I Am Helpful For Long Term Energy Storage
Breaking News Today
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
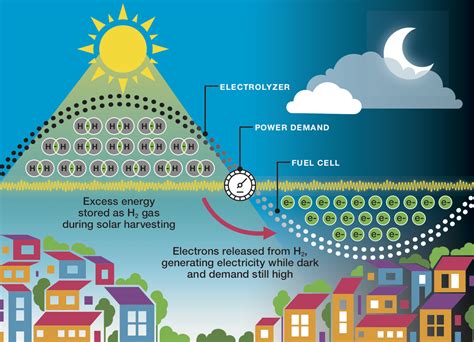
Table of Contents
I Am Helpful for Long-Term Energy Storage: Exploring the Future of Energy
The world is transitioning towards renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. However, a significant hurdle remains: the intermittent nature of these sources. The sun doesn't always shine, and the wind doesn't always blow. This intermittency necessitates robust and efficient long-term energy storage solutions to ensure a consistent and reliable power supply. This article delves into the critical role of various technologies in achieving this goal, exploring their advantages, disadvantages, and the future of long-term energy storage.
The Need for Long-Term Energy Storage
The demand for long-term energy storage is driven by several factors:
1. Balancing Renewable Energy Supply and Demand
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are inherently unpredictable. Their output fluctuates throughout the day and across seasons. Long-term storage solutions are crucial to bridge the gap between periods of high generation and periods of high demand, ensuring grid stability and preventing power outages.
2. Grid-Scale Energy Storage
Power grids require substantial energy storage capacity to manage peak demand, integrate renewable energy sources seamlessly, and maintain grid reliability. Long-term storage is vital for ensuring a stable and continuous supply of electricity, even during prolonged periods of low renewable energy generation.
3. Enhancing Energy Security and Independence
Reliable energy storage reduces dependence on fossil fuels and enhances national energy security. By storing excess renewable energy, countries can reduce their reliance on volatile global energy markets and minimize the risk of energy shortages.
4. Supporting Remote and Off-Grid Applications
Long-term energy storage is particularly crucial for remote communities and off-grid applications where access to the traditional electricity grid is limited or non-existent. These systems provide a reliable source of power, enabling access to essential services and improved living standards.
Technologies for Long-Term Energy Storage
Several promising technologies are being developed and deployed for long-term energy storage, each with its own strengths and limitations.
1. Pumped Hydroelectric Storage (PHS)
Pumped hydroelectric storage is a mature technology and currently the dominant form of large-scale energy storage. It involves pumping water uphill to a reservoir during periods of low electricity demand and then releasing it to generate electricity during peak demand.
Advantages: High efficiency, long lifespan, relatively low cost per kWh, and proven technology.
Disadvantages: Requires geographically suitable locations (mountains, valleys), significant land use, and potential environmental impacts (habitat disruption).
2. Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
Compressed air energy storage involves compressing air into underground caverns or other suitable containers during periods of low electricity demand and then releasing it to drive turbines and generate electricity when needed.
Advantages: Relatively inexpensive, can be located near existing power plants, and potentially scalable.
Disadvantages: Lower efficiency than PHS, potential for air leakage, and requires suitable geological formations.
3. Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
Battery energy storage systems, utilizing various battery chemistries like lithium-ion, flow batteries, and solid-state batteries, are gaining prominence. Lithium-ion batteries are currently the most prevalent, offering high energy density and relatively fast charging and discharging capabilities. However, other chemistries are being developed to address challenges such as cost, lifespan, and safety.
Advantages: Modular design, relatively quick deployment, scalable capacity, and improving cost-effectiveness.
Disadvantages: Limited lifespan compared to other technologies, environmental concerns regarding raw material extraction and disposal, and potential safety risks.
4. Thermal Energy Storage (TES)
Thermal energy storage involves storing energy in the form of heat or cold. This can be achieved using various methods, such as molten salts, underground aquifers, or phase-change materials. This technology is particularly suitable for integrating solar thermal power plants and providing seasonal energy storage.
Advantages: Potentially very high capacity, suitable for long-duration storage, and can be combined with other renewable energy sources.
Disadvantages: Lower efficiency compared to other methods, requires significant space, and technological challenges remain.
5. Gravity-Based Energy Storage
Gravity-based energy storage utilizes the potential energy of mass to store and release energy. This can be achieved by lifting weights using excess electricity and then lowering them to generate electricity when needed.
Advantages: Very long lifespan, high reliability, and relatively simple technology.
Disadvantages: Requires significant infrastructure, high initial capital costs, and limited scalability.
The Future of Long-Term Energy Storage
The future of long-term energy storage will likely involve a diverse portfolio of technologies, tailored to specific applications and geographical locations. Several trends are shaping this future:
1. Hybrid Energy Storage Systems
Combining multiple storage technologies can leverage the strengths of each, mitigating their individual weaknesses. For instance, a hybrid system might integrate pumped hydro for long-duration storage with batteries for rapid response to fluctuating demand.
2. Advanced Battery Technologies
Research and development efforts are focused on improving battery chemistries, increasing energy density, extending lifespan, and enhancing safety. Solid-state batteries, for example, hold significant promise for next-generation energy storage.
3. Smart Grid Integration
Integrating energy storage systems with smart grids will enable more efficient management of energy flows, optimized utilization of storage capacity, and improved grid stability. Advanced control algorithms and data analytics will play a crucial role in achieving this.
4. Policy and Regulatory Support
Government policies and regulations play a vital role in driving innovation and deployment of long-term energy storage. Incentives, subsidies, and clear regulatory frameworks are needed to stimulate investment and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable and reliable energy system.
5. Cost Reduction
The cost of energy storage is a significant barrier to wider adoption. Ongoing technological advancements and economies of scale are expected to drive down costs, making energy storage more competitive with traditional power generation methods.
Conclusion: A Crucial Element in a Sustainable Energy Future
Long-term energy storage is not merely a technological challenge; it is a crucial element in achieving a sustainable and reliable energy future. The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources necessitates robust and efficient storage solutions to ensure grid stability, enhance energy security, and support a transition away from fossil fuels. The ongoing advancements in storage technologies, coupled with smart grid integration and supportive policies, are paving the way for a future where clean, reliable, and affordable energy is accessible to all. The technologies discussed here represent a significant step towards this goal, promising a more resilient and sustainable energy landscape for generations to come. Continuous innovation and collaboration across industry, academia, and government will be essential in unlocking the full potential of long-term energy storage and building a cleaner, more sustainable world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Es Mas Importante Doblar La Ropa Que Hablar Por Telefono
Apr 04, 2025
-
After Germanys Unification In 1871 Industrialization Accelerated And
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Nursing Theory Focuses On The Clients Self Care Needs
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Does Reagans Evidence Compare To The Available Data
Apr 04, 2025
-
Water Food And Sleep Are Examples Of
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about I Am Helpful For Long Term Energy Storage . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
