Like Electric Charges Repel Each Other. True Or False
Breaking News Today
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
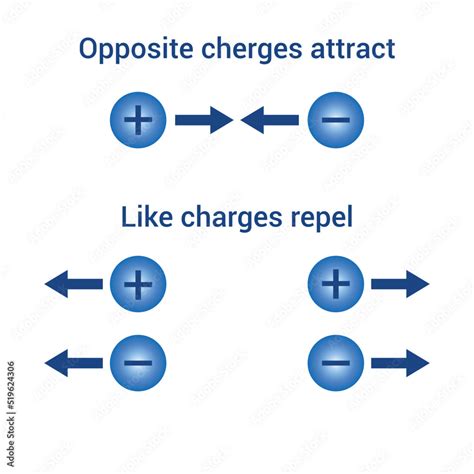
Table of Contents
- Like Electric Charges Repel Each Other. True Or False
- Table of Contents
- Like Electric Charges Repel Each Other: True or False? A Deep Dive into Electrostatics
- Understanding Electric Charge
- The Role of Protons and Electrons
- Conductors and Insulators
- Coulomb's Law: Quantifying Electric Force
- The Significance of the Equation
- Repulsion of Like Charges: A Detailed Explanation
- Microscopic Explanation
- Visualizing the Repulsion
- Real-World Examples of Like-Charge Repulsion
- Debunking Misconceptions
- Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Like-Charge Repulsion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Like Electric Charges Repel Each Other: True or False? A Deep Dive into Electrostatics
The statement "like electric charges repel each other" is unequivocally true. This fundamental principle of electrostatics governs a vast array of phenomena, from the behavior of everyday objects to the workings of complex technological devices. Understanding this principle is crucial for grasping the nature of electricity and its impact on our world. This article will delve into the intricacies of this principle, exploring its underlying mechanisms, providing real-world examples, and debunking any misconceptions.
Understanding Electric Charge
Before delving into the repulsion of like charges, it's essential to understand the concept of electric charge itself. Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter, much like mass. It exists in two forms: positive and negative. These charges aren't just labels; they represent distinct physical properties that interact with each other in predictable ways. The existence of these two types of charge is a key component of Coulomb's Law, which we will discuss later.
The Role of Protons and Electrons
At the atomic level, positive charge is carried by protons, located within the nucleus of an atom, while negative charge is carried by electrons, orbiting the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number and its identity as a particular element. Normally, an atom has an equal number of protons and electrons, resulting in a net charge of zero – it's electrically neutral. However, atoms can gain or lose electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge, forming what are known as ions. This imbalance in charge is the foundation of electrostatic interactions.
Conductors and Insulators
The ability of a material to allow the flow of electric charge determines whether it is a conductor or an insulator. Conductors, such as metals, readily allow electrons to move freely throughout their structure. Insulators, like rubber or glass, strongly resist the flow of electrons. This difference in conductivity significantly influences how materials behave in the presence of electric charges.
Coulomb's Law: Quantifying Electric Force
The force between charged objects is precisely described by Coulomb's Law. This law states that the force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their magnitudes and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Mathematically:
F = k * |q1 * q2| / r²
Where:
- F is the electrostatic force
- k is Coulomb's constant (a proportionality constant)
- q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the two charges
- r is the distance between the charges
The Significance of the Equation
This equation reveals several critical aspects of electrostatic interactions:
- Magnitude: The force is directly proportional to the product of the charges. Larger charges result in a stronger force.
- Distance: The force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. As the distance increases, the force decreases rapidly.
- Sign: The equation includes an absolute value, indicating that the force is always attractive or repulsive regardless of the sign, while the sign of the charges dictates whether the force is attractive or repulsive.
Repulsion of Like Charges: A Detailed Explanation
Now, let's specifically address the repulsion of like charges. When two objects with the same type of charge (both positive or both negative) are brought near each other, they experience a repulsive force. This repulsion is a direct consequence of Coulomb's Law. Since both charges have the same sign, the product q1 * q2 will be positive, leading to a positive force – a repulsive force.
Microscopic Explanation
At the microscopic level, this repulsion arises from the interaction of the fundamental charged particles within the objects. For example, if two negatively charged objects approach, their excess electrons repel each other due to their like charges. These electrons exert forces on each other, which ultimately manifest as a macroscopic repulsive force between the objects. Similarly, two positively charged objects would repel because of the mutual repulsion between their excess protons (though in practice, we generally deal with the movement of electrons rather than protons).
Visualizing the Repulsion
Imagine two balloons rubbed against your hair, acquiring a negative charge. When you bring them close together, they will push each other away. This is a clear demonstration of the repulsive force between like charges. The force is strong enough to overcome gravity and cause the balloons to visibly repel.
Real-World Examples of Like-Charge Repulsion
The repulsion of like charges isn't just a theoretical concept; it's a fundamental principle underlying numerous natural phenomena and technological applications:
-
Lightning: The build-up of like charges within a cloud (and between a cloud and the ground) can lead to a massive discharge of electricity – lightning. The immense repulsive force between these concentrated charges overcomes the air's insulating properties, resulting in a spectacular and potentially dangerous event.
-
Electrostatic Precipitators: These devices utilize the repulsion of like charges to remove pollutants from industrial exhaust gases. The pollutants are given a charge, and then they are repelled by a similarly charged electrode, effectively separating them from the clean gas stream.
-
Xerography (Photocopying): The process of photocopying relies heavily on electrostatic principles, including the repulsion of like charges. The charged toner particles are repelled by similarly charged areas on the drum, allowing for precise image formation.
-
Inkjet Printers: Inkjet printers use the principle of electrostatic repulsion to direct tiny droplets of ink onto the paper. The ink droplets are charged, and then deflected using charged plates to achieve precise placement.
-
Van de Graaff Generator: This device uses a moving belt to accumulate a large static charge on a metal dome. If you touch the dome, your hair will stand on end due to the repulsion between the like charges on your hair and the dome.
Debunking Misconceptions
Despite the clear evidence and established principles, some misconceptions about like-charge repulsion persist. It's important to address these to ensure a comprehensive understanding.
-
"Attraction always happens": Some people wrongly believe that all electric charges attract each other. This is inaccurate. Only opposite charges attract; like charges always repel.
-
"Only large charges repel": Repulsion occurs between any two like charges, regardless of their magnitude. While the force is weaker with smaller charges, the repulsive effect is still present.
-
"Repulsion only happens in a vacuum": The repulsive force between like charges exists in any medium, although the strength of the force might be affected by the medium's dielectric constant (a measure of how easily a material can be polarized).
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Like-Charge Repulsion
The principle that like electric charges repel each other is a cornerstone of electrostatics. It's not merely a theoretical concept confined to textbooks; it is a fundamental force shaping our world, influencing everything from the weather to the technology we use daily. A solid grasp of this principle, coupled with an understanding of Coulomb's Law, is crucial for comprehending the behavior of electricity and its countless applications. From the spectacular display of a lightning storm to the precise printing of a document, the repulsive force between like charges plays a vital role. By understanding this fundamental interaction, we gain a deeper appreciation for the elegance and power of the physical world. Further exploration into the related concepts of electric fields, potential, and capacitance can provide even deeper insights into this fascinating area of physics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Ati Capstone Leadership And Community Health Assessment Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Medication Is Indicated For Treating Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Extremism In The Defense Of Liberty Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Ati Pharmacology Made Easy 5 0 Infection Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Leading Risk Factor For Suicide Is Qpr Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Like Electric Charges Repel Each Other. True Or False . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
