Basic Functions Of The Liver Include Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
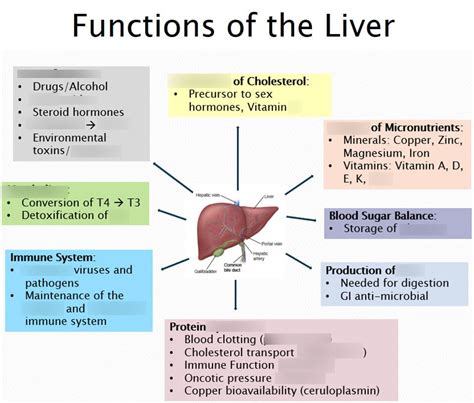
Table of Contents
Basic Functions of the Liver: A Comprehensive Guide
The liver, a vital organ residing in the upper right quadrant of your abdomen, is a powerhouse of biological processes. Its multifaceted functions are crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Understanding these basic functions is key to appreciating the liver's critical role in our bodies. This comprehensive guide will delve into the core functionalities of the liver, providing a detailed explanation suitable for both students and anyone interested in learning more about this remarkable organ. We'll explore each function in depth, using clear language and illustrative examples, and conclude with a quiz to test your knowledge.
1. Metabolism: The Liver's Central Role
The liver's metabolic prowess is unparalleled. It acts as the body's central metabolic hub, processing nutrients, synthesizing essential substances, and detoxifying harmful compounds. Let's break down its metabolic roles:
1.1 Carbohydrate Metabolism: Maintaining Blood Sugar
The liver plays a pivotal role in regulating blood glucose levels. It stores glucose in the form of glycogen, a readily available energy source. When blood sugar drops, the liver breaks down glycogen into glucose and releases it into the bloodstream, preventing hypoglycemia. Conversely, when blood sugar is high, the liver converts excess glucose into glycogen for storage. This intricate balancing act is crucial for maintaining consistent energy levels.
1.2 Lipid Metabolism: Processing Fats and Cholesterol
The liver is central to lipid metabolism, processing fats from dietary intake and synthesizing lipids needed by the body. It breaks down fats for energy production, synthesizes cholesterol (although excess cholesterol can be detrimental), and produces lipoproteins—packages that transport fats and cholesterol through the bloodstream. Dysfunction in lipid metabolism can lead to conditions like hyperlipidemia and fatty liver disease.
1.3 Protein Metabolism: Building Blocks and Detoxification
The liver's role in protein metabolism is equally significant. It synthesizes various plasma proteins, including albumin (crucial for maintaining blood osmotic pressure) and clotting factors (essential for blood coagulation). It also deaminates amino acids, removing the nitrogen-containing amino group to form urea, a less toxic compound excreted by the kidneys. This process prevents the buildup of ammonia, a highly toxic substance.
2. Detoxification and Excretion: The Liver as a Filter
The liver acts as a sophisticated filter, removing toxins and waste products from the blood. This detoxification process involves several mechanisms:
2.1 Biotransformation of Drugs and Toxins
The liver transforms many drugs and toxins into less harmful metabolites. This crucial process, often referred to as biotransformation, involves a series of enzymatic reactions that modify the chemical structure of the substance. These modified compounds are then more easily excreted from the body. This is why liver health is critical for individuals taking medications.
2.2 Bile Production and Excretion
Bile, a crucial digestive fluid produced by the liver, is vital for the digestion and absorption of fats. Bile salts emulsify fats, breaking them down into smaller droplets, increasing their surface area for enzymatic digestion. Bile also helps in the excretion of bilirubin, a byproduct of hemoglobin breakdown. Bilirubin's accumulation can lead to jaundice, a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes.
3. Storage: A Reservoir for Essential Nutrients
The liver serves as a storage depot for several essential nutrients, releasing them into the bloodstream as needed:
3.1 Glycogen Storage: Energy Reserve
As previously mentioned, the liver stores glucose as glycogen, providing a readily available energy source when blood glucose levels decline. This glycogen reserve helps maintain consistent energy levels throughout the day.
3.2 Vitamin and Mineral Storage: Essential Nutrients
The liver stores several vitamins, including vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12, as well as minerals like iron and copper. These nutrients are released as needed to support various bodily functions. Iron, in particular, is crucial for red blood cell production.
4. Synthesis and Secretion: Creating Essential Substances
Beyond its metabolic and detoxifying roles, the liver synthesizes and secretes various essential substances:
4.1 Protein Synthesis: Building Blocks of Life
The liver synthesizes numerous proteins crucial for various bodily functions. Albumin, the most abundant plasma protein, maintains blood osmotic pressure. Clotting factors are synthesized to ensure proper blood coagulation. Several other plasma proteins are also produced in the liver.
4.2 Hormone Production: Regulating Bodily Functions
The liver plays a role in producing and modifying several hormones, contributing to the endocrine system's overall function. It helps metabolize hormones like insulin and growth hormone, influencing their activity and duration of action.
4.3 Bile Production: Crucial for Fat Digestion
As previously discussed, the liver synthesizes and secretes bile, a crucial digestive fluid that aids in the digestion and absorption of fats. Bile salts emulsify fats, making them more accessible to digestive enzymes.
Understanding Liver Function Tests (LFTs)
Liver function tests (LFTs) are blood tests that measure levels of enzymes and other substances produced by the liver. Abnormal LFT results may indicate liver damage or disease. Commonly tested enzymes include alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT). Bilirubin levels are also frequently measured. LFTs provide valuable insights into liver health and assist in diagnosing liver conditions.
Quiz: Test Your Liver Knowledge
Now, let's test your understanding of the liver's basic functions. Answer the following multiple-choice questions:
1. Which of the following is NOT a primary function of the liver? a) Carbohydrate metabolism b) Detoxification of toxins c) Production of red blood cells d) Protein synthesis
2. The liver stores glucose in the form of: a) Glucose-6-phosphate b) Glycogen c) Fructose d) Sucrose
3. Which of these is a crucial component of bile, essential for fat digestion? a) Amylase b) Lipase c) Bile salts d) Pepsin
4. The process of converting ammonia to a less toxic substance (urea) occurs primarily in the: a) Kidneys b) Liver c) Lungs d) Intestines
5. Which of the following plasma proteins is primarily synthesized by the liver? a) Immunoglobulin G (IgG) b) Albumin c) Fibrinogen d) Both b and c
Answer Key:
- c) Production of red blood cells (Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow.)
- b) Glycogen
- c) Bile salts
- b) Liver
- d) Both b and c (Albumin and fibrinogen are both synthesized by the liver.)
This comprehensive guide has explored the intricate and multifaceted functions of the liver. Understanding these functions is crucial for appreciating the liver's pivotal role in maintaining overall health. Remember, a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, is crucial for supporting optimal liver function. If you have any concerns about your liver health, consult a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice and assess your individual needs.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Compared To Terrestrial Planets Jovian Planets Are
Apr 02, 2025
-
Nurse Logic 2 0 Knowledge And Clinical Judgment Advanced Test
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Describe How To Communicate Pals
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Hair Below The Crest Is Known As The
Apr 02, 2025
-
Managerial Strategy Are The Odds In Atlantic Hotels Favor
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Basic Functions Of The Liver Include Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
