Identify The Primary Causes Of Adrenal Insufficiency Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
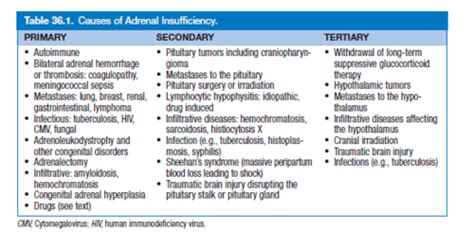
Table of Contents
Identifying the Primary Causes of Adrenal Insufficiency: A Comprehensive Guide
Adrenal insufficiency, also known as hypoadrenalism, is a rare but serious condition characterized by the adrenal glands' inability to produce sufficient cortisol and often aldosterone. Understanding its primary causes is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management. This comprehensive guide explores the key etiologies, focusing on clarity and accuracy for both medical professionals and individuals seeking information.
What are the Adrenal Glands and Their Functions?
Before delving into the causes of adrenal insufficiency, let's briefly review the adrenal glands and their vital roles. These small, triangular glands sit atop each kidney and consist of two distinct layers:
-
Cortex: The outer layer produces steroid hormones, including cortisol (crucial for regulating metabolism, stress response, and immune function), aldosterone (regulates salt and water balance), and androgens (contribute to sexual development and function).
-
Medulla: The inner layer produces catecholamines, such as epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine, involved in the "fight-or-flight" response.
Adrenal insufficiency primarily stems from problems within the adrenal cortex, affecting the production of cortisol and often aldosterone.
Primary Adrenal Insufficiency: The Focus of Our Exploration
Primary adrenal insufficiency, also known as Addison's disease, directly involves the adrenal glands themselves. The glands are unable to produce sufficient steroid hormones, leading to a deficiency. This contrasts with secondary adrenal insufficiency, where the problem lies in the pituitary gland's inability to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates cortisol production in the adrenal glands. This guide primarily focuses on the primary causes.
Primary Causes of Adrenal Insufficiency: A Detailed Overview
Several factors can lead to primary adrenal insufficiency. These include:
1. Autoimmune Diseases: The Most Common Culprit
Autoimmune adrenalitis is the leading cause of primary adrenal insufficiency in many parts of the world. In this condition, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the adrenal cortex cells responsible for hormone production. This process is often gradual, leading to a slow onset of symptoms. The exact triggers for autoimmune adrenalitis remain unclear, but genetic predisposition and environmental factors may play a role.
Identifying Autoimmune Adrenalitis: Diagnosis relies on clinical presentation, blood tests revealing low cortisol and aldosterone levels, and often the presence of other autoimmune diseases like type 1 diabetes, thyroid disease (Hashimoto's thyroiditis or Graves' disease), and vitiligo.
2. Adrenal Infections: Bacterial, Fungal, and Tuberculosis
Infections can severely damage the adrenal glands, disrupting hormone production. Several pathogens can be involved:
-
Bacterial infections: While less frequent, bacterial infections can reach the adrenal glands, causing significant damage.
-
Fungal infections: Opportunistic fungal infections, especially in immunocompromised individuals, can lead to adrenal insufficiency. Histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, and candidiasis are among the potential culprits.
-
Tuberculosis (TB): Tuberculosis remains a significant cause of adrenal insufficiency in some regions of the world. Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection can directly destroy adrenal tissue, leading to significant hormone deficiencies.
Identifying Infection-Related Adrenal Insufficiency: Diagnosis often involves imaging studies (CT or MRI scans) to visualize adrenal gland involvement, along with cultures and other tests to identify the specific infecting organism.
3. Adrenal Hemorrhage: Bleeding into the Adrenal Glands
Adrenal hemorrhage, or bleeding into the adrenal glands, can be a life-threatening event resulting in acute adrenal insufficiency. This can be triggered by various factors, including:
-
Sepsis: A severe bloodstream infection can lead to widespread clotting abnormalities, increasing the risk of adrenal hemorrhage.
-
Anticoagulation therapy: Individuals on blood thinners are at a higher risk of adrenal hemorrhage.
-
Trauma: Significant physical injury can also cause adrenal hemorrhage.
-
Malignancy: Cancer can infiltrate the adrenal glands, resulting in bleeding and damage.
Identifying Adrenal Hemorrhage: Diagnosis often involves imaging (CT or MRI) to detect the bleeding within the adrenal gland. Symptoms are typically acute and severe, requiring immediate medical attention.
