation of Apoptosis: Disease Implications
Disruptions in the apoptotic pathway can lead to various pathological conditions:
- Cancer: Inhibition of apoptosis allows damaged or mutated cells to survive and proliferate, leading to tumor formation and metastasis.
- Autoimmune diseases: Failure to eliminate self-reactive lymphocytes can result in autoimmune disorders.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Excessive apoptosis can contribute to the loss of neurons seen in Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's disease.
- Infectious diseases: Some viruses and pathogens can inhibit apoptosis to evade the immune system.
Apoptosis and Quizlet: A Learning Tool
Quizlet, a popular online learning platform, can be a valuable tool for students learning about apoptosis. Quizlet provides various interactive study modes, including flashcards, matching games, and quizzes, that can help reinforce understanding of key concepts, pathways, and molecules involved in apoptosis. Students can create their own sets of flashcards focusing on:
- Key terms: Apoptosis, necrosis, caspases, Bcl-2 family, mitochondria, death receptors, etc.
- Pathways: Intrinsic vs. extrinsic pathway, detailed steps involved in each pathway.
- Molecular players: Functions of specific proteins involved in apoptosis regulation.
- Disease implications: How dysregulation of apoptosis contributes to various diseases.
Using Quizlet can enhance learning through active recall and spaced repetition, improving knowledge retention and comprehension. By creating and sharing sets of flashcards, students can collaborate and reinforce their learning in a supportive environment.
Conclusion: A Vital Process with Far-Reaching Implications
Apoptosis is a fundamental process with profound implications for health and disease. Its intricate molecular mechanisms and tight regulation underscore its importance in maintaining tissue homeostasis and preventing various pathologies. Understanding the intricacies of apoptosis is crucial for advancing research in areas like cancer therapy, autoimmune disease treatment, and neuroprotection. Incorporating interactive learning tools like Quizlet can significantly enhance understanding and retention of this complex topic, ultimately contributing to a broader appreciation of the vital role of programmed cell death in biological systems. Further research into the nuances of apoptotic pathways and their dysregulation holds immense promise for developing new therapeutic strategies to combat diseases associated with aberrant apoptosis. The ongoing investigation into the intricate interplay of proteins, signaling cascades, and regulatory mechanisms involved in this fundamental cellular process continues to reveal new insights and opportunities for medical advancement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Dying Patient Is In The Depression Stage
Apr 02, 2025
-
Research Has Shown That Competent Communicators Achieve Effectiveness By
Apr 02, 2025
-
Wireless Wearable Fitness Devices Are Authorized Within Scifs
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True Of Equilibrium
Apr 02, 2025
-
For Accounts Receivable The Longer An Account Is Outstanding
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Apoptosis Refers To Cell Death And Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
