How Does Therapy Help In The Treatment Of Depression Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
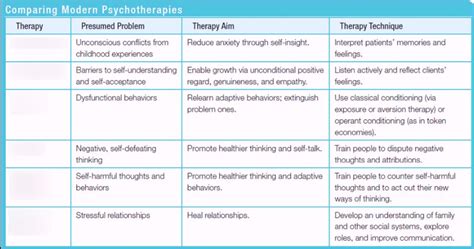
Table of Contents
How Does Therapy Help in the Treatment of Depression?
Depression, a pervasive mood disorder affecting millions globally, significantly impacts daily life, hindering social interactions, work productivity, and overall well-being. While medication plays a vital role in managing depression's biological aspects, therapy offers a powerful tool for addressing its emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. This article delves into the mechanisms through which various therapeutic approaches effectively treat depression. We will explore how these therapies help individuals understand, manage, and ultimately overcome depressive symptoms.
Understanding the Multifaceted Nature of Depression
Before exploring the therapeutic interventions, it's crucial to grasp the complexity of depression. It's not simply "feeling sad"; it's a multifaceted disorder involving:
- Biological factors: Imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine are implicated. Genetic predispositions also play a significant role.
- Psychological factors: Negative thought patterns, low self-esteem, learned helplessness, and rumination contribute significantly to the persistence of depressive symptoms.
- Social factors: Stressful life events, loss, social isolation, and lack of social support can trigger or exacerbate depression.
Effective treatment needs to address these interwoven factors, and this is where therapy excels. It provides a personalized approach, tailoring interventions to the individual's unique experiences and needs.
Types of Therapy Effective for Depression
Several types of therapy have demonstrated effectiveness in treating depression. The choice of therapy depends on factors such as the individual's preferences, the severity of their depression, and the presence of co-occurring conditions.
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is arguably the most researched and widely used therapy for depression. It focuses on the interconnectedness of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. The core principle lies in identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and replacing them with more realistic and helpful ones.
Key Techniques in CBT for Depression:
- Cognitive restructuring: Identifying and challenging negative automatic thoughts (NATs) – those fleeting, often unconscious, negative thoughts that pop into our minds. This involves examining the evidence supporting and refuting these thoughts.
- Behavioral activation: Increasing engagement in pleasurable activities and rewarding behaviors. Depression often leads to withdrawal, and behavioral activation helps break this cycle.
- Exposure therapy (for specific phobias or anxieties contributing to depression): Gradually exposing individuals to feared situations or objects to reduce avoidance and anxiety.
- Problem-solving skills training: Developing strategies to effectively address challenges and overcome obstacles.
How CBT Helps: By modifying negative thought patterns and increasing engagement in positive activities, CBT helps individuals regain a sense of control over their lives and improve their mood.
2. Interpersonal Therapy (IPT)
IPT focuses on improving interpersonal relationships and resolving interpersonal problems that contribute to or worsen depression. It's particularly helpful for individuals whose depression is linked to relationship difficulties, grief, role transitions (such as job loss or retirement), or interpersonal disputes.
Key Aspects of IPT:
- Identifying and addressing problematic interpersonal relationships: This involves exploring communication patterns, conflict resolution strategies, and boundary setting.
- Grief resolution: Helping individuals process grief and loss in a healthy way.
- Role disputes: Resolving conflicts and misunderstandings within significant relationships.
- Role transitions: Adapting to major life changes and navigating new roles.
How IPT Helps: By improving communication, resolving conflicts, and strengthening relationships, IPT helps individuals feel more supported and connected, reducing feelings of loneliness and isolation.
3. Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychodynamic therapy explores unconscious patterns and past experiences that may contribute to current emotional difficulties. It delves deeper into the individual's history, examining early childhood experiences and their impact on current relationships and emotional functioning.
Key Focus Areas in Psychodynamic Therapy:
- Unconscious processes: Identifying unconscious thoughts, feelings, and motivations that influence behavior and emotional responses.
- Early childhood experiences: Exploring how past relationships and experiences shape current emotional patterns.
