In An Inverted Organization Who Is At The Top
Breaking News Today
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
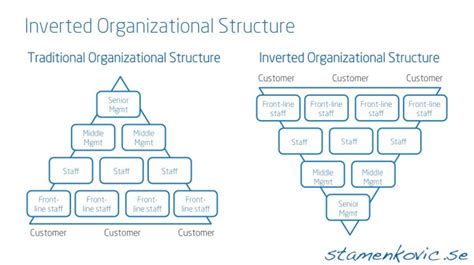
Table of Contents
In an Inverted Organization, Who's Really at the Top? Rethinking Leadership and Hierarchy
The traditional organizational chart, with its hierarchical pyramid, is a familiar sight. The CEO sits at the apex, power flowing downwards through layers of management. But in recent years, a radical alternative has emerged: the inverted organization. This model flips the traditional structure on its head, placing the customer or the frontline employee at the top. This raises a crucial question: if the hierarchy is inverted, who truly holds the power and influence? The answer is complex and multifaceted, requiring a deeper understanding of the principles and dynamics of this unconventional organizational structure.
Understanding the Inverted Organization Structure
Before exploring the question of leadership in an inverted organization, it's crucial to establish a clear understanding of what defines this structure. Unlike the traditional pyramid, an inverted organization prioritizes empowerment and decentralization. The customer or the frontline employee becomes the focal point, with senior management acting as a support system rather than a controlling entity.
Key Characteristics of an Inverted Organization:
- Customer-centricity: The entire organization revolves around meeting customer needs effectively and efficiently.
- Empowered Employees: Frontline employees have significant autonomy and decision-making power. They are encouraged to solve problems and innovate without needing extensive approval from higher levels.
- Decentralized Decision-Making: Decisions are made at the level closest to the problem or opportunity, fostering agility and responsiveness.
- Supportive Leadership: Leaders act as facilitators, mentors, and resource providers, empowering their teams rather than directing them.
- Open Communication: Information flows freely throughout the organization, fostering transparency and collaboration.
- Flatter Hierarchy: The organizational structure is significantly flatter, reducing layers of management and improving communication efficiency.
Who is at the Top in an Inverted Organization? It's Not Who You Think
The question "Who is at the top?" in an inverted organization cannot be answered with a single name or title. It's a fundamental shift in perspective. The traditional notion of a single leader at the apex is replaced by a distributed leadership model. Several key players share the influence and responsibility:
1. The Customer: The Ultimate Authority
In a truly inverted organization, the customer reigns supreme. Their needs, feedback, and satisfaction dictate the organization's direction. Every decision, process, and strategy is ultimately evaluated based on its impact on the customer experience. This isn't just lip service; it's a deeply ingrained cultural principle.
2. The Frontline Employees: The Engine of Innovation
Frontline employees – those who directly interact with customers – are the driving force of the organization. They possess invaluable insights into customer needs, operational challenges, and potential improvements. Empowered to make decisions and take initiative, they become innovators and problem-solvers. Their expertise and experience are highly valued, making them crucial decision-makers in their respective domains.
3. Supportive Leadership: The Enablers of Success
Senior management in an inverted organization plays a crucial, albeit different, role. They are not top-down managers but instead serve as facilitators, coaches, and resource providers. Their primary function is to support and empower frontline employees and ensure they have the resources and tools to excel. They focus on:
- Strategic Vision: Defining the overall direction and goals of the organization.
- Resource Allocation: Ensuring the availability of necessary resources (financial, technological, human) to support employees.
- Removing Obstacles: Identifying and eliminating roadblocks that hinder employee performance.
- Developing Talent: Investing in the growth and development of employees through training and mentorship.
- Building Culture: Fostering a culture of empowerment, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
The Challenges of Implementing an Inverted Organization
While the inverted organization offers many benefits, its implementation presents significant challenges:
1. Cultural Shift: Overcoming Traditional Hierarchies
One of the biggest hurdles is shifting the organizational culture away from traditional hierarchical thinking. Employees accustomed to top-down management may find it challenging to embrace empowerment and autonomy. Building trust and fostering a culture of collaboration is crucial.
2. Empowerment Requires Training and Development:
Empowering employees requires providing them with the necessary skills, knowledge, and tools. Investing in training and development programs is essential to equip them with the capabilities to make informed decisions and solve problems effectively.
3. Measuring Success: Redefining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Traditional KPIs may not be suitable for an inverted organization. Success needs to be measured beyond individual performance and focused on collective achievements, customer satisfaction, and overall organizational effectiveness. New metrics reflecting customer-centricity and employee empowerment need to be developed and implemented.
4. Communication and Collaboration: Maintaining Open Dialogue
Effective communication is vital in an inverted organization. Open dialogue, transparent information sharing, and collaborative problem-solving are essential for maintaining alignment and coordination across the organization. Technology and tools that support seamless communication are important.
The Benefits of an Inverted Organizational Structure
Despite the challenges, the potential benefits of adopting an inverted organizational structure are considerable:
1. Increased Employee Engagement and Morale:
Empowerment and autonomy boost employee morale and engagement. When employees feel valued and trusted, their commitment and productivity improve significantly.
2. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction:
By prioritizing customer needs and empowering employees to address them directly, inverted organizations achieve higher levels of customer satisfaction.
3. Improved Agility and Responsiveness:
Decentralized decision-making enables faster responses to market changes and customer demands, providing a significant competitive advantage.
4. Fostering Innovation and Creativity:
When employees are empowered to think creatively and solve problems independently, innovation flourishes.
5. Stronger Organizational Culture:
Inverted organizations often develop a stronger, more positive organizational culture characterized by trust, collaboration, and mutual respect.
Examples of Inverted Organizations (Illustrative, not endorsements)
While truly inverted organizations are relatively rare, several companies have implemented aspects of this structure, demonstrating its potential. These organizations often highlight employee empowerment, customer-centricity, and flat organizational structures. Many companies use variations of these principles rather than a complete inversion. Researching specific companies' organizational models is encouraged to fully understand their approaches.
Conclusion: A Paradigm Shift in Leadership
The inverted organization represents a significant paradigm shift in how we think about leadership and organizational structure. It's not about eliminating hierarchy entirely, but rather about redefining its purpose and distributing leadership across the organization. While challenges exist, the potential benefits – increased employee engagement, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced agility – make it a compelling model for organizations seeking to thrive in a dynamic and competitive environment. The "top" in an inverted organization is a shared space occupied by the customer and the empowered employee, with supportive leadership facilitating their success. It's a model that prioritizes collaboration, empowerment, and a shared commitment to excellence. The question of "who is at the top" is ultimately answered by acknowledging the collective power and influence driving the organization's success.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Traffic Ticket For Speeding In A Work Zone
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Multinational Corporation Is A Company That Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Force Acting Over A Distance Is The Definition Of Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Information Is Most Important When Passing Near A Lighthouse
Mar 31, 2025
-
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Adhd Is Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In An Inverted Organization Who Is At The Top . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
