Describe The Symptoms And Treatment For Athlete's Foot. Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
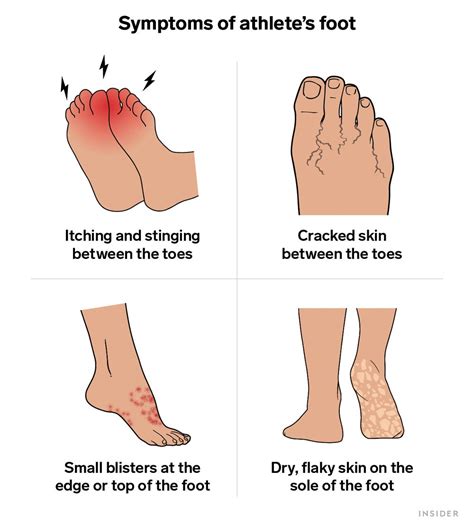
Table of Contents
Athlete's Foot: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Athlete's foot, medically known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection affecting the skin on the feet. It's highly contagious and thrives in warm, moist environments, making it prevalent among athletes and individuals who frequently wear enclosed shoes and socks. Understanding its symptoms, treatment options, and preventative measures is crucial for effective management and avoidance. This comprehensive guide will explore these aspects, equipping you with the knowledge to combat this bothersome condition.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Athlete's Foot
Identifying athlete's foot early is key to preventing its spread and ensuring effective treatment. Symptoms can vary in severity and presentation, but common signs include:
Common Symptoms:
- Itching: Intense itching, often the first noticeable symptom, is frequently experienced between the toes, on the soles, and on the sides of the feet.
- Burning: A burning sensation may accompany the itching, particularly in areas with significant inflammation.
- Scaling and Flaking: Dry, flaky skin is a characteristic sign, often appearing as white or grayish scales that can peel off.
- Cracking and Fissuring: The skin between the toes may crack and become deeply fissured, making the area susceptible to further infection and bleeding.
- Redness and Inflammation: Affected areas become red and inflamed, indicating an active infection. This redness may spread beyond the initial area.
- Blistering: In some cases, small blisters may form, often filled with clear fluid that can become cloudy or even pus-filled if a secondary bacterial infection develops. These blisters can be quite painful.
- Sores: In severe cases, open sores or ulcers may develop. These should be treated promptly to avoid complications.
Different Types of Athlete's Foot:
Athlete's foot presents in various forms, depending on the location and severity of the infection:
- Interdigital Tinea Pedis: This is the most common type, affecting the skin between the toes, typically the space between the fourth and fifth toes. It's characterized by maceration (softening of the skin) and scaling.
- Moccasin-Type Tinea Pedis: This type involves a widespread infection covering the soles and sides of the feet. The skin may become thickened (hyperkeratotic) and scaly. It often spreads gradually and is more difficult to treat.
- Vesicular Tinea Pedis: This is characterized by the formation of numerous small blisters, usually on the soles and sides of the feet. It’s often more itchy and painful than other forms.
- Ulcerative Tinea Pedis: This is a severe form of the infection leading to deep fissures and ulcers, particularly in people with diabetes or compromised immune systems.
Effective Treatment Options for Athlete's Foot
Treatment for athlete's foot typically involves antifungal medications, available in various forms. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the infection and individual preferences.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Antifungal Medications:
-
Topical Creams and Ointments: These are readily available at pharmacies and are often the first line of treatment for mild to moderate cases. Active ingredients commonly include clotrimazole, miconazole, terbinafine, and tolnaftate. These should be applied to the affected area twice daily for at least 2-4 weeks, even after symptoms subside to prevent recurrence. Ensure the area is thoroughly dry before application.
-
Topical Sprays and Powders: These are beneficial for keeping the affected area dry and preventing further fungal growth. They often contain antifungal ingredients such as miconazole or tolnaftate.
Prescription Antifungal Medications:
For severe or persistent cases of athlete's foot, a doctor may prescribe stronger antifungal medications:
-
Oral Antifungal Medications: These are systemic medications taken by mouth and are effective in treating more widespread or stubborn infections. Common oral antifungals include terbinafine (Lamisil) and itraconazole (Sporanox). Treatment usually lasts several weeks.
