Check All Items That Are A Function Of Cerebrospinal Fluid
Breaking News Today
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
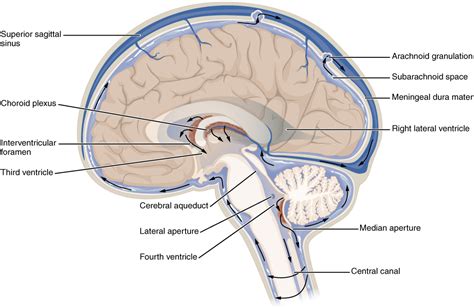
Table of Contents
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): Functions and Importance
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It's often described as the brain's "cushion," but its role extends far beyond simple protection. Understanding the multifaceted functions of CSF is crucial to comprehending the health and well-being of the central nervous system (CNS). This article delves into the comprehensive roles of CSF, exploring its protective, metabolic, and homeostatic functions in detail.
The Protective Role of CSF: Cushioning and Buoyancy
One of the most widely known functions of CSF is its protective capacity. This protection manifests in two primary ways:
1. Mechanical Protection: Cushioning Against Impact
The brain, a delicate and highly complex organ, floats within the CSF-filled subarachnoid space. This buoyant environment significantly reduces the weight of the brain, preventing it from being crushed by its own mass. This "floating" mechanism is vital in mitigating the impact of trauma. When the head sustains an impact, the CSF acts as a shock absorber, dispersing the force and minimizing damage to the delicate brain tissue. Without this crucial cushioning effect, even minor impacts could cause severe injury. The intricate network of CSF-filled spaces further enhances this protective function by distributing the force of impact over a larger area.
2. Preventing Harmful Chemical Interactions
CSF also acts as a chemical barrier, preventing harmful substances from reaching the brain. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is the primary defense mechanism, but the CSF plays a supportive role. By constantly circulating and clearing metabolic waste products and toxins, the CSF maintains a stable and protective chemical environment around the brain and spinal cord. This is particularly critical in preventing inflammatory responses and protecting against neurodegenerative diseases. The controlled composition of CSF contributes to the overall health and functionality of the CNS by maintaining a balanced chemical milieu.
The Metabolic Role of CSF: Nutrient Supply and Waste Removal
Beyond its protective role, CSF plays a vital metabolic role in the CNS. It's not merely a passive fluid; it's an active participant in the intricate chemical processes within the brain.
1. Nutrient Transport and Delivery
CSF serves as a medium for transporting essential nutrients and other vital substances from the blood to the brain tissue. Glucose, amino acids, and other metabolites are transported across the blood-brain barrier and then distributed throughout the CNS via the CSF. This constant supply of nutrients is essential for the metabolic processes of brain cells, ensuring their proper functioning and survival. The constant flow of CSF guarantees that every part of the CNS receives the necessary building blocks for optimal performance.
2. Waste Product Removal: The Glymphatic System
The efficient removal of metabolic waste products is crucial for maintaining brain health. The discovery of the glymphatic system has revolutionized our understanding of CSF's role in waste clearance. This system, a network of perivascular channels, uses CSF flow to flush out metabolic waste, including amyloid-beta plaques associated with Alzheimer's disease and other toxins. This process is particularly active during sleep, highlighting the importance of adequate rest for brain health. The efficiency of the glymphatic system directly impacts the overall health and function of the brain, preventing the accumulation of potentially harmful substances.
3. Neurotransmitter Regulation
CSF participates in the intricate regulation of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that facilitate communication between neurons. By transporting and regulating the concentration of neurotransmitters, CSF influences neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission. This subtle control is crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of neuronal activity in the brain, impacting various cognitive functions such as mood, sleep, and attention. Dysregulation of neurotransmitter levels within the CSF can contribute to various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
The Homeostatic Role of CSF: Maintaining a Stable Intracranial Environment
CSF plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the cranial cavity, ensuring the optimal functioning of the brain.
1. Regulation of Intracranial Pressure (ICP)
The volume of CSF is tightly regulated to maintain a stable intracranial pressure (ICP). Changes in ICP can have severe consequences, potentially leading to brain damage. The constant production and absorption of CSF help to buffer fluctuations in brain volume and maintain a stable ICP. The intricate balance between CSF production and absorption is a key factor in protecting the brain from injury due to pressure changes. Mechanisms involved in ICP regulation include changes in CSF production rate and alterations in CSF absorption.
2. Temperature Regulation
CSF contributes to the thermoregulation of the brain. Its constant circulation helps to dissipate heat generated by neuronal activity, maintaining a stable brain temperature. This temperature regulation is crucial for optimal brain function, as extreme temperatures can impair neuronal activity and lead to damage. The close proximity of CSF to brain tissue facilitates effective heat exchange, ensuring the brain operates within its ideal temperature range.
3. pH and Ionic Balance
CSF helps regulate the pH and ionic balance within the intracranial environment. It buffers fluctuations in pH and ion concentrations, maintaining an optimal environment for neuronal function. This precise control over the chemical composition of the CSF ensures the stability of the neuronal microenvironment and promotes optimal neuronal signaling. Disruptions to this delicate balance can have profound effects on neuronal excitability and overall brain function.
Clinical Significance of CSF Analysis: Diagnosis and Monitoring
Analysis of CSF is a critical tool in the diagnosis and monitoring of various neurological disorders. The composition and characteristics of CSF can reveal valuable information about the health of the CNS.
1. Infectious Diseases
CSF analysis is crucial in diagnosing infections of the CNS, such as meningitis and encephalitis. The presence of inflammatory cells, bacteria, viruses, or fungi in the CSF provides strong evidence of CNS infection. The characteristics of the CSF, such as its appearance, cell count, and protein levels, help differentiate between different types of infections and guide treatment strategies. Rapid and accurate CSF analysis is essential for effective management of CNS infections.
2. Neurological Disorders
CSF analysis can aid in the diagnosis of various neurological disorders, including multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Specific markers in the CSF can indicate the presence of these conditions. For example, oligoclonal bands in the CSF are a characteristic finding in multiple sclerosis. The information obtained from CSF analysis contributes significantly to the accurate diagnosis and effective management of neurological disorders.
3. Traumatic Brain Injury
Following traumatic brain injury, CSF analysis can help assess the severity of the injury and monitor the patient's progress. The presence of blood, elevated protein levels, or specific biomarkers in the CSF can indicate the extent of brain damage and guide treatment decisions. Serial CSF analysis allows clinicians to track the patient's recovery and adjust treatment as needed. This continuous monitoring is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes following traumatic brain injury.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Brain Health
Cerebrospinal fluid, though often overlooked, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the health and function of the central nervous system. From its crucial protective functions to its metabolic and homeostatic roles, CSF is essential for optimal brain function. Understanding its multifaceted functions allows us to appreciate its significance in brain health and opens avenues for further research into the prevention and treatment of neurological disorders. The importance of CSF cannot be overstated; it truly is the unsung hero of brain health. Further research into the intricate mechanisms governing CSF production, circulation, and absorption promises to unlock new insights into the pathogenesis of neurological diseases and lead to innovative therapeutic approaches. The continuing exploration of the CSF's functions will undoubtedly reveal even more about its critical role in maintaining the health and well-being of the brain and spinal cord.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Ecological Relationship Between A Shark And Jack
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Factor Is The Only Way To Lower Bac
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Statement Is True Regarding A Minor Beneficiary
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Superheated Gas With Charged Particles Is Called
Mar 14, 2025
-
Explain How Poor Physical Health May Affect Your Social Health
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Check All Items That Are A Function Of Cerebrospinal Fluid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
