How Many Lines Of Reflectional Symmetry Does The Trapezoid Have
Breaking News Today
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
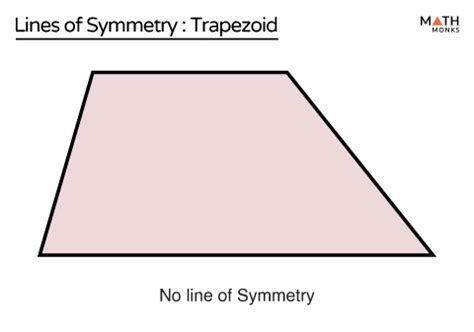
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Reflectional Symmetry Does a Trapezoid Have?
Understanding symmetry, particularly reflectional symmetry (also known as line symmetry or mirror symmetry), is crucial in geometry. This article delves deep into the concept of reflectional symmetry, focusing specifically on trapezoids and answering the central question: how many lines of reflectional symmetry does a trapezoid possess? We'll explore different types of trapezoids, their properties, and the implications for their symmetry.
Defining Reflectional Symmetry
Reflectional symmetry occurs when a shape can be folded along a line, creating two identical halves that perfectly overlap. This line is called the line of symmetry or axis of symmetry. When a shape is reflected across its line of symmetry, the resulting image is congruent to the original shape. Think of it like looking at your reflection in a mirror – the image is a perfect match but reversed.
Types of Trapezoids
Before we can determine the number of lines of symmetry a trapezoid has, we must clarify the different types of trapezoids. Trapezoids are quadrilaterals (four-sided polygons) characterized by having at least one pair of parallel sides. These parallel sides are called bases. The other two sides are called legs.
We categorize trapezoids based on the lengths of their legs and the angles formed by their sides:
-
Isosceles Trapezoid: This type of trapezoid has congruent (equal length) legs. The base angles (angles at the base) are also congruent.
-
Scalene Trapezoid: This trapezoid has legs of unequal length, and all its angles are unequal.
-
Right Trapezoid: A right trapezoid has at least one right angle (90-degree angle).
Analyzing Symmetry in Different Trapezoids
Now let's examine the symmetry of each trapezoid type:
Isosceles Trapezoid: The Exception
An isosceles trapezoid is the only type of trapezoid that can possess a line of reflectional symmetry. This line of symmetry is perpendicular to the bases and passes through the midpoints of both bases. It acts as a mirror, reflecting one half of the trapezoid perfectly onto the other. Therefore, an isosceles trapezoid has one line of reflectional symmetry.
Consider the properties of an isosceles trapezoid. The congruent legs and base angles contribute to this single line of symmetry. If you were to fold the trapezoid along this line, the legs would perfectly overlap, as would the corresponding base angles. This perfect overlap is the hallmark of reflectional symmetry.
Scalene and Right Trapezoids: The Lack of Symmetry
Scalene trapezoids, with their unequal sides and angles, lack any lines of reflectional symmetry. No matter where you try to draw a line through the shape, you won't find a line that divides it into two perfectly congruent halves. The asymmetry inherent in the unequal side lengths prevents the existence of any reflectional symmetry.
Similarly, right trapezoids generally lack reflectional symmetry. While a right trapezoid might have one right angle, this doesn't guarantee symmetry. The unequal lengths of the legs and the potentially disparate angles prevent the formation of a line that could reflect the shape onto itself. Unless a right trapezoid is also an isosceles trapezoid (a rare special case), it will lack any lines of reflectional symmetry.
Visualizing the Symmetry (or Lack Thereof)
Imagine trying to fold each type of trapezoid to create two identical halves. With an isosceles trapezoid, it's easily done along the single line of symmetry. However, with a scalene trapezoid or a typical right trapezoid, no matter how you fold it, the two halves will never perfectly align. This visual demonstration powerfully illustrates the absence of reflectional symmetry in these trapezoid types.
Rotational Symmetry: A Related Concept
While this article focuses on reflectional symmetry, it's important to briefly mention rotational symmetry. Rotational symmetry refers to the ability of a shape to be rotated around a central point (a point of rotation) and still look identical.
Neither an isosceles trapezoid nor any other type of trapezoid possesses rotational symmetry, unless it's a special case with certain angles. A trapezoid typically does not look identical after any rotation less than a full 360 degrees.
Practical Applications of Understanding Trapezoid Symmetry
Understanding the symmetry (or lack thereof) of trapezoids has various applications in:
-
Engineering and Design: Symmetry is essential in structural design, ensuring balance and stability. Knowing a trapezoid's symmetry (or lack thereof) influences its use in constructing buildings, bridges, and other structures.
-
Art and Architecture: Artists and architects use symmetry to create visually appealing and balanced designs. An understanding of trapezoid symmetry can inform the creative process and the aesthetic impact of their work.
-
Tessellations: Certain shapes, including specific types of trapezoids, can be used to create tessellations (patterns that cover a surface without gaps or overlaps). An understanding of symmetry helps in designing such tessellations.
Further Exploration: Advanced Geometric Concepts
The concept of symmetry extends beyond simple shapes like trapezoids. More complex shapes and even three-dimensional objects can possess various types of symmetry, including reflectional, rotational, and even translational symmetry. Exploring these advanced concepts provides a deeper understanding of geometry and its applications in various fields.
Conclusion: The Bottom Line on Trapezoid Symmetry
To reiterate the central point: a trapezoid typically has zero lines of reflectional symmetry. The exception is the isosceles trapezoid, which possesses one line of reflectional symmetry. This difference highlights the importance of differentiating between the various types of trapezoids when analyzing their geometric properties, specifically their symmetries. Understanding these properties is fundamental to grasping geometry and its diverse applications in various disciplines. The absence of reflectional symmetry in most trapezoids showcases the rich variety of shapes and their unique characteristics within geometry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
If The Unemployment Rate Is 8 Percent Then This Means
Mar 20, 2025
-
Family Is Important To The Socialization Process Because
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Did Advanced Weaponry Help Europe During New Imperialism
Mar 20, 2025
-
Domain 3 Lesson 1 Fill In The Blanks
Mar 20, 2025
-
In A Nation State What Role Does Shared Religion Play
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Reflectional Symmetry Does The Trapezoid Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
