Explain How Microevolution And Migration Can Affect An Ecosystem
Breaking News Today
Mar 13, 2025 · 7 min read
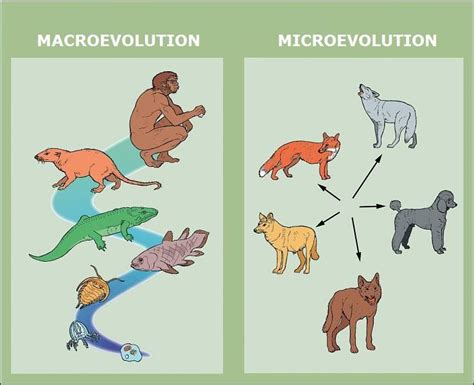
Table of Contents
How Microevolution and Migration Reshape Ecosystems: A Deep Dive
Ecosystems are dynamic entities, constantly evolving in response to a multitude of factors. Two particularly influential forces are microevolution and migration. While seemingly disparate, these processes are intricately intertwined, driving significant changes in species composition, biodiversity, and the overall structure and function of ecosystems. This article will explore the intricate ways in which microevolution and migration shape the ecological landscape, examining their individual and combined effects.
Microevolution: The Engine of Adaptation
Microevolution refers to small-scale evolutionary changes that occur within a population over relatively short periods. It’s the raw material for larger-scale evolutionary processes, driven primarily by four fundamental mechanisms:
1. Mutation: The Source of Variation
Mutations are random changes in an organism's DNA sequence. These changes can be beneficial, neutral, or harmful, depending on their impact on the organism's fitness. Beneficial mutations provide the raw material for adaptation, allowing organisms to better survive and reproduce in their environment. The accumulation of these beneficial mutations over time leads to changes in the genetic makeup of a population. For instance, a mutation conferring resistance to a specific pesticide in an insect population would be highly beneficial in an environment where that pesticide is used.
2. Gene Flow: The Mixing of Genes
Gene flow involves the movement of genes between populations through migration and interbreeding. This process can introduce new genetic variations into a population, increasing genetic diversity and potentially enhancing the population's ability to adapt to environmental changes. Conversely, excessive gene flow can homogenize populations, reducing local adaptation and potentially making them vulnerable to environmental shifts. Imagine a population of birds with a gene for drought resistance migrating into a population lacking that gene; this migration introduces the beneficial gene, boosting the overall population's resilience.
3. Genetic Drift: Chance Events Shaping Populations
Genetic drift is the random fluctuation of gene frequencies within a population, particularly pronounced in small populations. Chance events, such as natural disasters or bottlenecks (sudden reductions in population size), can drastically alter the genetic makeup of a population, even eliminating beneficial alleles or fixing harmful ones. This random process can significantly impact the adaptive potential of a population, particularly in the face of environmental changes. A small isolated population, for example, might lose valuable genetic diversity due to chance events, leaving it more vulnerable to disease or environmental stressors.
4. Natural Selection: The Survival of the Fittest
Natural selection is the non-random process by which individuals with traits better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on those advantageous traits to their offspring. This process acts upon the variation generated by mutation and reshaped by gene flow and genetic drift. Over time, natural selection leads to adaptations that improve the fitness of a population within its specific environment. Consider the classic example of Darwin's finches; the beak shapes of different finch species evolved through natural selection in response to the availability of different food sources.
Migration: The Movement of Individuals and Genes
Migration, the movement of individuals from one location to another, plays a crucial role in shaping ecosystem dynamics. It involves both the movement of organisms into (immigration) and out of (emigration) a particular area. Migration influences ecosystems in numerous ways:
1. Altering Species Composition and Distribution
Migration can significantly alter the species composition and distribution within an ecosystem. The arrival of new species through immigration can lead to increased biodiversity, introducing new ecological interactions and potentially altering existing food webs. Conversely, emigration can lead to the local extinction of a species if the departing individuals represent a significant portion of the population. Consider the impact of migratory birds on forest ecosystems; their seasonal arrival brings nutrients and seeds, influencing the plant community structure and the overall biodiversity.
