Explain How Smart Growth Promotes Long Term Sustainable Development
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
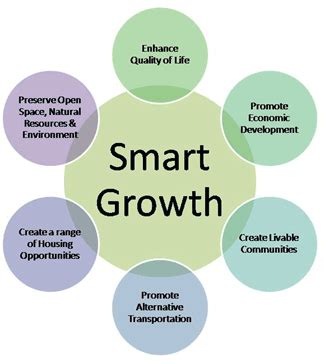
Table of Contents
Smart Growth: A Catalyst for Long-Term Sustainable Development
Smart growth, a multifaceted approach to urban planning and development, champions environmentally conscious, economically viable, and socially equitable communities. It stands in contrast to sprawling, unsustainable development patterns that often lead to environmental degradation, economic inequality, and social fragmentation. This article delves deep into the mechanisms through which smart growth fosters long-term sustainable development, examining its impact across environmental, economic, and social dimensions.
Environmental Sustainability through Smart Growth
Smart growth strategies directly address key environmental challenges by minimizing urban sprawl and maximizing the efficient use of existing infrastructure and resources. Several key aspects contribute to its environmental sustainability:
1. Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Urban sprawl, characterized by low-density development and long commutes, significantly contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Cars become the primary mode of transportation, increasing reliance on fossil fuels. Smart growth, by promoting higher-density development, walkability, and access to public transportation, dramatically reduces the need for private vehicle use, thus lessening carbon emissions. This shift towards active transportation (walking and cycling) and public transit also improves air quality, leading to better public health outcomes.
2. Protection of Natural Resources and Biodiversity
Smart growth emphasizes preserving green spaces, protecting natural habitats, and minimizing the conversion of natural land into urban areas. By concentrating development in existing urban areas and strategically locating new development, it reduces pressure on environmentally sensitive ecosystems like wetlands, forests, and agricultural lands. This protection of natural resources is crucial for biodiversity conservation and helps maintain ecosystem services, such as clean water and air purification. Protecting these natural resources also offers significant economic benefits, boosting ecotourism and providing essential resources for the long term.
3. Efficient Use of Land and Resources
Smart growth principles promote the efficient use of land and resources through mixed-use zoning, infill development, and brownfield redevelopment. Mixed-use zoning integrates residential, commercial, and recreational uses in a single area, reducing the need for extensive travel and maximizing land utilization. Infill development involves building within existing urban areas, making better use of existing infrastructure and minimizing the need for new roads, utilities, and other infrastructure. Redeveloping brownfields (abandoned or underutilized industrial sites) prevents further sprawl and remediates contaminated land, improving environmental quality. This efficient use of resources also translates to economic savings in the long run.
4. Water Conservation and Management
Smart growth strategies encourage water-efficient landscaping, rainwater harvesting, and the use of permeable pavements. These measures help to reduce stormwater runoff, minimize water pollution, and conserve water resources. By promoting denser development, smart growth also reduces the overall demand for water per capita, contributing to the long-term sustainability of water resources. Investing in efficient water management is crucial for future generations, particularly in regions experiencing water scarcity.
Economic Benefits of Smart Growth
Smart growth initiatives are not only environmentally beneficial but also yield considerable economic advantages:
1. Increased Property Values and Tax Base
By creating vibrant, walkable, and amenity-rich neighborhoods, smart growth tends to increase property values. This enhanced property value translates to a higher tax base for local governments, providing more resources for essential services such as education, public safety, and infrastructure maintenance. This economic boost contributes to long-term fiscal stability.
2. Reduced Infrastructure Costs
Concentrating development in existing urban areas reduces the need for extensive infrastructure investments. Existing roads, utilities, and other infrastructure can serve a larger population, minimizing the costs associated with building new infrastructure. This cost savings can be channeled into other essential community improvements.
3. Enhanced Economic Competitiveness
Smart growth fosters economically vibrant and attractive communities. The presence of diverse housing options, walkable neighborhoods, access to public transportation, and a variety of amenities makes these communities attractive to businesses and residents alike. This boosts economic competitiveness, attracting investment and creating jobs. A strong economy, in turn, enhances the community’s long-term sustainability.
4. Support for Local Businesses
Smart growth encourages the development of local businesses by fostering walkable neighborhoods and creating a vibrant commercial environment. This supports local economies and creates job opportunities within the community, reducing reliance on external businesses and promoting economic independence. Local businesses are integral to the character and sustainability of a community.
Social Equity and Smart Growth
Smart growth is not solely about environmental and economic sustainability; it’s deeply intertwined with social equity:
1. Increased Access to Opportunities
Smart growth strategies aim to provide equitable access to jobs, education, healthcare, and other essential services. By creating mixed-income housing and providing access to public transportation, smart growth promotes social inclusion and reduces disparities between different socioeconomic groups. Access to opportunities fosters a more equitable and just society.
2. Improved Public Health and Well-being
The walkability and accessibility features promoted by smart growth encourage physical activity, reduce air pollution, and enhance social interaction. These factors contribute to improved public health and well-being, leading to a healthier and happier community. Investment in public health is an investment in the long-term sustainability of the community.
3. Stronger Communities and Social Cohesion
Smart growth fosters a sense of community and social cohesion by creating vibrant public spaces, mixed-use developments, and opportunities for social interaction. These factors build stronger and more resilient communities, promoting a sense of belonging and mutual support. Strong communities are essential for the long-term sustainability of any society.
4. Reduced Social Inequality
Smart growth addresses social inequalities by promoting affordable housing, providing access to essential services, and creating diverse communities where people from all backgrounds can thrive. This commitment to equity ensures that the benefits of development are shared by all members of the community, enhancing overall social sustainability.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Smart Growth
While the benefits of smart growth are substantial, its implementation faces several challenges:
- Political Resistance: Existing zoning regulations and vested interests often hinder the implementation of smart growth initiatives. Overcoming political resistance requires strong community engagement and leadership.
- Funding Constraints: Implementing smart growth requires significant upfront investment in infrastructure and planning. Securing sufficient funding is crucial for success.
- Public Perception: Some people may resist changes to traditional development patterns, requiring effective communication and community engagement to build support.
- Implementation Complexity: Smart growth involves coordinating various stakeholders and navigating complex regulatory processes. Effective project management and coordination are essential.
Conclusion: A Vision for the Future
Smart growth is not merely a set of planning strategies; it represents a paradigm shift towards a more sustainable and equitable future. By integrating environmental, economic, and social considerations, smart growth promotes long-term sustainability across all dimensions of community development. While challenges exist, the long-term benefits of embracing smart growth principles – healthier environments, stronger economies, and more equitable societies – far outweigh the hurdles. As we navigate the challenges of the 21st century, embracing smart growth is crucial for building thriving and resilient communities for generations to come. Investing in smart growth today is an investment in a sustainable and prosperous future for all.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Letrs Unit 4 Session 4 Check For Understanding
Mar 22, 2025
-
A Way To Make Lower Toned Instruments Would Be To Use
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Are Examples Of Mutual Respect Acls
Mar 22, 2025
-
True Or False You Can Trust A Dissembler
Mar 22, 2025
-
A Driver May Pass Another Vehicle When Safe If
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Explain How Smart Growth Promotes Long Term Sustainable Development . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
