Match The Term With Its Correct Description
Breaking News Today
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
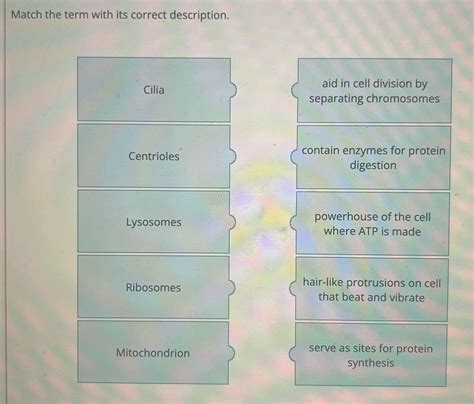
Table of Contents
Match the Term with its Correct Description: A Comprehensive Guide to Key Concepts
Matching terms with their correct descriptions is a fundamental skill across numerous disciplines. Whether you're studying for an exam, working on a research project, or simply expanding your knowledge, understanding the nuances of different concepts is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into various fields, providing clear explanations and examples to help you accurately match terms with their descriptions. We’ll cover a range of topics, ensuring a robust understanding of key concepts across disciplines. This guide aims to not only help you match terms but also deepen your overall comprehension of each subject.
Science and Technology
This section will explore terms commonly encountered in science and technology fields, pairing each with its accurate definition and providing illustrative examples.
Physics
-
Term: Newton's Third Law of Motion
- Description: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object simultaneously exerts a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction on the first object. Example: When you jump, you push down on the Earth, and the Earth pushes back up on you with an equal and opposite force, propelling you upwards.
-
Term: Inertia
- Description: The tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion. An object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Example: A book resting on a table will remain at rest unless someone picks it up. A hockey puck sliding on frictionless ice will continue to slide indefinitely.
-
Term: Gravity
- Description: The force of attraction between any two objects with mass. The more massive the objects, and the closer they are, the stronger the gravitational force between them. Example: The Earth's gravity pulls everything towards its center, keeping us grounded. The Moon's gravity influences the Earth's tides.
-
Term: Kinetic Energy
- Description: The energy an object possesses due to its motion. The faster an object moves, and the more massive it is, the greater its kinetic energy. Example: A speeding car possesses significant kinetic energy, which is why it's dangerous to collide with it.
-
Term: Potential Energy
- Description: Stored energy that has the potential to be converted into kinetic energy. This often relates to an object's position or state. Example: A ball held high above the ground has potential energy due to its height. This potential energy converts to kinetic energy as it falls.
Biology
-
Term: Photosynthesis
- Description: The process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll. Example: Plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose (a sugar) and oxygen.
-
Term: Cellular Respiration
- Description: The process by which cells break down glucose and other food molecules to release energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Example: This process occurs in the mitochondria and provides energy for cellular processes.
-
Term: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
- Description: A self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information. Example: DNA determines an organism's traits, from eye color to susceptibility to certain diseases.
-
Term: Natural Selection
- Description: The process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring. Example: The development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria is a prime example of natural selection.
-
Term: Meiosis
- Description: A type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes. Example: This process is crucial for sexual reproduction, ensuring genetic diversity.
Chemistry
-
Term: Atom
- Description: The basic unit of a chemical element. Example: Hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon are all examples of atoms.
-
Term: Molecule
- Description: A group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction. Example: Water (H₂O) is a molecule composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
-
Term: Chemical Reaction
- Description: A process that involves rearrangement of the molecular or ionic structure of a substance, as opposed to a change in physical form or a nuclear reaction. Example: Burning wood is a chemical reaction where wood combines with oxygen to produce ash, carbon dioxide, and water.
-
Term: pH Scale
- Description: A measure of how acidic or basic a solution is. The scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Values below 7 indicate acidity, and values above 7 indicate basicity (alkalinity). Example: Lemon juice has a low pH (acidic), while baking soda has a high pH (basic).
-
Term: Molar Mass
- Description: The mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is a unit of measurement representing Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10²³) of particles. Example: The molar mass of water (H₂O) is approximately 18 grams per mole.
Social Sciences
This section explores crucial terms within the social sciences, ensuring accurate matching with their descriptions and providing insightful examples.
Psychology
-
Term: Cognitive Dissonance
- Description: The mental discomfort experienced by a person who holds two or more contradictory beliefs, ideas, or values. Example: Smoking despite knowing it causes cancer creates cognitive dissonance.
-
Term: Classical Conditioning
- Description: A learning process that occurs through associations between an environmental stimulus and a naturally occurring stimulus. Example: Pavlov's dogs associating the bell with food.
-
Term: Operant Conditioning
- Description: A learning process through which the strength of a behavior is modified by reward or punishment. Example: A child learning to clean their room after receiving praise.
-
Term: Bystander Effect
- Description: The phenomenon where individuals are less likely to offer help to a victim when other people are present. Example: Multiple witnesses to an emergency may each assume someone else will intervene.
-
Term: Confirmation Bias
- Description: The tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or values. Example: Only reading news articles that align with one's political viewpoints.
Sociology
-
Term: Social Stratification
- Description: A system by which a society ranks categories of people in a hierarchy. Example: Social classes based on wealth, power, and prestige.
-
Term: Socialization
- Description: The lifelong process of inheriting and disseminating norms, customs, values, and ideologies, providing an individual with the skills and habits necessary for participating within his or her own society. Example: Learning societal norms and expectations from family, peers, and institutions.
-
Term: Cultural Relativism
- Description: The principle of understanding other cultures on their own terms, rather than judging them based on one's own cultural standards. Example: Recognizing that certain practices considered taboo in one culture may be acceptable in another.
-
Term: Social Deviance
- Description: Behavior that violates significant social norms and expectations. Example: Crime, substance abuse, and public nudity.
-
Term: Cultural Diffusion
- Description: The spread of cultural beliefs and social activities from one group to another. Example: The spread of food, clothing styles, and music across cultures.
Conclusion
Matching terms with their descriptions requires a thorough understanding of the underlying concepts. This comprehensive guide has covered a broad range of disciplines, providing clear explanations and illustrative examples. Remember that consistent study and practice are key to mastering this fundamental skill. By actively engaging with the material and applying the concepts to real-world scenarios, you can strengthen your understanding and build a robust knowledge base across various fields. This will not only improve your ability to match terms accurately but also deepen your overall understanding of the world around you. Remember to always seek additional resources and expand your learning beyond this guide to further enhance your knowledge.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Three Legal Considerations In The Supervisory Relationship Are
Apr 02, 2025
-
Who Is Liable When An Insured Suffers A Loss
Apr 02, 2025
-
The San Andreas Fault In California Is An Example Of
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Best Characterizes Ferromagnesian Silicates
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Last Common Ancestor Of All Animals Was Probably A
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Match The Term With Its Correct Description . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
