Fluid Electrolyte And Acid-base Regulation Ati Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
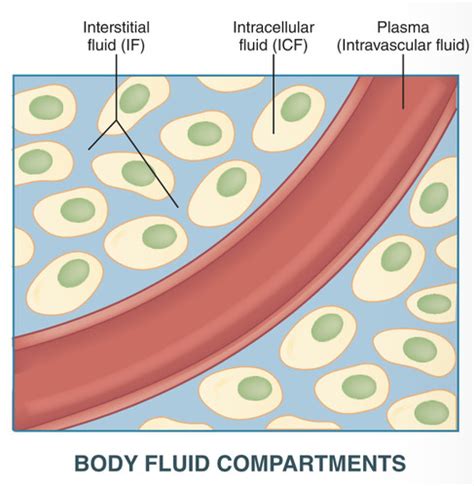
Table of Contents
Mastering Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Regulation: A Comprehensive Guide
Fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance are critical for maintaining homeostasis and overall health. Dysregulation in any of these areas can lead to serious consequences, impacting numerous bodily functions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base regulation, providing a detailed understanding to help you ace that ATI quizlet and beyond. We'll explore the key concepts, processes, and clinical implications, equipping you with a robust knowledge base.
Understanding Fluid Balance: The Body's Internal Sea
Our bodies are approximately 60% water, distributed across various compartments: intracellular fluid (ICF), extracellular fluid (ECF) – which includes interstitial fluid and intravascular fluid (plasma). Maintaining the right volume and distribution of this fluid is crucial.
Fluid Intake and Output: The body meticulously regulates fluid balance through a dynamic interplay of intake and output. Intake primarily comes from drinking fluids and eating foods containing water. Output occurs through several routes:
- Urine: The kidneys play a pivotal role, adjusting urine volume and concentration to maintain fluid balance. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) regulates water reabsorption in the kidneys.
- Insensible Water Loss: This refers to water loss through respiration (breathing) and perspiration (sweating). These losses are typically unnoticed.
- Feces: A small amount of water is lost in the stool.
- Other: Fluid can also be lost through vomiting, diarrhea, and drainage from wounds.
Fluid Imbalances: Disruptions in fluid intake or output can lead to several imbalances:
- Hypovolemia (Fluid Volume Deficit): Characterized by decreased blood volume, leading to symptoms like hypotension, tachycardia, and decreased skin turgor. Causes include dehydration, hemorrhage, and excessive vomiting/diarrhea.
- Hypervolemia (Fluid Volume Excess): This involves an increase in total body fluid, often accompanied by edema (swelling), weight gain, and shortness of breath. Causes include heart failure, kidney disease, and excessive intravenous fluid administration.
- Third-Spacing: Fluid shifts from the intravascular space into the interstitial space, causing edema but without an overall change in total body fluid. This can occur in conditions like burns and peritonitis.
Electrolyte Balance: The Ions that Make Life Possible
Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electric charge when dissolved in water. They are vital for numerous bodily functions, including nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, and maintaining acid-base balance. Key electrolytes include:
- Sodium (Na+): The primary extracellular cation, crucial for fluid balance, nerve impulse transmission, and muscle contraction. Hyponatremia (low sodium) and hypernatremia (high sodium) can have serious consequences.
- Potassium (K+): The primary intracellular cation, essential for nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, and cardiac function. Hypokalemia (low potassium) and hyperkalemia (high potassium) are significant clinical concerns, especially regarding cardiac rhythm.
- Calcium (Ca2+): Important for muscle contraction, blood clotting, nerve impulse transmission, and bone health. Hypocalcemia (low calcium) and hypercalcemia (high calcium) can cause a variety of symptoms.
- Magnesium (Mg2+): Involved in muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and many enzyme reactions. Hypomagnesemia (low magnesium) and hypermagnesemia (high magnesium) can affect neuromuscular function and cardiac function.
- Chloride (Cl-): The primary extracellular anion, involved in maintaining fluid balance and acid-base balance.
- Phosphate (PO43-): Essential for bone health, energy metabolism, and acid-base balance.
Electrolyte Imbalances: Electrolyte imbalances can stem from various causes, including dietary deficiencies, renal dysfunction, hormonal imbalances, and gastrointestinal losses. Each electrolyte imbalance presents unique symptoms and requires specific management strategies. Accurate assessment and timely intervention are critical to prevent serious complications. Understanding the underlying cause of the imbalance is essential for effective treatment.
Acid-Base Regulation: Maintaining the Body's pH
The body maintains a narrow pH range (7.35-7.45) to ensure optimal enzyme function and cellular processes. This is achieved through several mechanisms:
- Buffers: Buffers are substances that resist changes in pH. The bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer system is a crucial blood buffer.
