If Fetal Arterial Pressure Begins To Fall Below Normal Levels
Breaking News Today
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
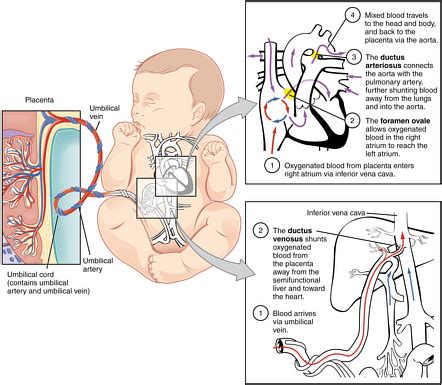
Table of Contents
If Fetal Arterial Pressure Begins to Fall Below Normal Levels: Understanding the Implications and Management
Fetal arterial pressure (FAP) is a crucial indicator of fetal well-being. A drop in FAP below normal levels signifies compromised fetal circulation and can have serious consequences. This article delves deep into the causes, implications, and management strategies related to decreased fetal arterial pressure. We will explore the complexities of fetal hemodynamics and provide a comprehensive overview for healthcare professionals and expectant parents alike.
Understanding Fetal Circulation and Arterial Pressure
Before exploring the implications of low FAP, it's crucial to understand the fundamentals of fetal circulation. Unlike adult circulation, the fetal circulatory system relies on the placenta for oxygen and nutrient exchange. The umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus, while the umbilical arteries return deoxygenated blood to the placenta.
The fetal heart plays a vital role, pumping blood through a unique circulatory pathway. The ductus venosus shunts a portion of the blood from the umbilical vein directly to the inferior vena cava, bypassing the liver. The foramen ovale, an opening between the atria, allows blood to flow directly from the right atrium to the left atrium, further reducing the amount of blood flowing through the pulmonary circulation. The ductus arteriosus shunts blood from the pulmonary artery to the aorta, again bypassing the lungs.
Fetal arterial pressure is a measure of the pressure exerted by the blood within the fetal arteries. Normal FAP varies depending on gestational age and the specific artery being measured (e.g., umbilical artery, descending aorta). However, generally, a sustained decrease in FAP indicates a problem. This decrease reflects a reduction in blood flow and oxygen delivery to vital fetal organs.
Causes of Decreased Fetal Arterial Pressure
Several factors can contribute to a drop in fetal arterial pressure. Identifying the underlying cause is critical for effective management. These causes can be broadly categorized as:
1. Placental Insufficiency:
This is a common cause of low FAP. Placental insufficiency refers to the placenta's inability to adequately deliver oxygen and nutrients to the fetus. This can be caused by various factors, including:
- Maternal hypertension: High blood pressure in the mother restricts blood flow to the placenta.
- Pre-eclampsia: A pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and proteinuria, significantly impacting placental perfusion.
- Chronic diseases: Conditions like diabetes and kidney disease can impair placental function.
- Placental abruption: The premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall.
- Uterine abnormalities: Structural abnormalities in the uterus can compromise placental blood flow.
2. Fetal Factors:
Fetal conditions can also lead to low FAP:
- Fetal growth restriction (FGR): A fetus that is smaller than expected for gestational age often experiences reduced blood flow.
- Fetal anemia: A deficiency of red blood cells reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
- Congenital heart defects: Structural abnormalities in the fetal heart can impair blood flow.
- Fetal infection: Infections like cytomegalovirus or toxoplasmosis can compromise fetal circulation.
- Cord complications: Umbilical cord compression or knots can restrict blood flow to the fetus.
3. Maternal Factors:
Beyond placental issues, maternal conditions can impact FAP:
- Maternal dehydration: Reduced blood volume in the mother decreases blood flow to the placenta.
- Maternal hypotension: Low blood pressure in the mother compromises placental perfusion.
- Severe maternal illness: Any condition that significantly compromises maternal health can affect the fetus.
