Cvp Analysis Focuses On How Profits Are Affected By Blank______.
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
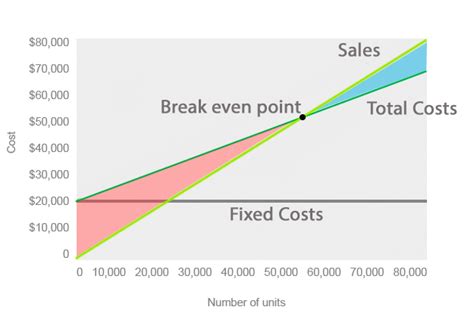
Table of Contents
CVP Analysis Focuses on How Profits Are Affected by Sales Volume
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis is a crucial managerial accounting tool that helps businesses understand the relationship between three key elements: costs, sales volume, and profits. It's a powerful technique for planning, decision-making, and evaluating the financial implications of various business strategies. At its core, CVP analysis focuses on how profits are affected by sales volume. This seemingly simple relationship underpins a complex interplay of fixed costs, variable costs, and selling price, all of which can significantly impact a company's bottom line.
This comprehensive guide will delve deep into CVP analysis, explaining its core components, underlying assumptions, various applications, and limitations. We'll explore how changes in sales volume directly influence profitability and how managers can leverage this knowledge to make informed decisions.
Understanding the Core Components of CVP Analysis
Before diving into the intricacies of CVP analysis, let's define its fundamental components:
1. Costs:
CVP analysis categorizes costs into two primary types:
-
Fixed Costs: These are expenses that remain constant regardless of the production volume or sales level. Examples include rent, salaries of administrative staff, insurance premiums, and depreciation. These costs remain the same whether you produce 100 units or 10,000 units.
-
Variable Costs: These costs directly relate to the production or sale of goods or services. They increase or decrease proportionally with the changes in production or sales volume. Examples include direct materials, direct labor (for some businesses), and sales commissions. If production doubles, variable costs generally double as well.
2. Sales Volume:
This refers to the number of units sold or the revenue generated from sales. It's a critical factor because it directly influences both revenue and variable costs. An increase in sales volume usually leads to higher revenue, but also higher variable costs. The net effect on profit depends on the relationship between these increases.
3. Profit:
Profit is the ultimate focus of CVP analysis. It represents the difference between total revenue and total costs (fixed costs + variable costs). Understanding how changes in sales volume impact costs and revenue allows businesses to predict and manage their profitability.
The CVP Equation and its Applications
The basic CVP equation provides a foundational understanding of the relationship between these elements:
Profit = (Sales Price per Unit * Sales Volume) - (Fixed Costs + (Variable Cost per Unit * Sales Volume))
This equation can be manipulated to solve for various unknowns, making it a versatile tool for various business scenarios. Here are some key applications:
1. Break-Even Point Analysis:
The break-even point is the level of sales at which total revenue equals total costs, resulting in zero profit. Determining this point is crucial for businesses to understand the minimum sales required to avoid losses. It can be calculated using the following formula:
Break-Even Point (in Units) = Fixed Costs / (Sales Price per Unit - Variable Cost per Unit)
Understanding the break-even point allows businesses to set realistic sales targets and assess the viability of new products or services.
2. Target Profit Analysis:
This involves determining the required sales volume to achieve a specific target profit. The formula is an extension of the break-even point calculation:
Sales Volume (in Units) to Achieve Target Profit = (Fixed Costs + Target Profit) / (Sales Price per Unit - Variable Cost per Unit)
This is invaluable for setting sales goals and making informed pricing decisions.
3. Sales Mix Analysis:
For businesses selling multiple products, CVP analysis can be expanded to include sales mix. This analysis considers the proportion of each product sold and its contribution margin to determine the overall profitability. Understanding the sales mix is vital for optimizing product offerings and resource allocation.
