Fluctuations In The Phosphorus Cycle In Aquatic Ecosystems _______.
Breaking News Today
Mar 15, 2025 · 7 min read
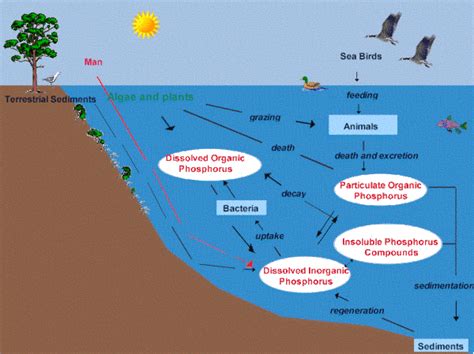
Table of Contents
Fluctuations in the Phosphorus Cycle in Aquatic Ecosystems: A Comprehensive Overview
Phosphorus, a vital element for life, plays a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems. Unlike carbon and nitrogen, which have significant atmospheric reservoirs, phosphorus primarily cycles through terrestrial and aquatic environments. This makes aquatic phosphorus dynamics particularly sensitive to external influences and internal processes, leading to substantial fluctuations with significant ecological consequences. Understanding these fluctuations is critical for managing water quality and maintaining the health of aquatic ecosystems.
The Phosphorus Cycle in Aquatic Ecosystems: A Primer
The phosphorus cycle in aquatic ecosystems involves a series of interconnected processes that govern the movement and transformation of phosphorus. These processes include:
1. Weathering and Erosion:
Phosphorus, initially bound within rocks and minerals, is released into the environment through weathering and erosion. Rainfall and runoff carry dissolved phosphorus (orthophosphate) and particulate phosphorus (bound to soil particles) into aquatic systems. This influx is often highly variable, depending on factors such as rainfall intensity, soil type, and land use practices. Intensive agriculture, for instance, significantly increases phosphorus runoff due to fertilizer use.
2. Biological Uptake:
Phytoplankton, the foundation of most aquatic food webs, readily absorb dissolved orthophosphate for growth and reproduction. Zooplankton, in turn, consume phytoplankton, incorporating phosphorus into their tissues. This biological uptake represents a crucial step in the cycle, as it transfers phosphorus from the inorganic to the organic form. The rate of uptake is influenced by phosphorus availability, light intensity, and water temperature.
3. Sedimentation:
Phosphorus can be lost from the water column through sedimentation. Dead organic matter, including phytoplankton and zooplankton, sinks to the bottom, carrying phosphorus with it. This process can be particularly significant in slow-moving or stratified water bodies. Sedimentation represents a long-term sink for phosphorus, albeit one that can be recycled through internal processes.
4. Internal Cycling:
Phosphorus in sediments isn't permanently lost. Internal cycling involves the release of phosphorus from sediments back into the water column. This release can be driven by various factors, including:
- Decomposition: Microbial decomposition of organic matter in sediments releases phosphorus.
- Redox reactions: Changes in oxygen levels (redox potential) in sediments can affect the solubility of phosphorus. Under anaerobic conditions (low oxygen), phosphorus bound to iron and other metals can be released.
- Physical disturbance: Physical disturbances like storms or dredging can resuspend sediments, releasing phosphorus back into the water column.
5. External Inputs:
Besides weathering and erosion, aquatic ecosystems receive phosphorus from other external sources, including:
- Wastewater discharge: Wastewater often contains high concentrations of phosphorus from detergents and human waste. Untreated or poorly treated wastewater can significantly impact aquatic ecosystems.
- Atmospheric deposition: Although less significant than terrestrial inputs, atmospheric deposition can contribute to phosphorus loading, particularly in areas with high industrial activity or agricultural practices.
Factors Causing Fluctuations in the Phosphorus Cycle
The phosphorus cycle in aquatic ecosystems is rarely stable; it exhibits considerable fluctuations in response to both natural and anthropogenic factors:
1. Climatic Variability:
Rainfall patterns significantly influence phosphorus inputs. Heavy rainfall events can lead to increased runoff and erosion, resulting in pulses of phosphorus entering aquatic systems. Droughts, conversely, can reduce phosphorus inputs, potentially leading to phosphorus limitation. Changes in rainfall patterns associated with climate change are expected to exacerbate these fluctuations.
2. Land Use Changes:
Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural intensification significantly alter phosphorus cycling. Deforestation increases soil erosion, leading to higher phosphorus runoff. Urbanization increases the input of phosphorus from wastewater and stormwater runoff. Intensive agriculture, with its heavy reliance on phosphorus fertilizers, represents a major source of phosphorus pollution in many aquatic ecosystems.
3. Eutrophication:
Excessive nutrient enrichment, known as eutrophication, is a major consequence of phosphorus fluctuations. When phosphorus levels exceed the capacity of the ecosystem to process it, it can lead to:
- Algal blooms: Excessive phosphorus fuels rapid growth of algae and cyanobacteria, often leading to harmful algal blooms (HABs) that produce toxins and deplete oxygen.
