Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation Is A Procedure In Which Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
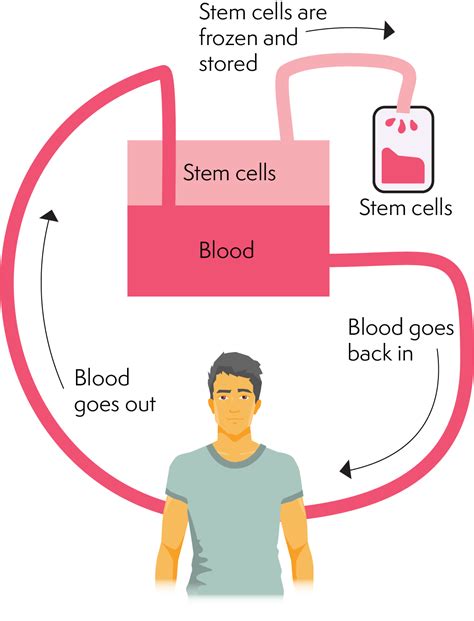
Table of Contents
Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation: A Comprehensive Guide
Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is a complex medical procedure with significant implications for patients battling various life-threatening diseases. Understanding its intricacies is crucial, not just for medical professionals, but also for patients and their families navigating this challenging journey. This comprehensive guide delves into the process, benefits, risks, and considerations surrounding ASCT.
What is Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation?
ASCT is a type of bone marrow transplant where a patient receives their own stem cells. Unlike allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT), which uses stem cells from a donor, ASCT utilizes the patient's own hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). These HSCs are the precursors to all blood cells – red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
The Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The ASCT procedure involves several key stages:
1. Stem Cell Mobilization and Collection:
- Stimulation: Before stem cells can be harvested, they need to be mobilized from the bone marrow into the bloodstream. This is achieved through the administration of medications, most commonly growth factors like granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). These factors stimulate the bone marrow to release a larger-than-normal number of HSCs into the peripheral blood.
- Apheresis: Once the stem cells are circulating in the bloodstream, they are collected through a process called apheresis. This procedure is similar to donating blood, where blood is drawn from one arm, the stem cells are separated using a cell separator, and the remaining blood components are returned to the patient through the other arm. This process is typically repeated over several days until a sufficient number of stem cells are collected.
2. High-Dose Chemotherapy or Radiation Therapy:
- Consolidation Therapy: After stem cell collection, the patient undergoes a high-dose chemotherapy regimen or radiation therapy. This intense treatment aims to eliminate cancerous cells or other diseased cells, which is often not possible with standard-dose therapies. This is a crucial step because it eradicates the diseased cells while also potentially damaging the patient's own healthy bone marrow.
3. Stem Cell Infusion:
- Repopulation: Once the high-dose therapy is complete, the patient's previously collected stem cells are infused back into their bloodstream. These cells then migrate to the bone marrow, where they begin to repopulate it and regenerate the blood cell production. This process takes time and is crucial for the patient's recovery.
4. Recovery and Monitoring:
- Engraftment: The time it takes for the transplanted stem cells to engraft, or successfully establish themselves in the bone marrow, is a critical factor in ASCT. Close monitoring of blood counts is essential during this period to detect any complications or delays in engraftment.
- Post-transplant Care: Post-transplant care involves managing potential side effects of the high-dose therapy and monitoring for any signs of infection, bleeding, or other complications. This phase requires ongoing medical support and careful management.
Conditions Treated with ASCT:
ASCT is a treatment option for a range of hematological malignancies and some non-malignant diseases. The most common applications include:
- Multiple Myeloma: A cancer of plasma cells in the bone marrow. ASCT is a cornerstone of treatment for multiple myeloma, often used in combination with other therapies.
- Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma: A group of cancers affecting the lymphatic system. ASCT can be used in certain types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, particularly aggressive forms.
