How Does Co2 Level Affect Oxygen Production
Breaking News Today
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
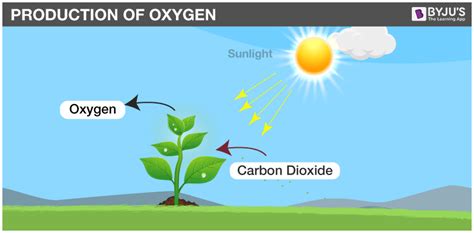
Table of Contents
How Does CO2 Level Affect Oxygen Production? A Deep Dive into Photosynthesis and Global Implications
The delicate balance between carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen (O2) in Earth's atmosphere is crucial for life as we know it. This balance is primarily governed by photosynthesis, the remarkable process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, producing oxygen as a byproduct. Understanding how CO2 levels affect oxygen production is therefore paramount to comprehending the Earth's climate, ecosystems, and ultimately, our own survival.
The Fundamental Role of CO2 in Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis, the engine driving oxygen production, is a complex biochemical process occurring in chloroplasts, specialized organelles within plant cells. The process can be simplified into two main stages:
1. The Light-Dependent Reactions:
Sunlight's energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments within the chloroplasts. This energy is used to split water molecules (H₂O) into oxygen (O₂), protons (H⁺), and electrons (e⁻). The oxygen is released as a byproduct into the atmosphere, while the protons and electrons are crucial for the subsequent stage.
2. The Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle):
This stage doesn't directly require sunlight. The energy captured in the light-dependent reactions is used to power the fixation of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. CO2 combines with a five-carbon sugar (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate) through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, ultimately producing glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), a simple sugar used by plants for energy and growth.
The crucial link: CO2 acts as the primary carbon source for this process. Without sufficient CO2, the Calvin cycle slows down, significantly reducing the rate of glucose production and, consequently, the rate of oxygen production. This is because the enzyme RuBisCO, responsible for fixing CO2, has a limited capacity and its efficiency is directly tied to CO2 concentration. Therefore, higher CO2 levels, within a certain range, generally lead to increased photosynthetic rates and, consequently, higher oxygen production.
The Impact of Elevated CO2 Levels on Oxygen Production: A Complex Relationship
While increased CO2 generally boosts photosynthesis, the relationship isn't linear and is affected by several interacting factors:
1. Saturation Point of Photosynthesis:
Plants have a photosynthetic capacity limit. At a certain CO2 concentration, increasing CO2 further won't significantly enhance photosynthetic rates. This is because other factors, such as light intensity, water availability, and nutrient levels, become limiting. This point of saturation varies significantly depending on the plant species, its age, and environmental conditions.
2. Nutrient Limitations:
Even with ample CO2, plants require various nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.) for growth and photosynthesis. A deficiency in any of these essential nutrients can limit photosynthetic efficiency, irrespective of CO2 levels. This is often observed in intensive agriculture where CO2 enrichment is used without optimizing nutrient management.
3. Water Availability:
Water stress significantly impacts photosynthesis. Stomata, tiny pores on plant leaves, regulate gas exchange (CO2 intake and O2 release). During water stress, stomata close to conserve water, reducing CO2 uptake and thus oxygen production. This effect can overshadow the positive impact of elevated CO2.
4. Temperature Effects:
Temperature significantly influences enzyme activity, including RuBisCO. While slightly elevated temperatures can initially boost photosynthesis, excessively high temperatures can damage enzymes and reduce photosynthetic efficiency, negating the benefits of increased CO2. This is particularly relevant in the context of climate change, where rising temperatures are expected to counteract some of the positive effects of higher CO2 on oxygen production.
The Paradox of Increased CO2 and Decreasing Oxygen: Indirect Effects
The seemingly straightforward relationship between CO2 and oxygen production is complicated by several indirect effects:
1. Increased Plant Respiration:
While photosynthesis produces oxygen, plants also respire, consuming oxygen and releasing CO2. Increased CO2 levels can stimulate plant growth, leading to higher respiration rates, partially offsetting the increased oxygen production from photosynthesis. The net effect on atmospheric oxygen depends on the balance between enhanced photosynthesis and increased respiration.
2. Changes in Ecosystem Composition:
Elevated CO2 can alter the composition of plant communities. Some plant species may thrive under higher CO2 conditions, while others may be outcompeted. These shifts in species distribution can affect the overall rate of photosynthesis and oxygen production across different ecosystems. For example, C4 plants, which are less sensitive to CO2 limitations, might become more dominant, altering the overall oxygen production dynamics.
3. Ocean Acidification:
Increased atmospheric CO2 leads to ocean acidification as CO2 dissolves in seawater, forming carbonic acid. This acidification negatively impacts marine life, particularly shell-forming organisms like corals and shellfish. These organisms play a crucial role in the marine carbon cycle and their decline could have indirect consequences on the global oxygen cycle.
4. Feedback Mechanisms:
Complex feedback mechanisms within the Earth's system can further complicate the relationship. For instance, increased CO2 can lead to warming, which in turn can affect cloud cover and precipitation patterns, influencing plant growth and photosynthesis. These indirect effects can either amplify or dampen the initial impact of increased CO2 on oxygen production.
Long-Term Implications and Future Research
Predicting the long-term effects of elevated CO2 on atmospheric oxygen levels is challenging due to the complex interplay of factors discussed above. While initially, increased CO2 might boost photosynthesis and oxygen production, the indirect effects and saturation points might limit the extent of this increase. Furthermore, the potential for decreased oxygen due to other factors like ocean acidification and ecosystem shifts remains a significant concern.
Future research should focus on:
- Improving our understanding of the saturation point of photosynthesis under various environmental conditions. This includes understanding how different plant species respond to varying CO2 levels and other environmental stressors.
- Developing more sophisticated models that incorporate the complex feedback loops and interactions between various components of the Earth's system. These models can help predict the long-term effects of elevated CO2 on the global oxygen cycle.
- Investigating the impacts of CO2 on marine ecosystems and their contribution to the global oxygen cycle. Understanding the consequences of ocean acidification on marine life and their role in oxygen production is critical.
- Monitoring changes in atmospheric oxygen levels and linking them to changes in CO2 levels and other environmental variables. Long-term monitoring data are essential for validating models and assessing the actual impact of CO2 on global oxygen production.
Conclusion: A Delicate Balance
The relationship between CO2 levels and oxygen production is far more nuanced than a simple direct correlation. While higher CO2 levels initially stimulate photosynthesis, leading to increased oxygen production, the interplay of multiple factors—nutrient limitations, water availability, temperature effects, plant respiration, and ecosystem changes—significantly modifies the overall impact. Understanding these complex interactions is critical for accurately predicting the future of Earth's atmosphere and the potential consequences of rising CO2 levels for life on our planet. Continued research and rigorous monitoring are vital to navigate this delicate balance and ensure the sustainability of our planet's oxygen supply.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
All Anthropologists Agree On The Definition Of Culture
Apr 04, 2025
-
Volumes Of Prisms And Cylinders Quick Check
Apr 04, 2025
-
Organizations Reorganize To Empower Frontline Workers To
Apr 04, 2025
-
Choose The Best Translation Necklace Bolso Manga Collar Boton
Apr 04, 2025
-
A Person Who Is Low In Practical Intelligence Might
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does Co2 Level Affect Oxygen Production . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