-
Stronger Topical Antifungals: Doctors might prescribe stronger topical creams or solutions than those available over-the-counter.
Additional Treatment Considerations:
-
Hygiene: Maintaining good foot hygiene is essential for both treatment and prevention. This includes washing your feet daily with soap and water, thoroughly drying them, especially between the toes, and changing socks frequently.
-
Footwear: Avoid wearing tight-fitting shoes and socks that trap moisture. Opt for breathable materials like cotton or moisture-wicking fabrics. Allow your feet to air out regularly, especially after physical activity.
-
Avoiding Shared Spaces: Do not share towels, socks, shoes, or other personal items that could spread the fungus.
-
Managing Underlying Conditions: Individuals with diabetes or weakened immune systems should consult their doctors for appropriate treatment to manage both the athlete's foot and their underlying condition. Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to serious complications.
-
Home Remedies: While not a replacement for antifungal medications, some home remedies may offer supplemental relief from itching and discomfort. These may include soaking feet in diluted vinegar or Epsom salts. However, these should not be considered primary treatments.
Preventing Athlete's Foot: Proactive Strategies
Preventing athlete's foot is often easier than treating it. By adopting the following preventative measures, you can significantly reduce your risk:
-
Keep Feet Clean and Dry: Regularly wash your feet with soap and water, paying close attention to the spaces between your toes. Dry your feet thoroughly after washing, particularly between the toes. Consider using a hairdryer on a low setting to ensure complete dryness.
-
Wear Breathable Socks and Shoes: Choose socks made of natural fabrics like cotton or wool. Avoid nylon or other synthetic materials that trap moisture. Opt for shoes that are well-ventilated and allow your feet to breathe. Avoid wearing the same pair of shoes two days in a row. Rotate footwear to allow them to dry completely.
-
Change Socks Frequently: Change your socks at least once a day, especially if your feet have been sweating.
-
Avoid Walking Barefoot in Public Places: Public showers, locker rooms, and pool areas are common breeding grounds for fungi. Always wear sandals or flip-flops in these environments.
-
Use Antifungal Powder: Sprinkling antifungal powder inside your shoes and socks can help absorb moisture and prevent fungal growth.
-
Treat Existing Foot Conditions: Address any existing foot conditions such as excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) or cracks in the skin, as these can make you more susceptible to athlete's foot.
-
Maintain a Healthy Immune System: A strong immune system can help fight off infections. Maintain a healthy diet, get regular exercise, and manage stress levels to support your immune function.
When to See a Doctor
While many cases of athlete's foot can be treated successfully with over-the-counter medications, you should consult a doctor if:
- Symptoms worsen or don't improve after two weeks of self-treatment.
- You develop severe pain, blistering, or open sores.
- You have diabetes or another underlying health condition that could complicate the infection.
- You have a weakened immune system.
- The infection spreads beyond your feet.
- You have recurring infections despite treatment.
A doctor can accurately diagnose the condition and recommend appropriate treatment, especially if more aggressive measures are necessary.
Athlete's Foot and Quizlet: A Study Aid
While this article provides a comprehensive overview of athlete's foot, using supplementary study aids like Quizlet can enhance your understanding and retention of the information. Quizlet allows you to create flashcards and practice quizzes, helping you learn and memorize key terms, symptoms, treatments, and preventative measures related to athlete's foot. This interactive approach can be particularly beneficial for students studying dermatology or healthcare professionals seeking to refresh their knowledge.
In conclusion, athlete's foot is a common but treatable fungal infection. By understanding its symptoms, employing effective treatment strategies, and implementing preventative measures, you can minimize your risk and effectively manage this condition. Remember to seek professional medical advice if your symptoms are severe or persistent. Maintaining good foot hygiene and adopting proactive preventative habits are crucial for both avoiding and treating athlete’s foot, ensuring healthy and happy feet.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
An Organizational Psychologist Studies Such Topics As
Apr 01, 2025
-
Cuando Me Siento Mal El Doctor Me
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True About Depression
Apr 01, 2025
-
Why Is The Boss Suspicious Of George And Lennie
Apr 01, 2025
-
National Highway Safety Administration Drug And Alcohol Test Answers
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Describe The Symptoms And Treatment For Athlete's Foot. Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
