Decreasing Term Insurance Is Often Used To
Breaking News Today
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
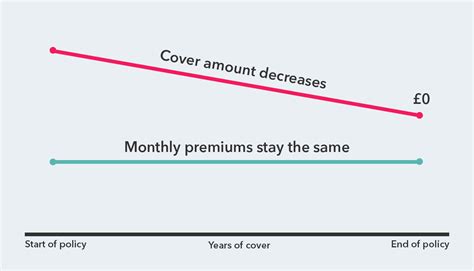
Table of Contents
Decreasing Term Insurance: Often Used To Cover Mortgages and Other Debts
Decreasing term insurance is a type of life insurance policy where the death benefit gradually decreases over time, while the premiums remain level. This type of policy is often used to cover a decreasing liability, such as a mortgage or other loan. Unlike level term insurance where the death benefit remains constant throughout the policy term, decreasing term insurance mirrors the declining balance of a loan, providing a payout that matches the remaining debt at the time of death. Understanding its applications and benefits is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
Why Choose Decreasing Term Insurance?
The primary advantage of decreasing term insurance lies in its affordability. Because the death benefit decreases, the premiums are generally lower than those of a level term insurance policy with the same initial death benefit. This makes it an attractive option for individuals seeking cost-effective life insurance coverage tied to a specific debt.
Aligns with Decreasing Liabilities:
The most common use is to cover a mortgage or other loan. As you pay down your debt, the insurance coverage decreases accordingly, ensuring that your beneficiaries receive enough to settle the remaining balance in case of your untimely death. This eliminates the possibility of leaving your family with a significant debt burden.
Cost-Effective Solution:
As mentioned, the premiums are typically lower than level term policies with comparable initial death benefits. This is because the insurance company's risk decreases over time as the death benefit diminishes. This cost-effectiveness makes it an accessible option for individuals with limited budgets.
Simplicity and Clarity:
Decreasing term insurance policies are relatively straightforward to understand. The terms and conditions are usually clear and uncomplicated, making it easy for policyholders to grasp the coverage details and implications.
Common Uses of Decreasing Term Insurance:
While mortgages are the most frequent application, decreasing term insurance can be used for other situations where the liability decreases over time.
Mortgage Protection:
This is the most prevalent use case. The decreasing death benefit mirrors the decreasing mortgage balance, providing coverage that ensures the mortgage is paid off in the event of the policyholder's death. This protects the surviving family members from the financial burden of an outstanding mortgage. This eliminates the risk of foreclosure and allows the family to maintain their home.
Other Loan Repayments:
Decreasing term insurance can also be used to cover other loans, such as personal loans, car loans, or business loans. The policy would be structured to match the decreasing balance of the loan, ensuring that the remaining debt is cleared if the policyholder passes away.
Business Debts:
For business owners, decreasing term insurance can provide a safety net for business loans. In case of the owner's death, the insurance payout can help settle outstanding business debts, preventing financial hardship for the business and its partners.
Specific Financial Goals:
While primarily used for debt coverage, some individuals might use decreasing term insurance to cover specific financial goals with a finite timeline. For example, if someone is saving for their children's education, they might structure a policy to provide a decreasing amount of money over the years to match the diminishing need for educational funds.
How Decreasing Term Insurance Works:
The core principle is the decreasing death benefit. At the start of the policy, the death benefit reflects the total amount to be covered (e.g., the initial mortgage amount). Over the policy term, as the underlying debt decreases, so does the death benefit. The rate of decrease is typically aligned with the amortization schedule of the loan.
Premiums Remain Constant:
Despite the diminishing death benefit, the premiums usually remain constant throughout the policy term. This predictable cost allows for easier budgeting and financial planning.
Policy Term:
The policy term is typically matched to the repayment period of the loan or debt being covered. For instance, a 25-year mortgage would likely be covered by a 25-year decreasing term insurance policy.
Choosing the Right Policy:
Selecting the right policy involves considering the amount of debt, the repayment period, and the desired level of coverage. It's essential to carefully assess your financial needs and consult with a financial advisor to determine the appropriate coverage amount and policy term.
Comparing Decreasing Term Insurance with Other Types:
Understanding the differences between decreasing term insurance and other types of life insurance is crucial for selecting the best option for your individual circumstances.
Decreasing Term vs. Level Term:
Level term insurance provides a constant death benefit throughout the policy term. While premiums might be higher than decreasing term insurance, it offers more comprehensive coverage if the insured's financial responsibilities remain constant or increase over time. Decreasing term insurance, as discussed, offers a decreasing death benefit and lower premiums, making it suitable for covering debts that decline over time.
Decreasing Term vs. Whole Life:
Whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage with a fixed death benefit and a cash value component that grows over time. While it offers lifelong protection, the premiums are significantly higher than decreasing term insurance. Decreasing term insurance is a more cost-effective solution for covering a specific, finite debt. Choosing between the two depends on whether you require lifelong coverage or short-term, debt-focused protection.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Decreasing Term Insurance:
Before purchasing a decreasing term insurance policy, several factors require careful consideration.
The Amount of Coverage:
The policy's death benefit should accurately reflect the outstanding debt at any given time. It's crucial to ensure the coverage adequately protects your beneficiaries from the remaining debt in case of your unexpected death.
The Policy Term:
The policy term should align with the repayment period of the loan. Choosing a term shorter than the loan repayment period leaves your beneficiaries exposed to potential debt after the policy expires.
The Premiums:
While premiums are generally lower than level term insurance, it's important to compare quotes from multiple insurers to ensure you're getting the most competitive rates. Don't solely focus on the lowest premium; ensure the coverage adequately matches your needs.
The Insurer's Financial Stability:
Selecting a financially stable and reputable insurance company is paramount. Research the insurer's financial strength ratings to ensure they can fulfill their obligations when the time comes.
Potential Drawbacks of Decreasing Term Insurance:
While advantageous for specific situations, decreasing term insurance has some limitations.
Limited Coverage After Debt Repayment:
Once the debt is paid off, the coverage ends, leaving you without life insurance protection unless you obtain a new policy.
No Cash Value:
Unlike whole life insurance, decreasing term insurance doesn't accumulate cash value. Therefore, you cannot borrow against the policy or withdraw funds.
Inability to Cover Increasing Liabilities:
It's unsuitable for situations where liabilities might increase over time. If your financial responsibilities grow, level term insurance might be a better fit.
Conclusion:
Decreasing term insurance is a valuable tool for managing the financial risks associated with decreasing liabilities, primarily mortgages. Its affordability and simplicity make it an attractive option for many individuals. However, it's essential to carefully evaluate your individual needs, understand its limitations, and compare it with other types of life insurance before making a decision. Consult with a financial advisor to determine if decreasing term insurance aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance. Remember to thoroughly research different insurers and compare quotes to secure the most suitable policy at a competitive price. By understanding the nuances of this type of insurance, you can make an informed decision that protects your family's financial future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Statements Are True Of Teams
Mar 27, 2025
-
A Group Of Biologists Is Studying The Competitive Relationships
Mar 27, 2025
-
The Keyword Tyranny In This Poster Is Primarily Used To
Mar 27, 2025
-
Irene Todavia No 1 Of 2 Lista Para Salir
Mar 27, 2025
-
A Bird Building Their Nest In A Tree
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Decreasing Term Insurance Is Often Used To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