4. Margin of Safety Analysis:
The margin of safety measures the difference between actual or projected sales and the break-even point. It indicates the cushion a business has before incurring losses. A higher margin of safety signifies a more financially stable position.
Margin of Safety = Actual Sales - Break-Even Sales
Assumptions Underlying CVP Analysis
While CVP analysis is a powerful tool, it relies on several key assumptions:
-
Linearity of Costs and Revenue: This assumes that both costs and revenue change linearly with changes in sales volume. In reality, this might not always hold true, especially at very high or very low production levels. Economies of scale, for instance, can lead to non-linear cost behavior.
-
Constant Sales Price: CVP analysis assumes a constant sales price per unit throughout the relevant range. In reality, businesses might offer discounts or adjust prices based on market conditions.
-
Constant Variable Costs per Unit: Similarly, the variable cost per unit is assumed to remain constant. However, factors like bulk purchasing discounts could influence this.
-
Relevant Range: CVP analysis is most accurate within the relevant range of activity, meaning the range of production where the assumed relationships between cost and volume hold. Outside this range, the assumptions may not be valid.
-
All Costs are Either Fixed or Variable: In reality, some costs might have both fixed and variable components (semi-variable or mixed costs). These need to be carefully separated for accurate CVP analysis. Techniques like the high-low method can help in separating these costs.
Limitations of CVP Analysis
While highly useful, CVP analysis has some limitations:
-
Simplicity: The model simplifies complex business realities by assuming linearity and constant costs and prices. This can lead to inaccuracies if these assumptions are significantly violated.
-
Ignoring Time Value of Money: CVP analysis doesn't consider the time value of money, meaning it ignores the impact of inflation and the opportunity cost of capital.
-
Uncertainty: The model often relies on projections and estimates, introducing uncertainty into the results. External factors and unforeseen events can significantly impact the accuracy of the analysis.
-
Difficulty in Cost Classification: Assigning costs to fixed or variable categories can be challenging and subjective, especially for mixed costs. Inaccurate cost classification can lead to flawed analysis.
Advanced CVP Analysis Techniques
To address some of the limitations of basic CVP analysis, more advanced techniques can be employed:
-
Sensitivity Analysis: This involves testing the impact of changes in key assumptions (e.g., sales price, variable costs, fixed costs) on the results. It helps to understand the range of possible outcomes and assess the risks involved.
-
Contribution Margin Ratio: This ratio expresses the contribution margin (sales revenue - variable costs) as a percentage of sales revenue. It is useful for understanding profitability and predicting changes in profitability given changes in sales volume.
-
Multiple Product CVP Analysis: This approach extends CVP analysis to businesses with a diverse product portfolio, considering the sales mix and contribution margin of each product. It helps to identify profitable products and allocate resources accordingly.
Conclusion: Mastering CVP Analysis for Enhanced Profitability
CVP analysis is an indispensable tool for managers seeking to understand the intricate relationship between costs, sales volume, and profitability. By carefully considering its core components, assumptions, and limitations, businesses can leverage this technique to make well-informed decisions regarding pricing, production levels, sales targets, and overall business strategy. While the basic model provides a strong foundation, incorporating advanced techniques like sensitivity analysis and multiple product analysis allows for a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the financial implications of different strategic choices. Ultimately, mastering CVP analysis empowers businesses to optimize their operations and enhance their profitability. Remember to critically evaluate the assumptions underlying the analysis and consider the limitations before making crucial business decisions based solely on CVP results. Coupling CVP analysis with other management accounting techniques and market research will provide a holistic and effective approach to decision-making.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Georgia State Parol Was Founded In 1937
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Statement About The Necessary And Proper Clause Is Accurate
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Things Should You Check During A Trip
Mar 21, 2025
-
Endurance Is Important For Participating In Sports Because It
Mar 21, 2025
-
How To Study For American Lit Eoc
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cvp Analysis Focuses On How Profits Are Affected By Blank______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