- Substance abuse: Smoking, alcohol, and drug use can negatively impact fetal development and circulation.
Implications of Low Fetal Arterial Pressure
A sustained decrease in FAP has several serious implications for the fetus:
- Hypoxia: Reduced oxygen levels in the fetal blood can lead to tissue damage and organ dysfunction.
- Acidosis: A buildup of acids in the fetal blood due to impaired oxygen delivery.
- Organ damage: Hypoxia and acidosis can damage vital organs like the brain, heart, and kidneys.
- Fetal distress: The fetus may exhibit signs of distress, such as decelerations in the fetal heart rate.
- Stillbirth or neonatal death: In severe cases, low FAP can lead to fetal demise.
- Long-term neurological consequences: Prolonged hypoxia can result in cerebral palsy and other neurological impairments.
Monitoring Fetal Arterial Pressure
Monitoring FAP is crucial in high-risk pregnancies. Several techniques are used:
- Umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry: This non-invasive technique measures blood flow velocity in the umbilical artery. Changes in waveform characteristics can indicate placental insufficiency.
- Fetal heart rate monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the fetal heart rate can detect signs of fetal distress associated with low FAP.
- Biophysical profile: This comprehensive assessment combines fetal heart rate monitoring, fetal breathing movements, fetal body movements, fetal tone, and amniotic fluid volume to evaluate fetal well-being.
- Amniotic fluid analysis: Analyzing the amniotic fluid can reveal indicators of fetal acidosis or infection.
Management of Low Fetal Arterial Pressure
Management strategies depend on the underlying cause and severity of the decreased FAP. They often involve:
- Close monitoring: Frequent monitoring of fetal well-being through techniques like those listed above is essential.
- Treatment of underlying causes: Addressing the underlying cause, such as managing maternal hypertension or treating an infection, is critical.
- Supportive care: This may involve bed rest, hydration, and oxygen therapy for the mother.
- Medication: Medications may be used to improve placental blood flow or treat specific conditions.
- Early delivery: If the fetus is in severe distress, early delivery may be necessary to prevent further complications.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes
The prognosis for a fetus with low FAP depends on several factors, including the underlying cause, the severity of the pressure drop, and the effectiveness of the management strategies employed. Early detection and intervention significantly improve the chances of a positive outcome. However, even with prompt management, some fetuses may experience long-term neurological or developmental problems.
The Role of Parental Support and Education
Expectant parents play a crucial role in managing pregnancies complicated by low fetal arterial pressure. Understanding the implications of low FAP, actively participating in monitoring appointments, and adhering to the healthcare provider's recommendations are essential. Emotional support is vital for parents during this challenging period.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research focuses on improving the accuracy of FAP monitoring and developing new strategies for managing pregnancies complicated by low fetal arterial pressure. Further investigations into the causes of placental insufficiency and the long-term effects of fetal hypoxia are crucial for improving outcomes.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Approach
Decreased fetal arterial pressure is a serious complication that requires a multidisciplinary approach involving obstetricians, neonatologists, and other healthcare professionals. Early detection, careful monitoring, and prompt management are critical to ensuring the best possible outcome for both the mother and the fetus. This complex issue necessitates a detailed understanding of fetal hemodynamics, potential underlying causes, and the multifaceted strategies required for successful management. Continued research and improved access to advanced monitoring techniques are essential for minimizing the risks associated with low fetal arterial pressure. Open communication and strong collaboration between healthcare providers and expectant parents are crucial in navigating this challenging situation and striving for the best possible outcome for the baby.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Partial Bath Includes Washing A Residents
May 12, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Describes A Net Lease
May 12, 2025
-
Nurse Logic 2 0 Knowledge And Clinical Judgment
May 12, 2025
-
Panic Disorder Is Characterized By All Of The Following Except
May 12, 2025
-
Positive Individual Traits Can Be Taught A True B False
May 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about If Fetal Arterial Pressure Begins To Fall Below Normal Levels . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.