2. Introducing Genetic Variation
As mentioned earlier, migration acts as a vector for gene flow, introducing new genetic variations into recipient populations. This infusion of novel genetic material can enhance a population's adaptive capacity, making it more resilient to environmental changes or pathogens. However, excessive gene flow can also homogenize populations, eroding local adaptations and potentially making them vulnerable to new challenges.
3. Affecting Population Dynamics
Migration can dramatically influence population size and density. Immigration can boost the size of a declining population, preventing local extinction. Conversely, emigration can reduce the size of a population, possibly increasing competition for resources among the remaining individuals. The migration patterns of herbivores, for instance, can significantly affect the distribution and abundance of plant species in an ecosystem.
4. Spreading Invasive Species
Migration can unfortunately facilitate the spread of invasive species. Invasive species, introduced to a new environment through human activities or natural migration, can outcompete native species for resources, disrupting ecological balance and potentially causing significant damage to the ecosystem. The introduction of the brown tree snake to Guam, causing the extinction of many native bird species, is a stark example of this negative impact.
The Interplay of Microevolution and Migration
Microevolution and migration are not independent processes; they are deeply intertwined, influencing each other in complex ways.
1. Migration Driving Microevolution
Migration facilitates gene flow, introducing new alleles into populations. These new alleles can be subjected to natural selection, leading to microevolutionary changes within the recipient population. The introduction of a novel allele conferring disease resistance through migration, for instance, could lead to the rapid spread of that beneficial allele within a population.
2. Microevolution Affecting Migration Patterns
Microevolutionary changes can influence an organism's ability to migrate. For example, adaptations that enhance flight efficiency in birds can influence their migratory range and the timing of their migrations. Similarly, changes in the physiology of fish that improve their tolerance to salinity might broaden their migratory pathways.
3. Combined Impacts on Ecosystem Structure and Function
The combined effects of microevolution and migration can profoundly impact the structure and function of ecosystems. Changes in species composition and distribution, resulting from both processes, alter interactions between species, affecting competition, predation, mutualism, and nutrient cycling. This can lead to shifts in ecosystem productivity, resilience, and overall stability. A warming climate, for instance, can induce both range shifts in species (migration) and microevolutionary adaptations within populations to tolerate higher temperatures. These combined effects dramatically reshape the ecosystem.
Case Studies: Observing Microevolution and Migration in Action
Several real-world examples highlight the intertwined roles of microevolution and migration in ecosystem dynamics.
-
The evolution of pesticide resistance in insects: The widespread use of pesticides has driven rapid microevolution in many insect populations, leading to the development of resistance. This resistance often necessitates the use of stronger pesticides or new control methods, with potential long-term ecological consequences.
-
The adaptation of plants to climate change: Plants are responding to climate change through both migration (shifting their ranges towards higher altitudes or latitudes) and microevolution (adapting to warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns). These changes are impacting plant community composition and overall ecosystem function.
-
The spread of antibiotic resistance in bacteria: The overuse of antibiotics has driven the rapid evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a significant threat to human and animal health. The spread of these resistant strains can be seen as a form of migration, further emphasizing the interconnectedness of these processes.
Conclusion: A Dynamic and Intertwined Relationship
Microevolution and migration are fundamental processes shaping ecosystem dynamics. They are not simply separate occurrences but are intricately intertwined, each influencing the other and contributing to the constant flux and adaptation of ecosystems. Understanding their interplay is crucial for predicting and managing ecosystem responses to environmental change, including climate change, habitat destruction, and invasive species. As ecosystems continue to face unprecedented challenges, appreciating the role of microevolution and migration becomes paramount for effective conservation strategies and ecosystem management. Further research exploring the complexities of these interactions will undoubtedly lead to a deeper understanding of the ecological resilience and vulnerability of our planet's ecosystems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
James Is Goal As Monarch Was To
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Happens When You Format A Filesystem On A Partition
Mar 13, 2025
-
Que Deseaba La Chona Mostrar A Los De Su Pueblo
Mar 13, 2025
-
Within The Context Of Rcr Compliance Primarily Refers To
Mar 13, 2025
-
A Claims Examiner Is Employed By A
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Explain How Microevolution And Migration Can Affect An Ecosystem . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
