How Are Stress And Physical Health Related Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
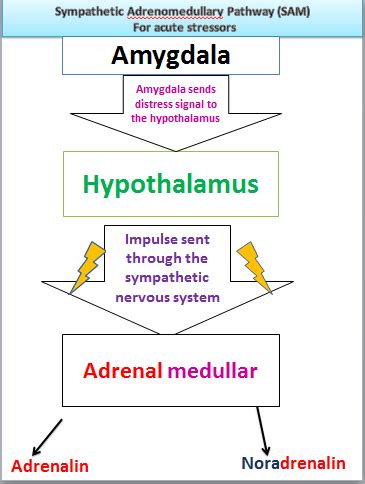
Table of Contents
- How Are Stress And Physical Health Related Quizlet
- Table of Contents
- How Are Stress and Physical Health Related? A Comprehensive Look
- The Stress Response: Your Body's Alarm System
- The Physiological Cascade:
- Chronic Stress: The Silent Killer
- Chronic Stress and Disease: A Dangerous Liaison
- Understanding the Mechanisms: How Stress Impacts the Body
- Coping with Stress: Protecting Your Physical Health
- Effective Stress Management Techniques:
- The Importance of Holistic Wellness
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Are Stress and Physical Health Related? A Comprehensive Look
Stress. It's a word we hear daily, a feeling we all experience. But how deeply intertwined is stress with our physical well-being? The relationship isn't merely anecdotal; it's a scientifically proven connection with far-reaching consequences. This article delves into the intricate relationship between stress and physical health, exploring the mechanisms, consequences, and strategies for managing this pervasive influence on our bodies.
The Stress Response: Your Body's Alarm System
When faced with a perceived threat – whether a looming deadline, a confrontation, or a physical danger – your body triggers a cascade of physiological responses known as the stress response, or the "fight-or-flight" response. This system, primarily driven by the sympathetic nervous system and the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, prepares you to either confront or escape the perceived danger.
The Physiological Cascade:
- Increased Heart Rate and Blood Pressure: Your heart beats faster to pump more blood to your muscles, preparing you for action. This sustained elevation can contribute to cardiovascular problems over time.
- Rapid Breathing: Your breathing becomes faster and shallower to increase oxygen intake. Chronic shallow breathing can negatively impact lung function.
- Muscle Tension: Muscles tense to prepare for physical exertion. Chronic muscle tension leads to headaches, back pain, and other musculoskeletal issues.
- Digestive System Slowdown: Blood flow is diverted away from the digestive system to vital organs. This can lead to indigestion, constipation, and other gastrointestinal problems.
- Immune System Suppression: Prolonged stress suppresses the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Sustained high cortisol levels disrupt the delicate balance of hormones in your body, affecting various bodily functions.
Chronic Stress: The Silent Killer
While acute stress – short-term stress – can be beneficial in motivating action and enhancing performance, chronic stress – prolonged and unremitting stress – is profoundly damaging to physical health. The constant activation of the stress response wears down the body's systems, leading to a multitude of health problems.
Chronic Stress and Disease: A Dangerous Liaison
- Cardiovascular Disease: Chronic stress significantly increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and hypertension. The persistent elevation of heart rate and blood pressure damages blood vessels and increases the risk of plaque buildup.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Chronic stress impairs insulin sensitivity, making it harder for your body to regulate blood sugar levels. This increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Gastrointestinal Problems: The consistent suppression of the digestive system contributes to irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), ulcers, and other gastrointestinal disorders.
- Mental Health Issues: Chronic stress is a major risk factor for depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The interplay between mental and physical health is undeniable.
- Weakened Immune System: Constant immune suppression increases vulnerability to infections, autoimmune diseases, and even cancer.
- Sleep Disturbances: Stress significantly disrupts sleep patterns, leading to insomnia, poor sleep quality, and daytime fatigue. Sleep deprivation further exacerbates the effects of stress.
- Obesity: Chronic stress can lead to increased cortisol levels, which promote fat storage, particularly around the abdomen. This increases the risk of obesity and related health problems.
- Skin Conditions: Stress can exacerbate existing skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis, and even trigger new ones.
- Headaches and Migraines: Muscle tension and hormonal imbalances associated with stress are major triggers for headaches and migraines.
- Reproductive Issues: Chronic stress can affect fertility in both men and women, leading to difficulties conceiving.
Understanding the Mechanisms: How Stress Impacts the Body
The effects of stress on physical health aren't simply a matter of coincidence; there are specific mechanisms through which stress impacts bodily functions:
- Inflammation: Chronic stress triggers chronic inflammation throughout the body, contributing to a wide range of diseases. Inflammation is a key player in many chronic illnesses.
- Telomere Shortening: Stress accelerates telomere shortening, which are protective caps on the ends of chromosomes. Shorter telomeres are associated with aging and increased risk of disease.
- Neurotransmitter Imbalances: Stress affects the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, impacting mood, sleep, and overall well-being. Neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine play critical roles in various bodily functions.
- Gut-Brain Axis: The gut and brain communicate constantly through the gut-brain axis. Stress significantly disrupts this communication, leading to both gastrointestinal and mental health problems.
Coping with Stress: Protecting Your Physical Health
Managing stress is crucial for safeguarding your physical well-being. Adopting healthy coping mechanisms is essential for mitigating the detrimental effects of stress.
Effective Stress Management Techniques:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity is a powerful stress reliever. Exercise releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation helps regulate the stress response and promote relaxation.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These mind-body practices combine physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation to reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep, slow breaths activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which counteracts the effects of the stress response.
- Sufficient Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Sleep deprivation exacerbates the effects of stress.
- Healthy Diet: Nourishing your body with a balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients to support your physical and mental health.
- Social Support: Connecting with supportive friends and family provides emotional resilience and reduces feelings of isolation.
- Time Management: Effective time management reduces feelings of overwhelm and improves your ability to cope with demands.
- Setting Boundaries: Learning to say "no" to commitments that add unnecessary stress is crucial.
- Hobbies and Interests: Engaging in activities you enjoy provides a much-needed break from stressors.
- Professional Help: If you are struggling to manage stress, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor is essential. They can provide guidance and support in developing coping strategies.
The Importance of Holistic Wellness
The link between stress and physical health is undeniable. Addressing stress effectively is not merely about alleviating discomfort; it's about protecting your long-term physical well-being. A holistic approach that integrates physical activity, mental wellness practices, and healthy lifestyle choices is paramount in mitigating the negative consequences of stress and promoting overall health.
Regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial for monitoring your physical health and addressing any potential problems early. Open communication with your healthcare provider about your stress levels allows for a collaborative approach to managing both your mental and physical health.
By understanding the intricate connection between stress and physical health, we can equip ourselves with the knowledge and tools necessary to manage stress effectively and protect our bodies from its detrimental effects. Remember, prioritizing your well-being is not a luxury; it's an investment in a healthier and happier future. Taking proactive steps to manage stress is an act of self-care with far-reaching benefits for your physical and mental health. This proactive approach contributes not only to improved well-being but also to increased longevity and a richer quality of life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Danger Of A Single Story Commonlit Answers
Mar 26, 2025
-
Interactive Grammar Tutorial Forming Questions In Spanish
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Student Is Given Two 10g Samples
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Term Aerotolerant Anaerobe Refers To An Organism That
Mar 26, 2025
-
With Regard To Facility Safety Nfpa 1500
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Are Stress And Physical Health Related Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
