Control Valves Used For Steam Heating Coils Are Typically
Breaking News Today
Mar 27, 2025 · 7 min read
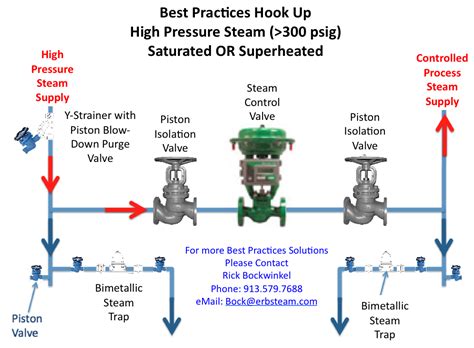
Table of Contents
Control Valves Used for Steam Heating Coils Are Typically…
Steam heating coils, ubiquitous in industrial processes and building heating systems, require precise control to maintain optimal temperatures. The heart of this control lies in the control valve, a crucial component responsible for regulating the flow of steam into the coil. Understanding the types of control valves commonly employed and their specific characteristics is critical for efficient and safe operation. This article delves into the details of control valves typically used for steam heating coils, exploring their functionalities, advantages, and disadvantages.
Types of Control Valves for Steam Heating Coils
Several types of control valves are suitable for regulating steam flow in heating coils, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The choice depends on factors such as steam pressure, temperature, flow rate requirements, and budget considerations.
1. Globe Valves
Globe valves, perhaps the most common type, are well-suited for steam applications due to their simple design and excellent throttling capabilities. They feature a disc that moves up and down within a valve body, controlling the flow of steam. The disc's position is regulated by an actuator, which receives signals from a temperature controller.
Advantages:
- Excellent throttling: Globe valves excel at precisely controlling steam flow, allowing for fine adjustments to maintain the desired temperature.
- Relatively inexpensive: Compared to other valve types, globe valves are generally more cost-effective.
- Wide range of sizes and materials: They are available in various sizes and materials to suit different applications.
Disadvantages:
- Pressure drop: Globe valves inherently cause a significant pressure drop across the valve, which can impact overall system efficiency.
- Potential for cavitation: At high steam velocities, cavitation (the formation and collapse of vapor bubbles) can occur, leading to valve erosion and damage.
- Maintenance: While generally robust, globe valves require regular maintenance to ensure proper operation and prevent leaks.
2. Ball Valves
Ball valves offer a simple on/off control, less suited for precise temperature regulation in steam heating coils compared to globe valves. The valve uses a rotating ball with a central bore to control steam flow. A fully open ball allows unrestricted flow, while a closed ball completely stops the flow.
Advantages:
- Quick on/off operation: Ball valves are ideal for quickly opening or closing the steam supply, making them suitable for emergency shutdowns or rapid temperature adjustments.
- Low pressure drop (when fully open): When fully open, the ball offers minimal resistance to steam flow, resulting in a lower pressure drop compared to a partially throttled globe valve.
- Compact design: Ball valves often have a smaller footprint than comparable globe valves.
Disadvantages:
- Poor throttling: Ball valves are not recommended for precise temperature control as they are not designed for fine adjustments of steam flow. They operate best in fully open or fully closed positions.
- Susceptible to wear: Frequent throttling (even though not recommended) can lead to premature wear on the ball and seat.
- Limited lifespan in aggressive steam environments: Depending on the materials, ball valves may have a shorter lifespan in demanding high-temperature, high-pressure steam applications compared to globe valves.
3. Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves use a rotating disc to control steam flow. Similar to ball valves, they are better suited for on/off control rather than precise throttling. The disc, shaped like a butterfly, rotates around a central shaft, blocking or allowing steam passage.
Advantages:
- Compact design: Butterfly valves offer a compact design, making them suitable for space-constrained applications.
- Low cost: They are generally less expensive than globe valves, particularly in larger sizes.
- Simple operation: Their simple design contributes to ease of operation and maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- Poor throttling: Like ball valves, butterfly valves are not ideal for precise temperature regulation in steam heating coils due to their poor throttling characteristics.
- Higher pressure drop: While typically less than globe valves when fully open, they can exhibit higher pressure drop during throttling compared to other valve types.
