Motor Nerve Neuropathy Is Characterized By Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 7 min read
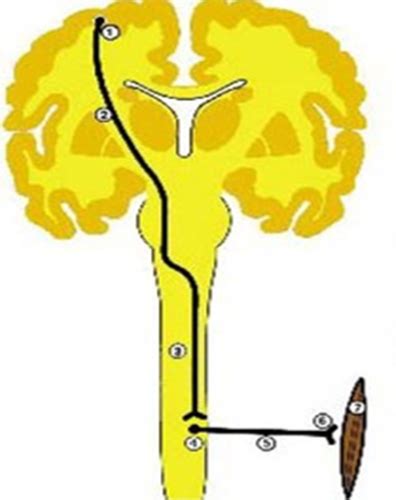
Table of Contents
Motor Nerve Neuropathy: A Comprehensive Overview
Motor nerve neuropathy, also known as motor neuronopathy, is a debilitating neurological condition characterized by damage to the motor nerves. These nerves transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, controlling voluntary movement. When these nerves are damaged, the muscles they innervate weaken, leading to a range of symptoms and significant functional limitations. This comprehensive guide delves into the characteristics of motor nerve neuropathy, providing a detailed explanation suitable for educational purposes, exceeding the typical scope of a simple quizlet definition.
Understanding the Basics: What are Motor Nerves and Neuropathy?
Before exploring the specifics of motor nerve neuropathy, it's crucial to understand the fundamental components involved:
Motor Nerves:
These specialized nerves are the communication highways between the central nervous system (CNS) – the brain and spinal cord – and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), specifically the skeletal muscles responsible for movement. They carry electrical signals, or impulses, that trigger muscle contraction, allowing us to perform actions like walking, talking, and writing. The health of these motor nerves is paramount for maintaining normal muscle function.
Neuropathy:
Neuropathy is a broad term referring to damage or dysfunction of the nerves. It encompasses a variety of conditions affecting different types of nerves – sensory nerves (responsible for sensations like touch, temperature, and pain), autonomic nerves (controlling involuntary functions like heart rate and digestion), and motor nerves (as discussed above). The damage can be due to numerous underlying causes, ranging from metabolic disorders to autoimmune diseases and injuries.
Motor Nerve Neuropathy: The Specifics
Motor nerve neuropathy focuses specifically on the damage to motor nerves. This damage interferes with the transmission of nerve impulses to muscles, leading to muscle weakness, atrophy (wasting away), and potentially paralysis. The severity and progression of the condition vary greatly depending on the underlying cause and the extent of nerve damage.
Causes of Motor Nerve Neuropathy: A Diverse Spectrum
The etiology of motor nerve neuropathy is remarkably diverse, encompassing a vast array of potential causes. Understanding these causes is critical for effective diagnosis and management.
Inherited (Genetic) Conditions:
Several genetic disorders can lead to motor nerve neuropathy. These inherited conditions often manifest early in life and progressively worsen over time. Examples include:
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT): This is the most common inherited neuropathy, characterized by progressive muscle weakness and atrophy, primarily affecting the distal limbs (hands and feet). Several subtypes of CMT exist, each with varying degrees of severity.
- Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA): This group of genetic disorders affects motor neurons in the spinal cord, leading to progressive muscle weakness and atrophy. SMA is classified into different types, with type I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease) being the most severe, often resulting in death in early childhood.
Acquired Conditions:
Many acquired conditions can damage motor nerves, often affecting individuals later in life. These include:
- Diabetes: Diabetic neuropathy is a prevalent complication of diabetes, affecting both sensory and motor nerves. High blood sugar levels damage nerve fibers, leading to a range of neurological symptoms.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) and myasthenia gravis can cause inflammation and damage to motor nerves. GBS is characterized by rapidly progressive muscle weakness, while myasthenia gravis involves fluctuating muscle weakness and fatigue.
- Infections: Certain viral or bacterial infections can trigger nerve damage, leading to motor neuropathy.
- Toxins: Exposure to heavy metals (e.g., lead, mercury), certain drugs, or industrial chemicals can damage motor nerves. Alcohol abuse is also a significant risk factor.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins like B1 (thiamine), B6 (pyridoxine), and B12 (cobalamin) can disrupt nerve function and contribute to motor neuropathy.
- Trauma: Physical injuries, such as nerve compression or crush injuries, can cause direct damage to motor nerves.
- Tumors: Tumors can compress or invade motor nerves, leading to weakness and other neurological symptoms.
Symptoms of Motor Nerve Neuropathy: A Varied Presentation
The symptoms of motor nerve neuropathy can vary widely depending on the underlying cause, the extent of nerve damage, and the specific nerves affected. However, some common symptoms include:
- Muscle Weakness: This is a hallmark symptom, often starting in the distal limbs (hands and feet) and gradually progressing proximally (toward the trunk).
- Muscle Atrophy: As the muscles are deprived of proper nerve stimulation, they begin to waste away, becoming smaller and weaker.
