Indica El Presente De Estos Verbos Reflexivos.
Breaking News Today
Mar 29, 2025 · 7 min read
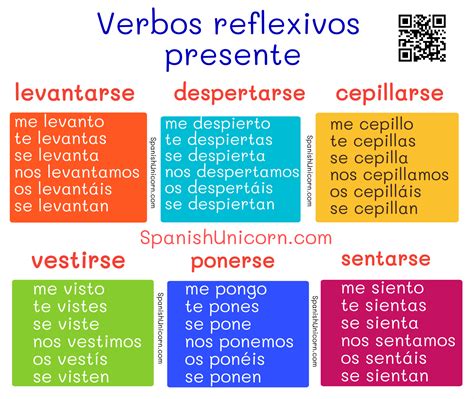
Table of Contents
Conjugating Reflexive Verbs in Spanish: A Comprehensive Guide
Learning Spanish reflexive verbs can seem daunting at first, but with a structured approach, mastering them becomes achievable. This comprehensive guide delves into the present tense conjugation of reflexive verbs, providing you with a clear understanding of their structure, usage, and variations. We will explore various examples, helping you confidently navigate this crucial aspect of Spanish grammar.
Understanding Reflexive Verbs
Reflexive verbs, also known as verbos reflexivos in Spanish, describe actions that the subject performs on themselves. The key characteristic is the use of reflexive pronouns, which indicate that the subject is both the actor and the receiver of the action. These pronouns agree in gender and number with the subject.
The reflexive pronouns are:
- me: myself
- te: yourself (informal singular)
- se: himself, herself, yourself (formal singular), themselves
- nos: ourselves
- os: yourselves (informal plural)
These pronouns are placed before the conjugated verb, similar to object pronouns. However, unlike object pronouns, reflexive pronouns cannot be attached to the infinitive or gerund form of the verb.
Present Tense Conjugation of Reflexive Verbs
The present tense conjugation of reflexive verbs follows a consistent pattern. You take the present tense conjugation of the regular verb and add the appropriate reflexive pronoun. Let's break it down with examples:
Regular -ar Verbs
Let's use the verb lavarse (to wash oneself) as our example. This is formed from the regular -ar verb lavar (to wash).
| Pronoun | Conjugation of Lavar | Reflexive Verb (Lavarse) | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yo (I) | lavo | me lavo | I wash myself |
| Tú (You - informal) | lavas | te lavas | You wash yourself |
| Él/Ella/Usted (He/She/You - formal) | lava | se lava | He/She/You wash himself/herself/yourself |
| Nosotros/Nosotras (We) | lavamos | nos lavamos | We wash ourselves |
| Vosotros/Vosotras (You - informal plural) | laváis | os laváis | You wash yourselves |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes (They/You - formal plural) | lavan | se lavan | They/You wash themselves/yourselves |
Notice that the reflexive pronoun changes depending on the subject pronoun. The verb itself conjugates like a regular -ar verb.
Regular -er Verbs
Let's take the verb peinarse (to comb oneself), derived from the regular -er verb peinar (to comb).
| Pronoun | Conjugation of Peinar | Reflexive Verb (Peinarse) | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yo (I) | peino | me peino | I comb myself |
| Tú (You - informal) | peinas | te peinas | You comb yourself |
| Él/Ella/Usted (He/She/You - formal) | peina | se peina | He/She/You comb himself/herself/yourself |
| Nosotros/Nosotras (We) | peinamos | nos peinamos | We comb ourselves |
| Vosotros/Vosotras (You - informal plural) | peináis | os peináis | You comb yourselves |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes (They/You - formal plural) | peinan | se peinan | They/You comb themselves/yourselves |
The conjugation follows the same principle as with -ar verbs; the reflexive pronoun changes, while the verb conjugates according to the regular -er pattern.
Regular -ir Verbs
Consider the verb dormirse (to fall asleep), derived from the regular -ir verb dormir (to sleep).
| Pronoun | Conjugation of Dormir | Reflexive Verb (Dormirse) | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yo (I) | duermo | me duermo | I fall asleep |
| Tú (You - informal) | duermes | te duermes | You fall asleep |
| Él/Ella/Usted (He/She/You - formal) | duerme | se duerme | He/She/You falls asleep |
| Nosotros/Nosotras (We) | dormimos | nos dormimos | We fall asleep |
| Vosotros/Vosotras (You - informal plural) | dormís | os dormís | You fall asleep |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes (They/You - formal plural) | duermen | se duermen | They/You fall asleep |
Again, the same principle applies: the reflexive pronoun adapts to the subject, and the verb conjugates according to the regular -ir pattern.