4. Adrenomyeloneuropathy (AMN): An Inherited Disorder
AMN, a genetic disorder affecting the adrenal glands and the nervous system, is associated with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD). This disorder leads to the accumulation of very long-chain fatty acids in the adrenal glands and myelin sheath of nerve cells. This accumulation disrupts adrenal function and causes progressive neurological damage.
Identifying AMN: Genetic testing is crucial for diagnosis, identifying mutations in the ABCD1 gene responsible for X-ALD.
5. Adrenal Metastases: Cancer Spread to the Adrenal Glands
Cancer from other parts of the body can spread (metastasize) to the adrenal glands. This can disrupt adrenal function, leading to insufficiency. Lung, breast, and kidney cancers are among those that can metastasize to the adrenals.
Identifying Adrenal Metastases: Imaging studies such as CT scans or MRI scans are essential for detecting metastases. Biopsy may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
6. Infiltrative Diseases: Conditions Affecting Adrenal Tissue
Certain diseases can infiltrate and damage the adrenal glands, leading to insufficiency. These include:
-
Amyloidosis: The abnormal buildup of amyloid protein can infiltrate and damage adrenal tissue.
-
Sarcoidosis: This inflammatory disease can affect multiple organs, including the adrenal glands.
-
Histoplasmosis: As previously mentioned, this fungal infection can significantly damage the adrenal glands.
Identifying Infiltrative Diseases: Diagnosis often requires a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and potentially tissue biopsy for histological examination.
7. Iatrogenic Adrenal Insufficiency: Medication-Induced
In some cases, medication use can contribute to adrenal insufficiency. This is often due to long-term use of corticosteroids like prednisone, which can suppress the adrenal glands' natural cortisol production. Abrupt cessation of these medications can lead to adrenal crisis.
Identifying Iatrogenic Adrenal Insufficiency: Careful medication history is crucial. Physicians must carefully manage corticosteroid dosages and monitor patients for signs of adrenal suppression. Gradual tapering of corticosteroids is essential to prevent adrenal crisis.
Recognizing Symptoms: Clues to Adrenal Insufficiency
Symptoms of adrenal insufficiency can vary widely depending on the severity and duration of the condition. Common signs and symptoms include:
-
Fatigue and weakness: These are often the initial and most common symptoms.
-
Weight loss: Unintentional weight loss can occur due to impaired metabolism and appetite changes.
-
Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain are possible.
-
Low blood pressure (hypotension): Due to aldosterone deficiency.
-
Salt craving: The body attempts to compensate for the loss of salt.
-
Hyperpigmentation: Darkening of the skin, especially in sun-exposed areas and skin creases.
-
Muscle aches and pains: Due to reduced cortisol levels.
-
Joint pain: Similar to muscle pain, this can also occur.
-
Mood changes: Depression, irritability, and anxiety are common.
-
Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar levels due to impaired glucose metabolism.
Severe Adrenal Insufficiency (Adrenal Crisis): This is a life-threatening condition characterized by severe hypotension, dehydration, shock, and loss of consciousness. Immediate medical attention is critical.
Diagnosis and Treatment: A Collaborative Approach
Diagnosing adrenal insufficiency requires a thorough medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Tests often include:
-
Cosyntropin stimulation test: Measures the adrenal glands' response to synthetic ACTH.
-
Blood tests: Measure cortisol, aldosterone, and ACTH levels.
-
Imaging studies (CT, MRI): Assess the adrenal glands' size and structure.
Treatment typically involves hormone replacement therapy with corticosteroids (like hydrocortisone) and often mineralocorticoids (like fludrocortisone) to maintain proper salt and water balance. Lifelong hormone replacement is usually necessary.
Conclusion: A Holistic Understanding for Better Management
Adrenal insufficiency, especially primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease), presents a complex array of potential causes. Recognizing these primary etiologies—ranging from autoimmune processes to infections, hemorrhage, inherited disorders, and malignancies—is paramount for timely diagnosis and effective management. A multidisciplinary approach, involving endocrinologists, infectious disease specialists, and other relevant healthcare professionals, is essential in providing comprehensive care and improving the quality of life for individuals with this condition. This detailed exploration aims to equip both healthcare providers and patients with a more comprehensive understanding of adrenal insufficiency, paving the way for improved diagnosis, treatment, and overall patient outcomes. Remember, this information is for educational purposes and should not substitute advice from a healthcare professional. Always consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Term Technological Diffusion Is Defined As
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Best Designed Saw For Cutting Miter Joints Is A
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Best Describes Communication In The United States Today
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Should You Do During An Extrication Procedure
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Do Larry Page And Jessica Jackley Have In Common
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Identify The Primary Causes Of Adrenal Insufficiency Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