- Muscle Cramps: Painful muscle spasms are common, often occurring at night or after exertion.
- Fasciculations: These are spontaneous, involuntary twitching of muscle fibers. They are visible beneath the skin and can be quite noticeable.
- Muscle Twitching: Similar to fasciculations, but often more pronounced and less localized.
- Loss of Reflexes: The deep tendon reflexes (e.g., knee-jerk reflex) may be diminished or absent.
- Foot Drop: Weakness of the muscles that lift the foot can lead to dragging of the foot during walking.
- Difficulty with Fine Motor Skills: Tasks requiring dexterity, such as buttoning clothes or writing, become challenging.
- Difficulty with Gait (Walking): Walking may become unsteady or impaired due to muscle weakness and loss of coordination.
- Paralysis: In severe cases, paralysis (complete loss of muscle function) may occur.
- Pain: While not always present, pain can be a significant symptom, particularly in cases of diabetic neuropathy.
Diagnosis of Motor Nerve Neuropathy: A Multifaceted Approach
Diagnosing motor nerve neuropathy involves a combination of techniques aimed at identifying the underlying cause and the extent of nerve damage. Key diagnostic procedures include:
- Detailed Medical History and Physical Examination: A thorough review of the patient's medical history, family history, and lifestyle factors, combined with a neurological examination to assess muscle strength, reflexes, and sensory function.
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): This test measures the speed and amplitude of electrical signals traveling along nerves. Slowed conduction speeds and reduced amplitudes indicate nerve damage.
- Electromyography (EMG): This test assesses the electrical activity of muscles. EMG can detect problems with muscle fibers and the communication between nerves and muscles.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify underlying metabolic disorders, infections, or autoimmune diseases that may be contributing to the neuropathy.
- Genetic Testing: If an inherited condition is suspected, genetic testing can be used to confirm the diagnosis.
- Nerve Biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of nerve tissue may be taken for microscopic examination. This is less commonly used due to the invasiveness of the procedure.
- Imaging Studies (MRI, CT): These techniques may be used to identify tumors, compression of nerves, or other structural abnormalities that could be causing the neuropathy.
Treatment of Motor Nerve Neuropathy: Managing Symptoms and Underlying Causes
The treatment of motor nerve neuropathy depends heavily on the underlying cause. Treatment strategies aim to manage symptoms, prevent further nerve damage, and address any underlying medical conditions.
Treating the Underlying Cause:
This is the cornerstone of effective management. For example, managing blood sugar levels in diabetic neuropathy is crucial. Similarly, treating autoimmune diseases with appropriate medications is essential.
Medications:
A range of medications may be used to alleviate symptoms, including:
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications can help manage pain.
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: These medications can reduce inflammation and swelling in nerves.
- Immunosuppressants: Used in autoimmune neuropathies to suppress the immune system's attack on nerves.
- Gabapentinoids: These medications can help manage neuropathic pain.
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy plays a vital role in improving muscle strength, range of motion, and functional abilities. Exercises designed to strengthen muscles, improve coordination, and maintain mobility are essential.
Occupational Therapy:
Occupational therapy helps patients adapt to their functional limitations and perform activities of daily living more efficiently. Adaptive devices and techniques may be employed to enhance independence.
Supportive Care:
This includes managing symptoms like pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances, ensuring proper nutrition, and addressing any psychosocial issues associated with the condition.
Prognosis and Outlook: Navigating the Long-Term Implications
The prognosis for motor nerve neuropathy varies considerably depending on the underlying cause, the severity of the nerve damage, and the individual's response to treatment. Some conditions are progressive, leading to gradual worsening of symptoms over time, while others may be stable or even improve with treatment. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are critical for improving the prognosis and enhancing the quality of life.
Regular medical checkups, adherence to prescribed medications, consistent physical and occupational therapy, and adopting healthy lifestyle choices are crucial for managing the condition effectively and preventing further complications. Support groups and counseling can also provide valuable emotional support and practical advice for navigating the challenges of living with motor nerve neuropathy.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Managing Motor Nerve Neuropathy
Motor nerve neuropathy is a complex neurological condition with a wide spectrum of causes and clinical presentations. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, recognizing the diverse range of symptoms, and employing a comprehensive diagnostic and management approach are critical for improving outcomes. This necessitates a collaborative effort involving medical professionals, therapists, and the individual experiencing the condition. By embracing a holistic approach, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms, enhance their quality of life, and navigate the long-term implications of this challenging neurological disorder.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Shows A Presidents Involvement In Civic Life
May 09, 2025
-
Connections Among Computers To Facilitate Communication And Sharing Of Resources
May 09, 2025
-
What Is A Chafing Block Designed To Do
May 09, 2025
-
The Basic Approaches To Cleaning Contaminated Soil Include
May 09, 2025
-
When Does A Health Insurance Policy Typically Become Effective
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Motor Nerve Neuropathy Is Characterized By Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.