Irregular Reflexive Verbs
Not all reflexive verbs follow these regular patterns. Many common verbs have irregular conjugations in the present tense. Mastering these irregularities is crucial for fluent Spanish. Let's examine a few:
irse (to go away)
This is an irregular reflexive verb derived from ir (to go).
| Pronoun | Conjugation of Ir | Reflexive Verb (Irse) | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yo (I) | voy | me voy | I go away |
| Tú (You - informal) | vas | te vas | You go away |
| Él/Ella/Usted (He/She/You - formal) | va | se va | He/She/You goes away |
| Nosotros/Nosotras (We) | vamos | nos vamos | We go away |
| Vosotros/Vosotras (You - informal plural) | vais | os vais | You go away |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes (They/You - formal plural) | van | se van | They/You go away |
Notice the significant irregularity in the conjugation of ir.
acordarse (to remember)
This reflexive verb, meaning "to remember," is derived from acordar (to agree), but its conjugation is irregular.
| Pronoun | Conjugation of Acordar (irregular) | Reflexive Verb (Acordarse) | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yo (I) | acuerdo | me acuerdo | I remember |
| Tú (You - informal) | acuerdas | te acuerdas | You remember |
| Él/Ella/Usted (He/She/You - formal) | acuerda | se acuerda | He/She/You remembers |
| Nosotros/Nosotras (We) | acordamos | nos acordamos | We remember |
| Vosotros/Vosotras (You - informal plural) | acordáis | os acordáis | You remember |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes (They/You - formal plural) | acuerdan | se acuerdan | They/You remember |
quejarse (to complain)
The verb quejarse (to complain) also showcases irregular conjugation patterns.
| Pronoun | Reflexive Verb (Quejarse) | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo (I) | me quejo | I complain |
| Tú (You - informal) | te quejas | You complain |
| Él/Ella/Usted (He/She/You - formal) | se queja | He/She/You complains |
| Nosotros/Nosotras (We) | nos quejamos | We complain |
| Vosotros/Vosotras (You - informal plural) | os quejáis | You complain |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes (They/You - formal plural) | se quejan | They/You complain |
These are just a few examples; many other reflexive verbs exhibit irregular conjugation patterns. It's essential to consult a comprehensive Spanish verb conjugation chart or dictionary to handle these effectively.
Placement of Reflexive Pronouns
The placement of reflexive pronouns is crucial. They typically precede the conjugated verb. However, there are exceptions, particularly with infinitives and gerunds.
-
Before conjugated verbs: This is the standard placement. For example: Ella se lava las manos. (She washes her hands.)
-
Attached to the infinitive: Reflexive pronouns cannot be attached to an infinitive, although they will come before it. For example: Quiero lavarme las manos. (I want to wash my hands.) Not: Quiero me lavar las manos.
-
Attached to the gerund: Similar to infinitives, they precede the gerund. For example: Está lavándose las manos. (He is washing his hands.) Not: Está se lavando las manos.
Understanding these placements prevents grammatical errors and ensures clear communication.
Using Reflexive Verbs Effectively
Mastering reflexive verbs isn't just about conjugation; it's about understanding their nuanced usage in context. Many verbs that are reflexive in Spanish are not necessarily reflexive in English. For instance:
-
Levantar(se): Levantar means "to lift," while levantarse means "to get up." The English equivalent isn't reflexive.
-
Vestir(se): Vestir means "to dress," and vestirse means "to get dressed." Again, a non-reflexive equivalent in English.
-
Bañar(se): Bañar means "to bathe (something)," while bañarse means "to bathe oneself" or "to take a bath."
Paying close attention to context and the specific meaning of each verb will help you use reflexive verbs correctly and naturally.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Reflexive Verbs
Conjugating reflexive verbs in Spanish involves understanding the interplay of reflexive pronouns and verb conjugations. While regular verbs follow predictable patterns, irregular verbs require focused attention and memorization. Through consistent practice and careful observation of usage, you can confidently incorporate these essential verbs into your Spanish vocabulary and conversation, enriching your understanding and fluency in the language. Remember to practice regularly, utilize resources like verb conjugation charts and dictionaries, and don't be afraid to immerse yourself in authentic Spanish materials to internalize these grammatical structures. With dedication, you will master the intricacies of reflexive verbs and elevate your Spanish proficiency to new heights.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Apes Unit 6 Progress Check Mcq Part A
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Project Network Provides The Basis For
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Food Safety Policy Is A Statement
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Cooking Company Wants To Identify A Target Market
Apr 01, 2025
-
Plants In The Rainforest Contribute To Precipitation There Through Transpiration
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Indica El Presente De Estos Verbos Reflexivos. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
