Concussions And Cerebral Infections Can Decrease The Effectiveness Of
Breaking News Today
Mar 27, 2025 · 7 min read
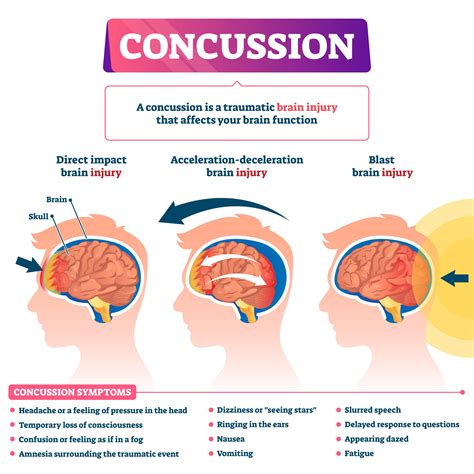
Table of Contents
Concussions and Cerebral Infections: Diminishing the Effectiveness of Cognitive Function, Physical Performance, and Overall Well-being
Concussions and cerebral infections represent significant threats to brain health, impacting cognitive function, physical performance, and overall well-being. While distinct in their origins, both conditions share a concerning overlap in their potential to significantly decrease the effectiveness of various bodily systems and mental processes. Understanding their individual mechanisms and the shared consequences is crucial for effective prevention, diagnosis, and management.
Understanding Concussions: A Traumatic Brain Injury
A concussion, a type of mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), occurs when a sudden impact to the head causes the brain to bounce back and forth or twist inside the skull. This jarring motion can disrupt normal brain function, leading to a range of symptoms. The severity of a concussion can vary greatly, ranging from mild symptoms resolving quickly to more severe cases requiring extended recovery periods.
Symptoms of Concussion: These can manifest immediately or appear days or even weeks after the injury.
- Cognitive Symptoms: Headache, dizziness, confusion, difficulty concentrating, memory problems (both short-term and long-term), slowed processing speed, difficulty with multitasking, and trouble with decision-making.
- Physical Symptoms: Fatigue, nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound (photophobia and phonophobia), balance problems, sleep disturbances, and blurred vision.
- Emotional/Behavioral Symptoms: Irritability, anxiety, depression, emotional lability (rapid shifts in mood), and personality changes.
How Concussions Decrease Effectiveness:
The immediate impact of a concussion disrupts normal neuronal communication. The brain's delicate electrochemical balance is thrown off, leading to impaired signaling between different brain regions. This disruption manifests as the various cognitive and physical symptoms described above. Furthermore, concussions can also lead to:
- Reduced processing speed: The brain struggles to process information efficiently, resulting in slower reaction times and difficulty with tasks requiring rapid mental processing.
- Impaired memory consolidation: The formation of new memories is hampered, leading to difficulties in learning and retaining information.
- Decreased attention span: Maintaining focus and concentration becomes challenging, affecting productivity and overall performance.
- Motor skill deficits: Coordination, balance, and fine motor skills can be impaired, affecting physical performance and daily activities.
- Increased risk of future concussions: The brain is more vulnerable to subsequent injury after a concussion, increasing the risk of long-term complications.
Cerebral Infections: A Threat From Within
Cerebral infections, also known as brain infections, encompass a range of conditions caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. These infections can directly invade the brain tissue (encephalitis) or the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord (meningitis).
Types of Cerebral Infections:
- Bacterial Meningitis: A serious infection that can cause inflammation of the meninges, leading to severe headache, fever, stiff neck, and potentially life-threatening complications.
- Viral Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain caused by a viral infection. Symptoms can range from mild flu-like symptoms to severe neurological impairment.
- Fungal Meningitis: A less common but potentially severe infection caused by fungi.
- Parasitic Infections: Rare but potentially serious infections caused by parasites that can reach the brain.
How Cerebral Infections Decrease Effectiveness:
Cerebral infections directly damage brain cells and disrupt normal brain function through various mechanisms:
- Inflammation and swelling: The immune system's response to infection causes inflammation and swelling in the brain, increasing pressure within the skull and impairing blood flow. This can lead to neurological dysfunction.
- Direct neuronal damage: Pathogens can directly attack and kill brain cells, leading to irreversible damage and neurological deficits.
- Neurotransmitter disruption: The infection can interfere with the production and function of neurotransmitters, chemicals that transmit signals between neurons. This disruption can cause cognitive impairment, motor problems, and mood disorders.
- Blood-brain barrier disruption: The infection can compromise the blood-brain barrier, a protective layer that shields the brain from harmful substances in the bloodstream. This can allow toxins and pathogens to enter the brain, exacerbating the damage.
Symptoms of Cerebral Infections:
Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of the infection, but may include:
- Fever and chills: Often the first signs of infection.
