Exchange Rate And Purchasing Power Quick Check
Breaking News Today
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
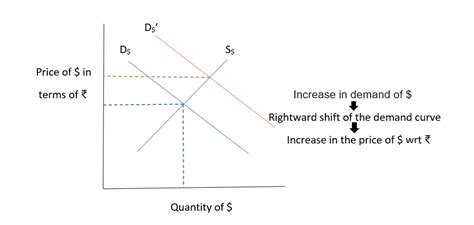
Table of Contents
Exchange Rate and Purchasing Power: A Quick Check and Deep Dive
Understanding the relationship between exchange rates and purchasing power is crucial for anyone involved in international trade, travel, or investment. While seemingly straightforward, the interplay between these two economic concepts is nuanced and can be significantly impacted by various factors. This article provides a quick check for grasping the basics, followed by an in-depth exploration of the complexities involved.
The Quick Check: Exchange Rates and Purchasing Power in a Nutshell
At its core, exchange rate refers to the value of one currency expressed in terms of another. For example, if the exchange rate is USD 1 = EUR 0.90, it means one US dollar can be exchanged for 0.90 Euros. This rate constantly fluctuates based on supply and demand in the foreign exchange market.
Purchasing power refers to the amount of goods and services that can be bought with a unit of currency. A higher purchasing power means your money can buy more. Inflation erodes purchasing power, meaning the same amount of money will buy fewer goods and services over time.
The relationship? A stronger exchange rate for your currency means you can buy more foreign goods (higher purchasing power abroad). Conversely, a weaker exchange rate means your currency buys less in foreign markets (lower purchasing power abroad). It’s a seesaw – a rise in one often correlates with a fall in the other, relative to a different currency.
Delving Deeper: Factors Affecting Exchange Rates and Purchasing Power
The seemingly simple relationship between exchange rates and purchasing power is influenced by a complex web of interacting factors:
1. Supply and Demand in the Foreign Exchange Market
The most significant driver of exchange rate fluctuations is the interplay of supply and demand. Factors influencing this include:
-
Interest Rates: Higher interest rates in a country tend to attract foreign investment, increasing demand for that currency and strengthening its exchange rate.
-
Economic Growth: Strong economic growth usually boosts demand for a country's currency, reflecting investor confidence and increased trade activity.
-
Political Stability: Political instability can lead to capital flight, reducing demand for a country's currency and weakening its exchange rate.
-
Government Intervention: Central banks can intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence the exchange rate of their currency. They might buy or sell their own currency to maintain a desired exchange rate level or to manage inflation.
-
Market Speculation: Short-term fluctuations are often driven by speculation, where traders bet on future exchange rate movements. This speculative element adds significant volatility to the market.
2. Inflation's Impact
Inflation, a general increase in the price level of goods and services, significantly affects purchasing power. High inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, meaning the same amount of money buys fewer goods and services. This impacts exchange rates as well:
- Purchasing Power Parity (PPP): This theory suggests that in the long run, exchange rates should adjust to equalize the purchasing power of different currencies. If inflation is higher in one country than another, its currency should depreciate to reflect this difference in purchasing power. However, PPP is not always a perfect predictor of exchange rate movements due to various market imperfections and non-traded goods.
3. Balance of Payments
A country's balance of payments summarizes its transactions with the rest of the world. A current account surplus (more exports than imports) generally strengthens the currency, while a deficit (more imports than exports) weakens it. However, capital flows (investment inflows and outflows) also play a crucial role, sometimes offsetting the effects of the current account.
4. Global Economic Events
Global events such as economic crises, political turmoil, or major shifts in commodity prices can significantly impact exchange rates and purchasing power. For example, a global recession may decrease demand for many currencies and impact import/export prices, while a major geopolitical event can cause significant volatility.
5. International Trade and Investment
International trade and investment significantly influence exchange rates. High demand for a country's exports can strengthen its currency, while significant foreign investment inflows also boost the demand and hence the value of the currency.
Practical Implications: Navigating the Exchange Rate and Purchasing Power Landscape
Understanding the dynamics of exchange rates and purchasing power has numerous practical implications for individuals and businesses:
For Travelers:
-
Budgeting: Exchange rates directly affect the cost of travel. A weak domestic currency makes travel abroad more expensive, while a strong domestic currency reduces travel costs.
-
Currency Exchange: Choosing the right time to exchange currency can save money. Monitoring exchange rates and using strategies like waiting for favorable fluctuations can make a difference.
For Businesses:
-
International Trade: Exchange rate fluctuations impact the profitability of international trade. A weaker domestic currency can make exports more competitive but imports more expensive. Conversely, a stronger domestic currency improves the purchasing power of imports but can make exports less competitive.
-
Foreign Investment: Businesses investing abroad must carefully consider exchange rate risks. Fluctuations can significantly impact the value of their investments. Hedging strategies, such as forward contracts or options, can mitigate these risks.
-
Pricing Strategies: Companies engaged in international trade need to adjust their pricing strategies based on exchange rate movements.
For Investors:
-
Portfolio Diversification: Investing in assets denominated in different currencies helps diversify risk and potentially improve returns.
-
Currency Trading: Foreign exchange trading involves speculating on currency movements. This is a high-risk activity that requires expertise and risk management.
Measuring and Monitoring Exchange Rates and Purchasing Power
Several tools and indicators are used to measure and monitor exchange rates and purchasing power:
-
Exchange Rate Indices: These indices track the value of a currency relative to a basket of other currencies. They provide a broader picture of a currency's strength or weakness.
-
Inflation Rates: These rates measure the rate at which prices are increasing in a country. High inflation erodes purchasing power.
-
Consumer Price Index (CPI): This is a widely used measure of inflation that tracks the average change in prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of consumer goods and services.
-
Big Mac Index: A lighthearted but often insightful measure that compares the price of a Big Mac in different countries to gauge purchasing power parity.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Relationship
The relationship between exchange rates and purchasing power is dynamic and constantly evolving. Various factors interact to influence these key economic indicators, creating both opportunities and risks for individuals and businesses alike. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and staying informed about relevant economic data and global events, one can navigate this landscape more effectively and make informed decisions. Consistent monitoring and a deep understanding of macroeconomic trends remain crucial for effective planning and risk management in this ever-changing environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Statement About Tuition Is The Most Accurate
Apr 03, 2025
-
Bach Created Masterpieces In Every Baroque Genre Except
Apr 03, 2025
-
A Defining Characteristic Of American Politics Is
Apr 03, 2025
-
Hardware Lab Simulation 7 1 Investigating Network Connection Settings
Apr 03, 2025
-
In Cell B9 Enter A Formula Using Npv
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Exchange Rate And Purchasing Power Quick Check . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
