Genetic Drift Refers To The Movement Of Individuals Between Population
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
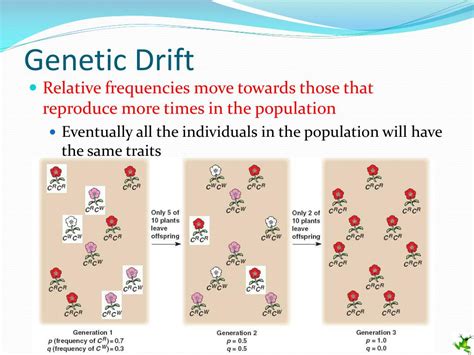
Table of Contents
Genetic Drift: A Misconception and the Reality of Gene Flow
The statement "genetic drift refers to the movement of individuals between populations" is incorrect. Genetic drift and gene flow are distinct, yet often confused, mechanisms of evolutionary change. While both influence allele frequencies within populations, they operate through different processes. This article will clarify the definition of genetic drift, explain its mechanisms, contrast it with gene flow, and explore its impact on population genetics and evolution.
Understanding Genetic Drift: Random Fluctuations in Allele Frequencies
Genetic drift is the random fluctuation of allele frequencies within a population, driven by chance events rather than selective pressures. It's particularly impactful in smaller populations, where stochastic events can significantly alter the genetic makeup across generations. Think of it as a lottery: the winning allele isn't necessarily the "best" allele; it just happens to be the one that, by random chance, gets passed on more frequently.
The Bottleneck Effect: A Dramatic Reduction in Population Size
One significant mechanism driving genetic drift is the bottleneck effect. This occurs when a population undergoes a drastic reduction in size due to a catastrophic event – a natural disaster, disease outbreak, or human intervention. This sudden decrease leaves behind a smaller, less genetically diverse population. The allele frequencies in the surviving population may differ significantly from the original population, purely due to chance. The alleles present in the surviving individuals, regardless of their adaptive value, will become the foundation of the future population's gene pool.
Example: Imagine a population of 1000 butterflies with equal frequencies of two alleles (A and a) for wing color. A sudden storm drastically reduces the population to only 50 individuals. By chance, the surviving individuals might have a higher frequency of allele A. Subsequent generations will reflect this skewed allele frequency, even if allele A didn't offer any survival advantage.
The Founder Effect: Establishing a New Population from a Small Group
Another crucial mechanism of genetic drift is the founder effect. This arises when a small group of individuals migrates to a new area and establishes a new population. The allele frequencies in this founder population will likely differ from the original source population, simply because the small founding group doesn't represent the full genetic diversity of the larger population. The new population's genetic makeup will be heavily influenced by the alleles present in the founders.
Example: A small group of birds from a large mainland population migrates to a remote island. The allele frequencies for beak shape in the island population might differ significantly from the mainland population due to the limited genetic variation brought by the founders. Rare alleles might become prevalent, while others might disappear completely.
Contrasting Genetic Drift with Gene Flow: The Movement of Alleles
Gene flow, also known as migration, is the transfer of alleles between populations. This occurs when individuals move from one population to another and breed with the resident population. Gene flow introduces new alleles into the recipient population and can alter allele frequencies. Unlike genetic drift, gene flow is a deterministic process; it's not driven by random chance. The effect of gene flow is predictable – it generally leads to a reduction in genetic differences between populations.
Key Differences:
| Feature | Genetic Drift | Gene Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Random chance events | Movement of individuals and their alleles |
| Impact | Changes allele frequencies randomly | Changes allele frequencies predictably |
| Population Size | More impactful in small populations | Significant in populations of any size |
| Directionality | Unpredictable; can increase or decrease diversity | Generally reduces genetic differences between populations |
| Adaptive Value | Irrespective of allele's adaptive value | Can introduce beneficial or harmful alleles |
The Impact of Genetic Drift on Evolutionary Processes
Genetic drift can have profound effects on the evolutionary trajectory of a population. While natural selection acts on the differential survival and reproduction of individuals based on their traits, genetic drift can lead to changes in allele frequencies irrespective of their adaptive value. This can have both positive and negative consequences:
- Loss of genetic diversity: Genetic drift, particularly in small populations, can lead to a loss of alleles, reducing genetic diversity. This can make the population less adaptable to environmental changes.
- Fixation of alleles: Drift can lead to the fixation of certain alleles, meaning that one allele becomes the only allele present at a specific locus in the population. This can be advantageous if the fixed allele is beneficial, but detrimental if it's harmful.
- Increased genetic differences between populations: Since drift acts independently in different populations, it can contribute to the divergence of populations and speciation.
Genetic Drift vs. Gene Flow: A Synergistic Interaction
Genetic drift and gene flow don't operate in isolation. They often interact, and their combined effects shape the genetic structure of populations. For instance, gene flow can counteract the effects of genetic drift, particularly in small populations. The influx of new alleles from other populations can increase genetic diversity and prevent the loss of rare alleles. Conversely, strong genetic drift can overcome the homogenizing effect of gene flow, leading to significant divergence between populations even with ongoing migration.
Studying Genetic Drift: Methods and Models
Researchers use various approaches to study genetic drift, including:
- Computer simulations: These are powerful tools for exploring the effects of drift under different conditions (population size, allele frequencies, etc.).
- Population genetic data analysis: Analyzing allele frequencies in natural populations allows scientists to infer the role of drift in shaping genetic diversity and differentiation.
- Experimental evolution: Manipulating populations in laboratory settings enables direct observation of drift's effects under controlled conditions.
Conclusion: A nuanced Understanding of Evolutionary Mechanisms
It's crucial to differentiate between genetic drift and gene flow. While gene flow involves the movement of alleles between populations, genetic drift is the random fluctuation of allele frequencies within a population, driven by chance events. Both are significant forces in evolution, often interacting to shape the genetic makeup of populations. Understanding these mechanisms and their interplay is fundamental to comprehending the complex dynamics of evolutionary change. The misconception of equating genetic drift with gene flow highlights the importance of precise terminology and a thorough understanding of the underlying processes in evolutionary biology. Further research into the interaction of these forces, especially in fragmented and endangered populations, is crucial for effective conservation strategies.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cardiac Arrest Is Often Due To A Blockage Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
When A Woman Presents With Abdominal Pain Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Was The Cuban Missile Crisis Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Postrenal Acute Kidney Injury May Be Caused By Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is A Sign Of Alcohol Overdose Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Genetic Drift Refers To The Movement Of Individuals Between Population . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