- Severe headache: Usually intense and persistent.
- Neck stiffness (meningismus): A characteristic symptom of meningitis.
- Nausea and vomiting: Often accompanying severe headaches.
- Confusion and disorientation: Can range from mild confusion to severe delirium.
- Seizures: Can occur in severe cases.
- Loss of consciousness: In advanced stages.
- Focal neurological deficits: Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, speech difficulties, visual problems.
Overlapping Consequences: The Shared Impact of Concussions and Cerebral Infections
Both concussions and cerebral infections share a common thread: they can significantly decrease the effectiveness of cognitive function, physical performance, and overall well-being. While the mechanisms differ, the consequences can overlap considerably.
Cognitive Impairment:
Both concussions and cerebral infections can lead to a broad spectrum of cognitive impairments, including:
- Memory problems: Difficulty remembering recent events, names, or faces.
- Attention deficits: Trouble concentrating, focusing, and maintaining attention.
- Executive dysfunction: Impaired planning, organization, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- Slowed processing speed: Difficulty processing information quickly and efficiently.
- Language difficulties: Problems with understanding or expressing language.
Physical Impairment:
Both conditions can cause physical impairments, such as:
- Fatigue and weakness: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Balance problems: Difficulty with coordination and maintaining balance.
- Motor skill deficits: Impaired fine motor skills and coordination.
- Sleep disturbances: Insomnia, difficulty falling asleep, or excessive daytime sleepiness.
- Headaches: Persistent headaches, often worsening with exertion.
Emotional and Behavioral Changes:
Both concussions and cerebral infections can significantly affect emotional and behavioral well-being:
- Irritability and mood swings: Increased irritability, anger, and emotional lability.
- Anxiety and depression: Increased risk of anxiety disorders and depression.
- Personality changes: Changes in personality, behavior, or social interactions.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): Especially relevant following a concussion, particularly if the injury was severe or involved a traumatic event.
Long-Term Effects: Living with the Consequences
The long-term effects of concussions and cerebral infections can be substantial and vary widely depending on the severity of the injury or infection and the individual's response to treatment. Some individuals may experience complete recovery, while others may live with persistent symptoms for months or even years. These long-term effects can impact various aspects of life, including:
- Academic and professional performance: Difficulty concentrating, remembering information, and performing tasks can affect academic achievement and job performance.
- Social relationships: Cognitive, emotional, and behavioral changes can strain relationships with family and friends.
- Quality of life: Persistent symptoms and functional limitations can significantly reduce overall quality of life.
- Increased risk of chronic health problems: Studies suggest a link between TBI and increased risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease later in life.
Prevention and Management: Strategies for Mitigation
Prevention and early intervention are key to minimizing the long-term consequences of concussions and cerebral infections.
Concussion Prevention:
- Wearing protective gear: Helmets are crucial for activities with a high risk of head injury, such as contact sports, cycling, and skateboarding.
- Safe driving practices: Following traffic laws and driving defensively can reduce the risk of car accidents.
- Home safety measures: Ensuring a safe home environment can prevent falls and other accidents that may lead to head injuries.
Cerebral Infection Prevention:
- Vaccination: Vaccinations are available for some types of meningitis and encephalitis.
- Good hygiene practices: Regular hand washing and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick can help reduce the risk of infection.
- Safe sexual practices: Practicing safe sex can reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections that can sometimes cause meningitis or encephalitis.
Management of Concussions and Cerebral Infections:
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are vital. Treatment strategies may include:
- Rest and recovery: Allowing the brain to heal is crucial for both concussions and cerebral infections. This may involve cognitive rest, limiting screen time, and avoiding strenuous activity.
- Medication: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antiviral or antibiotic medications may be used to manage symptoms and fight infection.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy may be needed to help individuals regain lost function.
- Psychological support: Counseling and psychotherapy can help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological effects of these conditions.
Conclusion: A Call for Awareness and Comprehensive Care
Concussions and cerebral infections represent significant threats to brain health, impacting cognitive function, physical performance, and overall well-being. While distinct in their etiology, both conditions share the potential for substantial and overlapping consequences. Raising awareness about these conditions, promoting preventive measures, and ensuring access to early diagnosis and comprehensive care are crucial for minimizing their impact and improving the lives of affected individuals. Further research into the long-term effects and effective treatment strategies remains a pressing need.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
You Are Reviewing Personnel Records Containing Pii When You Notice
Mar 30, 2025
-
When Using Estimation Data The Technician Uses
Mar 30, 2025
-
According To The Pluralist Theory Of Government
Mar 30, 2025
-
Hubbles Law Expresses A Relationship Between
Mar 30, 2025
-
The Cat6 Cable Is Part Of The Layer
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Concussions And Cerebral Infections Can Decrease The Effectiveness Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
