Cerebral Aneurysm Thrombosis Or Hemorrhage Can Be The Cause Of
Breaking News Today
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
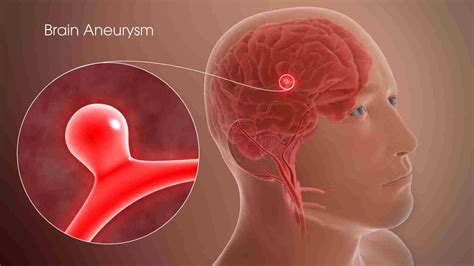
Table of Contents
Cerebral Aneurysm Thrombosis or Hemorrhage: Understanding the Causes and Consequences
Cerebral aneurysms, balloon-like bulges in the blood vessels of the brain, pose a significant threat to neurological health. While often asymptomatic, their rupture can lead to devastating consequences – either a cerebral hemorrhage (bleeding into the brain) or, less commonly, cerebral aneurysm thrombosis (blood clot formation within the aneurysm). Understanding the causes of both these life-threatening conditions is crucial for prevention and effective management. This comprehensive article explores the multifaceted factors contributing to cerebral aneurysm thrombosis and hemorrhage.
Risk Factors for Cerebral Aneurysm Rupture Leading to Hemorrhage or Thrombosis
The exact cause of a cerebral aneurysm is often unknown, but several risk factors significantly increase the likelihood of their formation and subsequent rupture. These factors can be broadly categorized as:
1. Genetic Predisposition and Family History
A strong family history of aneurysms is a major risk factor. Inherited conditions like autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome are linked to a higher incidence of cerebral aneurysms. Genetic mutations affecting connective tissue proteins, impacting vessel wall strength, also play a critical role. Specific genes are currently under investigation for their involvement in aneurysm formation.
2. Vascular Diseases and Conditions
Several vascular conditions increase the risk of aneurysm development and rupture. These include:
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): This is a leading risk factor. The constant high pressure on artery walls weakens them, making them prone to bulging.
- Smoking: Nicotine constricts blood vessels, increasing blood pressure and damaging artery walls. Smoking significantly elevates the risk of both aneurysm formation and rupture.
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of plaque within arteries reduces blood flow and weakens the vessel walls, increasing the vulnerability to aneurysms.
- Vasculitis: Inflammation of blood vessel walls, often caused by autoimmune disorders, can damage the artery structure, predisposing to aneurysm formation.
3. Age and Gender
Aneurysms are more prevalent in individuals aged 35-60, although they can occur at any age. Women are slightly more likely to experience a ruptured aneurysm than men, although the reasons remain partly unclear.
4. Head Trauma and Injury
While not a direct cause, head injuries, even minor ones, can potentially weaken blood vessel walls, making them susceptible to aneurysm formation over time. The precise mechanisms remain an area of ongoing research.
5. Drug Use
Cocaine use is strongly linked to increased cerebral aneurysm risk. The vasoconstrictive effects of cocaine can significantly raise blood pressure, leading to aneurysm rupture. Certain other illicit drugs may also contribute, although more research is needed to confirm their exact role.
6. Connective Tissue Disorders
As mentioned earlier, conditions affecting connective tissue, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, significantly increase the risk. These disorders weaken the structural integrity of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to bulging and rupture.
Cerebral Aneurysm Hemorrhage: The Rupture and its Consequences
When a cerebral aneurysm ruptures, it causes a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) – bleeding into the space between the brain and the skull. This is a life-threatening event that requires immediate medical attention. The severity of the hemorrhage depends on factors such as the size and location of the aneurysm, the amount of bleeding, and the individual's overall health.
Consequences of Cerebral Aneurysm Hemorrhage:
- Severe Headache: Often described as the "worst headache of their life," this is a hallmark symptom of SAH.
- Loss of Consciousness: This can range from brief fainting to prolonged coma.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Common symptoms due to brain irritation and pressure.
- Neck Stiffness (Nuchal Rigidity): Irritation of the meninges (brain coverings) causes stiffness.
- Seizures: Electrical disturbances in the brain due to bleeding and swelling.
- Neurological Deficits: These can include weakness, paralysis, speech problems (aphasia), vision problems, and cognitive impairments.
- Death: SAH has a high mortality rate, even with prompt medical intervention.
Cerebral Aneurysm Thrombosis: A Less Common but Serious Complication
Cerebral aneurysm thrombosis, the formation of a blood clot within the aneurysm sac, is less common than rupture. However, it still presents serious risks. While the clot may prevent rupture initially, it can lead to:
Consequences of Cerebral Aneurysm Thrombosis:
- Ischemic Stroke: If the clot dislodges and travels to a smaller blood vessel in the brain, it can block blood flow, causing an ischemic stroke.
- Aneurysm Growth: The presence of a clot may not fully halt the expansion of the aneurysm, and continued growth could increase the risk of rupture in the future.
- Pain and Pressure: The clot can cause localized pressure and pain in the affected area of the brain.
- Neurological Deficits: Depending on the location and size of the clot, neurological symptoms may develop.
Diagnosing Cerebral Aneurysms
Diagnosing cerebral aneurysms often involves a combination of imaging techniques:
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A fast and widely available method to visualize brain structures and identify bleeding.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scan: Provides more detailed images of brain tissue and blood vessels, helping to identify aneurysms and assess their size and location.
- Cerebral Angiography: A more invasive procedure involving injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels to visualize them in detail, allowing for precise aneurysm identification and characterization.
Treatment Options
Treatment strategies depend on several factors, including the size, location, and growth rate of the aneurysm, as well as the patient's overall health and risk factors. Options include:
- Surgical Clipping: A neurosurgical procedure where a small metal clip is placed at the base of the aneurysm to prevent blood flow into it.
- Endovascular Coiling: A less invasive procedure where platinum coils are inserted through a catheter into the aneurysm to fill it and prevent rupture.
- Observation: For small, asymptomatic aneurysms, watchful waiting with regular monitoring may be an option.
Prevention Strategies
While not all aneurysms are preventable, certain lifestyle modifications can reduce the risk:
- Controlling High Blood Pressure: Regular monitoring and medication management are crucial.
- Quitting Smoking: This significantly reduces the risk of aneurysm formation and rupture.
- Managing Cholesterol Levels: Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels helps prevent atherosclerosis.
- Regular Exercise: Improves cardiovascular health and blood flow.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes cardiovascular health.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Approach to Understanding and Managing Cerebral Aneurysms
Cerebral aneurysm thrombosis and hemorrhage are serious conditions with significant health implications. Understanding the underlying causes – from genetic predisposition to lifestyle factors – is essential for implementing preventative measures and choosing appropriate treatment strategies. While advancements in diagnostic and treatment techniques have improved outcomes, ongoing research continues to seek new ways to reduce the incidence and severity of these life-threatening conditions. Early detection, diligent management of risk factors, and prompt medical intervention remain crucial for improving the prognosis of individuals affected by cerebral aneurysms. This involves a collaborative approach between patients, healthcare professionals, and researchers dedicated to furthering our understanding and improving treatment of this complex medical issue.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Are The Elements Of A System Of Care Acls
Apr 06, 2025
-
Information Obtained Over Tlets Nlets May Be Disseminated To
Apr 06, 2025
-
A Companys Documented Philosophy Is Called Its
Apr 06, 2025
-
Why Is Early Onset An Important Factor In Crime
Apr 06, 2025
-
Ap Human Geography Unit 1 4 Review
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cerebral Aneurysm Thrombosis Or Hemorrhage Can Be The Cause Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