- Respiratory System: The lungs regulate carbon dioxide (CO2), a major acid in the body, through respiration. Increased ventilation eliminates excess CO2, increasing pH; decreased ventilation retains CO2, decreasing pH.
- Renal System: The kidneys play a critical role in regulating bicarbonate levels and excreting acids, such as hydrogen ions (H+). They can adjust the excretion of H+ and reabsorption of bicarbonate to maintain pH balance.
Acid-Base Imbalances: Disturbances in acid-base balance can be categorized into four main types:
- Respiratory Acidosis: Characterized by an increase in CO2 and a decrease in pH. Causes include hypoventilation (e.g., respiratory depression, pneumonia).
- Respiratory Alkalosis: Characterized by a decrease in CO2 and an increase in pH. Causes include hyperventilation (e.g., anxiety, high altitude).
- Metabolic Acidosis: Characterized by a decrease in bicarbonate and a decrease in pH. Causes include diabetic ketoacidosis, renal failure, and diarrhea.
- Metabolic Alkalosis: Characterized by an increase in bicarbonate and an increase in pH. Causes include vomiting, excessive diuretic use, and antacid abuse.
Analyzing Acid-Base Imbalances: The arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is the primary tool used to diagnose acid-base imbalances. It provides information on pH, PaCO2 (partial pressure of carbon dioxide), HCO3- (bicarbonate), and PaO2 (partial pressure of oxygen). Understanding how to interpret these values is crucial for appropriate clinical management. Analyzing the ABG results in conjunction with the patient's clinical presentation provides a holistic picture of the acid-base disturbance.
Clinical Implications and Nursing Considerations
Understanding fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base regulation is critical for nurses and healthcare professionals. Accurate assessment, monitoring, and interventions are necessary to prevent and manage imbalances. This includes:
- Thorough History and Physical Assessment: Gathering information on fluid intake and output, dietary habits, medications, and presenting symptoms is crucial. Physical assessments should include vital signs, skin turgor, edema, and neurological status.
- Laboratory Tests: Electrolyte panels, complete blood counts (CBC), ABG analysis, and urinalysis provide essential data for diagnosis and monitoring.
- Fluid and Electrolyte Management: Interventions may include intravenous fluid replacement, electrolyte supplements or restrictions, and dietary modifications.
- Acid-Base Management: Treatments may involve respiratory support (e.g., mechanical ventilation), bicarbonate administration (in metabolic acidosis), and addressing the underlying cause of the imbalance.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about fluid intake, dietary modifications, and medication adherence is vital for long-term management and prevention of recurrences.
Case Study Example: A patient presents with nausea, vomiting, and weakness. Laboratory results reveal hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis. The nurse would need to assess the patient's fluid status, monitor vital signs, and collaborate with the healthcare team to develop a plan of care, which might include intravenous potassium replacement and management of the underlying cause of vomiting.
Integrating Knowledge for Success on the ATI Quizlet and Beyond
Successfully navigating the ATI quizlet and mastering fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base regulation requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Thorough Understanding of Basic Principles: A solid grasp of the physiological mechanisms involved in fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base regulation is fundamental.
- Systematic Approach to Problem Solving: Develop a systematic approach to analyze clinical scenarios, interpret laboratory results, and identify the underlying causes of imbalances.
- Practice, Practice, Practice: Work through numerous practice questions, including those found on ATI quizlet, to reinforce your understanding and identify areas for improvement.
- Clinical Correlation: Relate theoretical knowledge to real-world clinical scenarios. This helps solidify understanding and improve problem-solving skills.
- Effective Study Strategies: Utilize effective study techniques such as flashcards, mind maps, and active recall to enhance learning and retention.
Mastering fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base regulation is a journey that requires dedication and consistent effort. By building a strong foundation in the underlying principles and employing effective study strategies, you can confidently tackle the ATI quizlet and excel in your clinical practice. Remember that continuous learning and clinical experience are essential for staying updated with the latest advancements in this crucial area of healthcare. This knowledge empowers you to provide safe, effective, and compassionate care to your patients.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In This Excerpt Schlosser Claims That Fast Food Restaurants Are
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Family Care Plan Coordinator Reports Directly To What Person
Mar 25, 2025
-
After Applying The Primer During A Sculptured Nail Service
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Can You Successfully Multitask While Driving A Vehicle
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Process Repairs Damage To A Preexisting Double Helix
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Fluid Electrolyte And Acid-base Regulation Ati Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