- Hodgkin's Lymphoma: Another type of lymphatic cancer. ASCT may be considered for patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma that hasn't responded well to other treatments.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): A cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells. ASCT can be a part of the treatment strategy for AML, often after initial chemotherapy.
- Autoimmune Diseases: In some cases, ASCT is being investigated as a treatment for severe autoimmune diseases where other therapies have failed. This is a more emerging application.
Advantages of ASCT:
- High Cure Rates: In several cancers, ASCT has demonstrated high cure rates, particularly when combined with other treatment modalities.
- Improved Remission Rates: Even if a complete cure is not achieved, ASCT can significantly prolong remission periods, providing patients with valuable time.
- Use of Patient's Own Cells: This eliminates the risk of graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), a serious complication that can occur with allo-SCT when donor cells attack the recipient's body.
- Potential for Long-Term Remission: For certain cancers, ASCT can lead to long-term remission, significantly improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Disadvantages and Risks of ASCT:
Despite its significant benefits, ASCT also carries several risks and potential complications:
- Infection: The high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy severely suppresses the immune system, increasing the risk of severe infections.
- Bleeding: Low platelet counts resulting from the therapy can lead to bleeding complications, ranging from minor bruising to life-threatening hemorrhage.
- Mucositis: Inflammation and sores in the mouth and throat are common side effects, causing pain and difficulty eating and swallowing.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These gastrointestinal side effects are common with chemotherapy and can be severe, requiring strong anti-nausea medications.
- Fatigue: Extreme tiredness and fatigue are frequent side effects that can persist for weeks or months after the procedure.
- Neurotoxicity: Some chemotherapy drugs can cause neurological side effects, such as peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage in the extremities).
- Cardiotoxicity: Certain chemotherapy drugs can damage the heart, potentially leading to heart failure.
- Secondary Cancers: The high-dose therapy, while effective in eliminating cancer cells, can increase the risk of developing secondary cancers later in life.
- Death: Unfortunately, ASCT carries a risk of mortality, although this is relatively low in specialized centers with experienced medical teams.
Preparing for ASCT:
Thorough preparation is crucial for a successful ASCT procedure. This includes:
- Physical Evaluation: A comprehensive medical evaluation to assess the patient's overall health and suitability for ASCT.
- Psychological Support: Patients undergoing ASCT will benefit greatly from psychological support to cope with the emotional and psychological challenges.
- Nutritional Counseling: Nutritional counseling can help patients maintain a healthy weight and ensure optimal nutrition before, during, and after the procedure.
- Family and Support System: A strong support system is vital for both the patient and their family throughout the process.
Post-ASCT Care:
Post-ASCT care is equally important as the procedure itself. It involves:
- Regular Blood Tests: Close monitoring of blood counts to track the engraftment of stem cells and detect any complications.
- Infection Prevention: Strict adherence to infection control measures to minimize the risk of infections.
- Symptom Management: Careful management of side effects such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and mucositis.
- Regular Follow-up Appointments: Ongoing medical follow-up to monitor for any recurrence of cancer or long-term complications.
Conclusion:
Autologous stem cell transplantation is a powerful tool in the fight against various life-threatening diseases. However, it's crucial to understand its complexities, risks, and benefits. The decision to undergo ASCT should be made in close consultation with a healthcare team experienced in this specialized area of medicine. Through thorough preparation, skilled medical care, and a strong support system, patients can navigate the ASCT journey and potentially achieve long-term remission or a cure. This information is for general knowledge and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider if you have questions about your health or need medical advice.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Structure Function Claim
Mar 25, 2025
-
A Behavior Becomes A Habit When It Has Been Repeated
Mar 25, 2025
-
Smoking May Be Permitted Only At The Bars
Mar 25, 2025
-
Multiple Sclerosis Is A Result Of Degeneration In The
Mar 25, 2025
-
You Are Driving On A Two Lane Highway
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation Is A Procedure In Which Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