- Leakage potential: Depending on the seal design, some leakage can occur, especially in older or poorly maintained valves.
4. Diaphragm Valves
Diaphragm valves use a flexible diaphragm to isolate the valve internals from the steam. The diaphragm moves up and down, controlling steam flow. This design offers several advantages in specific steam applications.
Advantages:
- Leak-free operation: The diaphragm provides a positive seal, minimizing the risk of steam leakage.
- Suitable for slurries and viscous fluids: While primarily used for other applications, their design can handle some materials that could damage other valves.
- Easy maintenance: The diaphragm can be replaced relatively easily without major disassembly.
Disadvantages:
- Limited pressure and temperature ranges: Diaphragm valves often have limitations on the maximum pressure and temperature they can handle compared to globe or ball valves, limiting their suitability for high-pressure steam systems.
- Throttling limitations: Similar to ball and butterfly valves, precise throttling can be challenging.
- Diaphragm life: The diaphragm has a finite lifespan and will eventually need replacement.
Selecting the Right Control Valve
Choosing the appropriate control valve for steam heating coils involves considering several factors:
- Steam pressure and temperature: High-pressure, high-temperature applications often necessitate valves designed for robust performance and durability.
- Required flow rate and control accuracy: Applications demanding precise temperature control typically require valves with excellent throttling capabilities, such as globe valves. On/off control applications may use ball or butterfly valves.
- Budgetary constraints: Different valve types have different costs, and selecting a cost-effective option without compromising performance is important.
- Space limitations: The physical dimensions of the valve are a consideration, particularly in confined spaces.
- Maintenance requirements: Consider the ease of maintenance and the frequency of required servicing when choosing a valve.
- Material compatibility: The valve materials must be compatible with the steam and any other fluids in the system. Consider corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength.
Actuators for Steam Control Valves
The control valve itself is only half the equation; the actuator is the muscle that moves the valve element. Actuators translate the control signal from a temperature controller into mechanical motion, positioning the valve to regulate steam flow.
Types of Actuators:
-
Pneumatic Actuators: These use compressed air to drive the valve. They are widely used due to their reliability, fail-safe mechanisms (e.g., air supply failure results in a specific valve position), and ability to handle large forces.
-
Electric Actuators: These use electric motors to drive the valve. They offer precise control and are well-suited for applications requiring automated control systems and remote monitoring.
-
Hydraulic Actuators: Used less frequently, these employ hydraulic fluid to power the valve. They are generally chosen for high-force applications.
The actuator selection depends on the required force, speed of operation, control precision, and integration with the overall control system.
Maintaining Steam Control Valves
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the efficient and safe operation of steam control valves. This includes:
-
Regular inspection: Visual inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of wear, leaks, or damage.
-
Cleaning: Accumulated dirt, debris, or scale can impede valve operation and should be regularly removed.
-
Lubrication: Proper lubrication of moving parts is essential to prevent wear and ensure smooth operation.
-
Testing: Periodic testing should be performed to verify the valve's response to control signals and its ability to maintain the desired steam flow.
-
Calibration: To ensure accuracy, the valve should be calibrated periodically, especially if it shows signs of drift or inaccuracy.
-
Replacement: Worn or damaged components should be promptly replaced to prevent failures.
Conclusion
The selection of control valves for steam heating coils is a critical aspect of designing and operating efficient and safe systems. Choosing the right valve type and actuator, combined with a diligent maintenance program, is paramount for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different valve types—globe, ball, butterfly, and diaphragm—allows engineers and technicians to make informed decisions based on specific application needs. Remember to factor in steam parameters, control precision requirements, budgetary constraints, and maintenance implications to achieve the best results. Investing in high-quality components and regular preventative maintenance will result in minimal downtime and maximum efficiency for your steam heating coil systems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Communicable Disease Refers To A Disease That Is
Mar 30, 2025
-
You Are Reviewing Personnel Records Containing Pii When You Notice
Mar 30, 2025
-
When Using Estimation Data The Technician Uses
Mar 30, 2025
-
According To The Pluralist Theory Of Government
Mar 30, 2025
-
Hubbles Law Expresses A Relationship Between
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Control Valves Used For Steam Heating Coils Are Typically . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