- Oxygen depletion: Decomposition of large algal blooms consumes substantial amounts of oxygen, resulting in hypoxia (low oxygen) or anoxia (no oxygen) conditions that can kill fish and other aquatic organisms.
- Changes in species composition: Eutrophication can alter the species composition of aquatic communities, favouring species tolerant of low oxygen conditions and potentially disrupting the food web.
4. Water Temperature:
Temperature influences various aspects of phosphorus cycling. Higher temperatures can increase the rate of biological processes, such as decomposition and algal growth, potentially accelerating phosphorus cycling. Temperature also affects the solubility of phosphorus and the stratification of water bodies. Changes in water temperature due to climate change can significantly affect phosphorus dynamics.
5. Water Level Fluctuations:
Changes in water level, particularly in shallow lakes and wetlands, can significantly impact phosphorus cycling. Low water levels can concentrate phosphorus, increasing its availability for algal growth. High water levels can dilute phosphorus concentrations but also increase the area of inundated land, potentially leading to increased phosphorus runoff.
Ecological Consequences of Phosphorus Fluctuations
The consequences of phosphorus fluctuations extend beyond eutrophication. They can impact various aspects of aquatic ecosystem health, including:
1. Biodiversity Loss:
Changes in water quality associated with phosphorus fluctuations can lead to biodiversity loss. Eutrophication can favour a few dominant species, reducing the overall diversity of aquatic communities. Hypoxia and anoxia can directly kill many aquatic organisms, altering the food web structure and ecosystem function.
2. Fisheries Decline:
Excessive phosphorus can negatively impact fisheries. Hypoxia and anoxia can kill fish directly, while changes in species composition can reduce the abundance of commercially important species. Algal blooms can also produce toxins that harm fish and other aquatic organisms.
3. Human Health Impacts:
Some algal blooms produce toxins that are harmful to humans, causing skin irritation, respiratory problems, and even neurological disorders. Consumption of contaminated shellfish or fish can also lead to health problems. Cyanotoxins, produced by certain cyanobacteria, are particularly concerning.
Managing Phosphorus Fluctuations in Aquatic Ecosystems
Effective management of phosphorus fluctuations requires a multifaceted approach:
1. Reducing Phosphorus Inputs:
This is a critical step in mitigating eutrophication. Strategies include:
- Improved wastewater treatment: Upgrading wastewater treatment plants to remove phosphorus more effectively.
- Best management practices in agriculture: Reducing fertilizer use, implementing buffer strips, and using cover crops to reduce phosphorus runoff from agricultural lands.
- Urban stormwater management: Improving stormwater management practices to reduce phosphorus runoff from urban areas.
2. Restoring Aquatic Habitats:
Restoring wetlands and riparian zones can help buffer phosphorus inputs and improve water quality. These habitats act as natural filters, removing phosphorus from runoff before it enters aquatic systems.
3. Biomanipulation:
Biomanipulation involves altering the food web structure to control algal growth. This can include introducing or removing specific species to reduce phosphorus availability or enhance grazing pressure on algae.
4. Monitoring and Modeling:
Regular monitoring of phosphorus levels and other water quality parameters is essential for tracking changes and assessing the effectiveness of management strategies. Mathematical models can help predict the impacts of different scenarios and guide management decisions.
5. Public Awareness and Education:
Raising public awareness about the importance of phosphorus management and the impact of human activities on water quality is crucial for achieving long-term sustainability.
Conclusion
Fluctuations in the phosphorus cycle represent a significant challenge for the management of aquatic ecosystems. These fluctuations, driven by both natural and anthropogenic factors, can lead to a cascade of ecological consequences, impacting biodiversity, fisheries, and human health. Effective management requires a holistic approach that integrates various strategies to reduce phosphorus inputs, restore aquatic habitats, and improve water quality. The long-term health and sustainability of aquatic ecosystems depend critically on our ability to address the complex dynamics of the phosphorus cycle. Continued research, effective policy implementation, and public engagement are crucial for ensuring the preservation of these vital resources. Furthermore, the growing recognition of climate change's influence on these cycles underscores the need for adaptive management strategies that account for evolving environmental conditions. A proactive, multi-pronged approach is crucial to mitigating the negative effects of phosphorus fluctuations and safeguarding the future of aquatic ecosystems worldwide.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Anki Deck Dirty Medicine
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Statement Accurately Describes The Inner Planets
Mar 15, 2025
-
Y Por Favor Tengan Cuidado Cuando Cocinen No Quiero Que
Mar 15, 2025
-
Match The Taxonomic Principles With Their Definitions
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Of These Scenarios Involves Commodity Money
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Fluctuations In The Phosphorus Cycle In Aquatic Ecosystems _______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
