Early Recognition Of Signs Of Infection And Subsequent Treatment Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
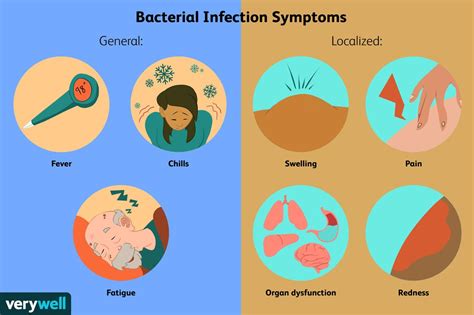
Table of Contents
Early Recognition of Signs of Infection and Subsequent Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
Early and accurate recognition of infection signs is crucial for effective treatment and preventing serious complications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various signs and symptoms of infection, focusing on how to identify them early, the importance of prompt medical attention, and the subsequent treatment options. We’ll also explore different types of infections and their specific characteristics, all designed to improve your understanding and preparedness. This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the Infection Process
Before delving into the signs and symptoms, it's crucial to understand the basic infection process. Infection occurs when harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, invade the body and multiply, causing damage to tissues and organs. The body's immune system typically fights off these invaders, but sometimes the infection overwhelms the immune response, leading to illness.
Factors Influencing Infection Development
Several factors can influence the development and severity of an infection:
-
The type of microorganism: Different pathogens have varying virulence (ability to cause disease) and mechanisms of action. A highly virulent organism can cause a severe infection even with a small inoculum.
-
The host's immune system: A weakened immune system, due to age, underlying medical conditions (like diabetes or HIV), or immunosuppressant medications, increases susceptibility to infection and makes it harder to fight off.
-
The route of entry: The way the pathogen enters the body (e.g., through a wound, respiratory tract, or gastrointestinal tract) influences the site and severity of the infection.
-
The number of microorganisms: A higher number of invading pathogens generally increases the likelihood of developing a noticeable infection.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Infection
Recognizing infection early is paramount. While symptoms can vary depending on the type of infection and the individual, some common signs and symptoms include:
Local Signs (at the site of infection):
-
Redness (erythema): Inflammation causes increased blood flow to the affected area, leading to redness.
-
Swelling (edema): Accumulation of fluid in the tissues causes swelling.
-
Pain or tenderness: Inflammation and tissue damage can cause pain or discomfort.
-
Warmth: Increased blood flow makes the infected area feel warmer than the surrounding tissue.
-
Pus (purulent drainage): This is a sign of a bacterial infection and often indicates a more serious infection.
-
Loss of function: The infected area may not function properly, like a stiff joint or difficulty moving a limb.
Systemic Signs (affecting the whole body):
-
Fever: This is a common sign of infection, indicating the body's attempt to fight off the invading pathogens. A fever above 100.4°F (38°C) is generally considered significant.
-
Chills: Feeling cold and shivering, often accompanied by a fever.
-
Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak.
-
Muscle aches: Generalized muscle pain.
-
Headache: Pain in the head.
-
Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms are common with various infections, particularly those affecting the gastrointestinal system.
-
Diarrhea: Frequent loose or watery stools.
Types of Infections and Their Specific Signs
Different types of infections present with varying signs and symptoms. Here are some examples:
Bacterial Infections:
Bacterial infections often present with localized signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, pain, warmth, and pus. Systemic signs like fever, chills, and fatigue are also common. Examples include:
-
Cellulitis: A bacterial skin infection characterized by redness, swelling, and pain.
-
Pneumonia: An infection of the lungs, often causing cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fever.
-
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI): Infection of the urinary system, often causing pain or burning during urination, frequent urination, and cloudy urine.
Viral Infections:
Viral infections may cause more generalized symptoms such as fever, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, and sometimes a cough or sore throat. Localized symptoms are less common than with bacterial infections. Examples include:
-
Influenza (flu): A respiratory illness causing fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and fatigue.
-
Common cold: A milder respiratory infection causing runny nose, sneezing, and sore throat.
-
Chickenpox: A highly contagious viral infection causing an itchy rash with small, fluid-filled blisters.
Fungal Infections:
Fungal infections can affect the skin, nails, and other parts of the body. They often present with itching, redness, and scaling. Examples include:
-
Athlete's foot: A fungal infection of the feet causing itching, scaling, and cracking of the skin.
-
Ringworm: A fungal infection of the skin causing a ring-shaped rash.
-
Candidiasis (yeast infection): A fungal infection that can affect the mouth, vagina, or other areas of the body. Symptoms vary depending on the location.
Parasitic Infections:
Parasitic infections can have a wide range of symptoms depending on the type of parasite and the site of infection. Some common signs include abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue.
The Importance of Prompt Medical Attention
Early recognition of infection signs and prompt medical attention are crucial for several reasons:
-
Preventing complications: Untreated or delayed treatment can lead to serious complications, such as sepsis (a life-threatening condition caused by the body's overwhelming response to infection), organ damage, and even death.
-
Effective treatment: Early intervention allows for appropriate treatment before the infection spreads or becomes more severe.
-
Reducing the spread of infection: Prompt treatment helps prevent the spread of infection to others.
-
Improved prognosis: Early diagnosis and treatment improve the chances of a complete recovery.
Subsequent Treatment Options
Treatment for infection depends on the type of pathogen, the site of infection, and the severity of the illness. Treatment options include:
-
Antibiotics: These medications are effective against bacterial infections. They kill bacteria or prevent them from multiplying. It's crucial to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better, to prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
-
Antivirals: These medications target viral infections. They don't kill viruses but can reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
-
Antifungals: These medications are used to treat fungal infections. They work by killing or inhibiting the growth of fungi.
-
Antiparasitics: These medications target parasitic infections. The specific medication will depend on the type of parasite.
-
Supportive care: This involves managing symptoms like fever, pain, and dehydration. It may include rest, fluids, pain relievers, and other measures to support the body's natural healing process.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing infections is crucial to maintaining good health. Key prevention strategies include:
-
Practicing good hygiene: Regular handwashing, showering, and keeping wounds clean can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
-
Getting vaccinated: Vaccines protect against many infectious diseases, such as influenza, pneumonia, and chickenpox.
-
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Eating a nutritious diet, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can strengthen the immune system.
-
Avoiding contact with infected individuals: This helps prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Conclusion
Early recognition of infection signs and symptoms is vital for effective treatment and preventing serious complications. By understanding the various signs and symptoms, the different types of infections, and the importance of prompt medical attention, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your health and well-being. Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for any concerns regarding infections or other health issues. Staying informed and taking preventative measures can significantly reduce your risk of infection and improve your overall health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Goods And Services Should Be Produced
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Is Streaming A Video Different From Downloading It
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Items Are Considered Employee Benefits
Apr 01, 2025
-
To Achieve A High Standard Of Living A Nation Should
Apr 01, 2025
-
Huipil Es Una De Las Ciudades Mas Importantes De Guatemala
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Early Recognition Of Signs Of Infection And Subsequent Treatment Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
