From Which Direction Does Foul Weather Typically Approach
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
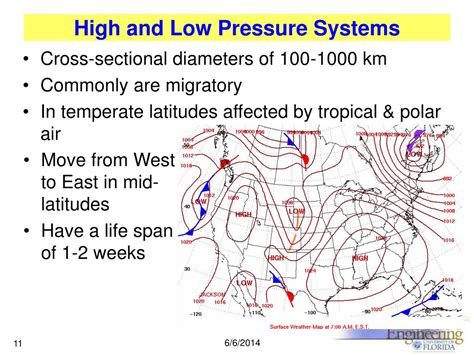
Table of Contents
From Which Direction Does Foul Weather Typically Approach?
Understanding where foul weather originates is crucial for anyone who spends time outdoors, from hikers and sailors to farmers and pilots. Knowing the typical approach of storms can significantly improve safety and preparedness. While there's no single definitive answer applicable globally, this article will explore the dominant weather patterns and their influence on the direction from which foul weather typically approaches in various regions. We'll delve into the science behind weather systems, examining prevailing winds, jet streams, and geographical features that shape the movement of storms.
The Role of Prevailing Winds
Prevailing winds, driven by global atmospheric circulation patterns, significantly influence the direction from which storms approach. These large-scale wind systems are largely responsible for the general weather patterns across different regions.
Westerlies: The Dominant Force in Mid-Latitudes
In the mid-latitudes, between the tropics and the poles, westerly winds dominate. This means storms generally move from west to east. This is particularly true in the Northern Hemisphere, where the prevailing westerlies steer weather systems across continents. However, the exact path of a storm is influenced by numerous factors, as we shall see.
Trade Winds: Shaping Weather in Tropical Regions
Closer to the equator, the trade winds blow from east to west. In tropical regions, storms often originate near the equator and are guided by these winds, initially moving westward. However, the development and movement of tropical cyclones (hurricanes and typhoons) are more complex and influenced by factors beyond just the trade winds. Their paths can curve significantly, making predicting their exact landfall location a challenging task for meteorologists.
Polar Easterlies: Affecting High-Latitude Regions
In polar regions, the polar easterlies blow from east to west. These winds influence the movement of smaller-scale weather systems in high-latitude areas, but the weather patterns in these regions are often more influenced by other factors such as Arctic oscillations and sea ice extent.
The Influence of Jet Streams
Jet streams are fast-flowing, narrow air currents found high in the atmosphere. These powerful rivers of air play a crucial role in guiding the movement of weather systems. The polar jet stream, for example, meanders across the mid-latitudes, significantly influencing the movement of extratropical cyclones (mid-latitude storms).
Jet Stream Dynamics and Storm Tracks
The position and strength of the jet stream are highly variable, influencing the track of storms. A strong, northward-displaced jet stream can push storms further north, while a southward-displaced weaker jet stream can steer them further south. This variability explains why the direction from which storms approach can be unpredictable, even within regions with generally consistent prevailing winds.
Geographical Features: Mountains, Coastlines, and Lakes
Geographical features significantly impact the movement and intensity of storms. Mountain ranges can act as barriers, deflecting storms or forcing them to rise, leading to increased precipitation on one side and a rain shadow on the other. Coastlines and large bodies of water also influence storm tracks, with storms often intensifying as they move over warmer water.
Orographic Effects: Mountains Shaping Weather
Mountain ranges often force air masses to rise, leading to cooling and condensation. This results in increased precipitation on the windward side of the mountains, while the leeward side experiences a rain shadow effect, characterized by drier conditions. The direction from which a storm approaches a mountain range will determine which side receives the brunt of the precipitation.
Coastal Effects: Water's Influence on Storms
The proximity to coastlines also influences storm tracks. Warm ocean currents can supply energy to storms, increasing their intensity. Conversely, cold ocean currents can weaken storms. The direction from which a storm approaches a coastline will determine the extent to which it is influenced by these ocean currents.
Seasonal Variations: Shifting Patterns
The direction from which foul weather approaches can vary significantly depending on the season. This is primarily due to the seasonal shift in atmospheric pressure systems, jet stream positions, and the availability of moisture.
Seasonal Shifts in Prevailing Winds
In many regions, the prevailing winds shift slightly with the seasons. These subtle shifts can lead to variations in the typical direction of storm approach. For instance, monsoon seasons in certain areas can dramatically change the dominant wind direction and significantly alter the path of storms.
Seasonal Changes in Storm Tracks
The tracks of major storm systems, such as extratropical cyclones, also shift with the seasons. In the Northern Hemisphere, during the winter, storms tend to track further south, while in the summer, they tend to track further north. This seasonal variation makes it crucial to consider the time of year when assessing the likely direction of storm approach.
Regional Variations: A Closer Look
The general principles discussed above apply globally, but the specific direction from which foul weather approaches varies significantly depending on the region.
North America: A Diverse Landscape
In North America, the direction of storm approach varies greatly depending on the location. The western coast experiences storms moving from the west, often associated with Pacific storms. The central plains experience storms moving from the west or southwest, while the eastern coast can experience storms from various directions, including the northeast, depending on the type of weather system.
Europe: Atlantic Influences
Europe experiences storms primarily from the Atlantic Ocean, often moving eastward across the continent. The specific direction can vary depending on the location and the type of storm. Mountain ranges, such as the Alps, can significantly alter storm tracks.
Asia: Monsoon Systems and Typhoons
Asia experiences a wide range of weather patterns, including monsoon systems and typhoons. Monsoon systems bring heavy rainfall from a specific direction, typically southwest in South Asia. Typhoons, on the other hand, can approach from various directions, depending on their formation and track.
Predicting Storm Approach: Tools and Techniques
Accurate prediction of the direction from which a storm will approach requires sophisticated meteorological tools and techniques. Meteorologists use a variety of models and data sources to forecast weather, including:
Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) Models
These complex computer models use mathematical equations to simulate atmospheric processes and predict future weather conditions. NWP models are crucial for forecasting the track and intensity of storms.
Satellite Imagery and Radar Data
Satellite imagery provides a broad view of weather systems, while radar data provides more detailed information on precipitation and wind speeds. These data sources are vital for tracking storm development and movement.
Surface Observations and Weather Stations
Ground-based weather stations provide essential data on temperature, pressure, wind speed, and precipitation, helping to refine weather forecasts.
Conclusion: Understanding is Key to Preparedness
The direction from which foul weather approaches varies significantly depending on numerous factors, including prevailing winds, jet streams, geographical features, and the season. While no single answer applies universally, understanding the general principles and regional variations outlined in this article can greatly improve safety and preparedness. By staying informed about weather forecasts and understanding the typical storm tracks in your region, you can better anticipate and prepare for foul weather events. Remember to always consult reputable weather sources for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Anatomical Term Means Toward The Midline Of The Body
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements About Ribosomes Is False
Mar 28, 2025
-
Rn Learning System Medical Surgical Respiratory Practice Quiz
Mar 28, 2025
-
The Scene Size Up At A Motor Vehicle Crash
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of These Would Be Deemed A Cybercrime
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about From Which Direction Does Foul Weather Typically Approach . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