- Defense mechanisms: Understanding how individuals cope with difficult emotions and experiences.
- Transference and countertransference: Analyzing the dynamics of the therapeutic relationship to gain insights into the individual's relational patterns.
How Psychodynamic Therapy Helps: By uncovering and processing unconscious conflicts, psychodynamic therapy helps individuals gain greater self-awareness and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
4. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
ACT emphasizes acceptance of difficult thoughts and feelings rather than fighting against them. It focuses on identifying values and taking committed action towards living a meaningful life, even in the face of emotional distress.
Core Principles of ACT:
- Acceptance: Learning to accept difficult thoughts and emotions without judgment.
- Cognitive defusion: Developing distance from thoughts, recognizing them as mental events rather than absolute truths.
- Self-as-context: Developing a sense of self that is separate from thoughts and emotions.
- Present moment awareness: Focusing on the present moment rather than dwelling on the past or worrying about the future.
- Values identification: Clarifying personal values and goals.
- Committed action: Taking steps towards living in accordance with one's values.
How ACT Helps: By fostering acceptance and promoting committed action, ACT helps individuals move forward despite their emotional challenges.
5. Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT)
MBCT combines elements of CBT and mindfulness meditation. It teaches individuals to observe their thoughts and emotions without judgment, fostering self-awareness and reducing reactivity to negative thoughts.
Key Components of MBCT:
- Mindfulness meditation: Practicing mindfulness techniques to cultivate present moment awareness.
- Cognitive techniques: Identifying and challenging negative automatic thoughts.
- Relabeling and reattribution: Recognizing negative thoughts as transient mental events rather than objective realities.
- Decentering: Developing a sense of distance from thoughts and emotions.
How MBCT Helps: By increasing self-awareness and reducing reactivity to negative thoughts, MBCT helps individuals develop more adaptive coping mechanisms and manage depressive symptoms.
The Role of the Therapist in Depression Treatment
The therapist's role extends beyond simply applying techniques. They serve as a crucial source of:
- Support and empathy: Providing a safe and non-judgmental space for the individual to explore their experiences.
- Collaboration and partnership: Working collaboratively with the individual to develop treatment goals and strategies.
- Accountability and motivation: Helping the individual stay motivated and engaged in the therapeutic process.
- Education and skill-building: Teaching the individual coping skills and strategies for managing depressive symptoms.
Combining Therapy with Medication
In many cases, a combination of therapy and medication is the most effective approach to treating depression. Therapy addresses the psychological and behavioral aspects of depression, while medication can help regulate neurotransmitter imbalances. The integration of these approaches offers a comprehensive and synergistic treatment plan.
Long-Term Benefits of Therapy for Depression
The benefits of therapy for depression extend far beyond symptom reduction. Therapy equips individuals with:
- Improved coping skills: Developing healthy strategies for managing stress, challenging negative thoughts, and resolving interpersonal conflicts.
- Enhanced self-awareness: Gaining a deeper understanding of their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
- Increased self-esteem: Developing a more positive self-image and greater self-acceptance.
- Stronger relationships: Improving communication skills and strengthening relationships with others.
- Greater resilience: Developing the ability to bounce back from setbacks and cope with future challenges.
Conclusion: Therapy as a Powerful Tool
Therapy is a powerful and effective treatment for depression. By addressing the multiple factors contributing to depression and providing individuals with skills and support, therapy helps individuals overcome their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and develop greater resilience to future challenges. The choice of therapeutic approach depends on individual needs and preferences, highlighting the importance of finding a therapist with whom one feels comfortable and connected. With consistent effort and the right support, recovery from depression is achievable. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Feature Of Secrets Management
May 09, 2025
-
The Maximum Height At Which A Catenary Scaffold
May 09, 2025
-
Name The Vertebral Projection Oriented In A Median Plane
May 09, 2025
-
Match Each Phrase To The Cardiovascular System Function It Describes
May 09, 2025
-
What Does All Food Contact Equipment Need To Be
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does Therapy Help In The Treatment Of Depression Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.