Match The Hormone Abbreviations With Their Function
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
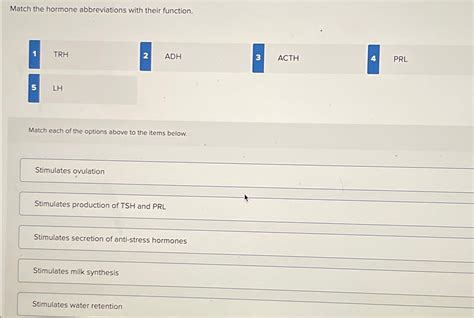
Table of Contents
Matching Hormone Abbreviations with Their Functions: A Comprehensive Guide
Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate various bodily functions. Understanding their abbreviations and functions is crucial for comprehending human physiology and various health conditions. This comprehensive guide aims to clarify the roles of key hormones, matching their abbreviations with their respective functions. We'll delve into the intricacies of endocrine system regulation and explore the implications of hormonal imbalances.
Understanding Hormone Abbreviations and Functions
Before diving into specifics, let's establish a foundational understanding. Hormones are secreted by glands and travel through the bloodstream to target cells, influencing metabolism, growth, reproduction, mood, and more. Abbreviations are used for brevity and convenience in medical and scientific literature. Misunderstanding these abbreviations can lead to confusion, so mastering them is essential.
Key to Understanding: This article focuses on common hormone abbreviations and their primary functions. The complexity of the endocrine system necessitates a simplified approach; the functions listed are not exhaustive, and some hormones play multiple roles depending on context and interaction with other hormones.
Major Hormone Groups and Their Functions
We'll categorize hormones into major groups to enhance understanding. Each section will detail specific hormones, their abbreviations, and their critical functions.
1. Pituitary Hormones: The Master Gland's Messengers
The pituitary gland, often called the "master gland," regulates many other endocrine glands. Its hormones are crucial for growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
- GH (Growth Hormone): Promotes growth and cell reproduction. Deficiency can lead to dwarfism, while excess can cause gigantism or acromegaly.
- TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone): Stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). Imbalances can cause hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
- ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone): Stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce cortisol and other corticosteroids. Plays a vital role in stress response.
- FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone): In women, stimulates follicle development in the ovaries and estrogen production. In men, stimulates sperm production in the testes.
- LH (Luteinizing Hormone): In women, triggers ovulation and progesterone production. In men, stimulates testosterone production.
- PRL (Prolactin): Stimulates milk production in mammary glands after childbirth. Also plays a role in immune function and other processes.
- ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone or Vasopressin): Regulates water balance by increasing water reabsorption in the kidneys. Plays a crucial role in maintaining blood pressure.
- Oxytocin: Stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and milk ejection during breastfeeding. Also involved in social bonding and emotional attachment.
2. Thyroid Hormones: Metabolism Regulators
The thyroid gland produces hormones crucial for metabolism, growth, and development.
- T3 (Triiodothyronine): A more active thyroid hormone, regulating metabolic rate, growth, and development.
- T4 (Thyroxine): A less active form of thyroid hormone, converted to T3 in the tissues. Plays a significant role in maintaining metabolic processes.
- Calcitonin: Lowers blood calcium levels by promoting calcium deposition in bones. Works antagonistically with parathyroid hormone.
3. Parathyroid Hormones: Calcium Regulators
The parathyroid glands produce a hormone essential for calcium homeostasis.
- PTH (Parathyroid Hormone): Raises blood calcium levels by promoting calcium release from bones and increasing calcium absorption in the intestines. Antagonistic to calcitonin.
4. Adrenal Hormones: Stress Response and More
The adrenal glands produce a variety of hormones essential for stress response, metabolism, and electrolyte balance.
- Cortisol: A glucocorticoid hormone; critical for stress response, glucose metabolism, and immune function. Chronic excess can have detrimental effects.
- Aldosterone: A mineralocorticoid hormone; regulates sodium and potassium balance, influencing blood pressure and fluid volume.
- Epinephrine (Adrenaline) & Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline): Catecholamines; crucial for "fight-or-flight" response, increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and alertness.
5. Pancreatic Hormones: Blood Sugar Control
The pancreas produces hormones vital for blood sugar regulation.
- Insulin: Lowers blood glucose levels by facilitating glucose uptake into cells. Deficiency leads to diabetes mellitus.
- Glucagon: Raises blood glucose levels by stimulating glycogen breakdown in the liver. Works antagonistically with insulin.
6. Gonadal Hormones: Reproductive Functions
The gonads (ovaries in females and testes in males) produce hormones essential for sexual development and reproduction.
- Estrogen (Estradiol, Estrone, Estriol): Primary female sex hormones; involved in sexual development, reproduction, and bone health.
- Progesterone: A female sex hormone; prepares the uterus for pregnancy and supports pregnancy.
- Testosterone: Primary male sex hormone; responsible for sexual development, muscle growth, and libido.
7. Pineal Hormone: Circadian Rhythm Regulation
The pineal gland produces a hormone crucial for regulating sleep-wake cycles.
- Melatonin: Regulates sleep-wake cycles (circadian rhythm). Production is influenced by light exposure.
Hormonal Imbalances and Their Implications
Understanding hormone abbreviations and functions is crucial for recognizing and managing hormonal imbalances. These imbalances can manifest in various ways, depending on the affected hormone and the severity of the imbalance.
For example, hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone levels) can cause fatigue, weight gain, and depression. Hyperthyroidism (high thyroid hormone levels) can lead to anxiety, weight loss, and rapid heartbeat. Similarly, insulin deficiency results in diabetes mellitus, characterized by high blood sugar levels. Cortisol excess (Cushing's syndrome) can cause weight gain, high blood pressure, and impaired immune function.
The impact of hormonal imbalances emphasizes the importance of regular health check-ups and seeking medical attention when experiencing symptoms suggestive of hormonal dysfunction.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments
Diagnosing hormonal imbalances often involves blood tests to measure hormone levels. Additional tests may be necessary depending on the suspected condition. Treatments vary depending on the specific hormone and the nature of the imbalance. They can range from lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise) to medication, hormone replacement therapy, or surgery.
Conclusion: Mastering Hormonal Knowledge
Mastering the abbreviations and functions of key hormones is crucial for understanding human physiology and various health conditions. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of major hormone groups and their roles. However, it’s essential to remember that this is a simplified representation of a complex system, and individual hormone actions can be nuanced and influenced by interactions with other hormones and factors. Always consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnoses and appropriate treatment plans related to hormonal health. Further research and consultation with medical professionals are strongly recommended for a more thorough understanding. This information is intended for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Exercise 40 Review Sheet Art Labeling Activity 1
May 09, 2025
-
Power Cords Can Be Damaged By Which Of The Following
May 09, 2025
-
Which Settlement Option Pays A Stated Amount To An Annuitant
May 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Potential Energy
May 09, 2025
-
Which Gland Is Not Matched With Its Type Of Secretion
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Match The Hormone Abbreviations With Their Function . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.