Neuropathy In Patients With Diabetes Is Caused By Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 7 min read
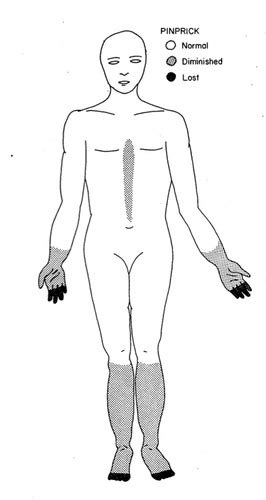
Table of Contents
Neuropathy in Patients with Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, significantly increases the risk of developing neuropathy. This article delves into the intricate relationship between diabetes and neuropathy, exploring the underlying causes, diverse symptoms, and available management strategies. Understanding this complex interplay is crucial for effective prevention and treatment, ultimately improving the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
The Link Between Diabetes and Neuropathy: A Deeper Dive
Neuropathy, encompassing a range of nerve disorders, manifests as damage to the peripheral nerves, impacting sensation, movement, and autonomic functions. In patients with diabetes, this nerve damage, often termed diabetic neuropathy, is a significant complication stemming from the prolonged exposure of nerves to high blood glucose levels. Hyperglycemia, the hallmark of diabetes, initiates a cascade of harmful processes that damage nerve cells.
Mechanisms of Diabetic Neuropathy: Unraveling the Complexity
Several mechanisms contribute to the development of diabetic neuropathy:
-
Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs): High blood glucose levels promote the formation of AGEs, which bind to nerve proteins, causing structural and functional alterations. These AGEs contribute to nerve cell damage and impaired nerve function.
-
Increased Oxidative Stress: Hyperglycemia leads to increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), causing oxidative stress that damages nerve cells and their supporting structures (myelin sheath). This oxidative damage further impairs nerve function and can lead to nerve degeneration.
-
Vascular Dysfunction: Diabetes-related vascular complications affect nerve blood supply. Reduced blood flow deprives nerves of essential nutrients and oxygen, contributing to nerve ischemia and damage. This is often termed ischemic neuropathy.
-
Activation of Inflammatory Pathways: Hyperglycemia triggers inflammation, contributing to nerve damage. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, released in response to hyperglycemia, damage nerve cells and their myelin sheaths.
-
Changes in Nerve Metabolism: Hyperglycemia alters nerve metabolism, disrupting crucial processes such as nerve conduction and signal transmission. This metabolic dysfunction contributes to impaired nerve function and the development of neuropathic symptoms.
Understanding these intricate mechanisms is critical for developing effective therapeutic strategies that target the underlying causes of diabetic neuropathy.
Types of Diabetic Neuropathy: A Spectrum of Manifestations
Diabetic neuropathy manifests in various forms, each impacting different parts of the nervous system and presenting unique symptoms:
1. Peripheral Neuropathy: The Most Common Type
Peripheral neuropathy is the most prevalent type of diabetic neuropathy, affecting the nerves in the hands and feet. It's characterized by:
-
Sensory Symptoms: Tingling, numbness, burning, prickling sensations (paresthesia), pain, and loss of sensation (hypesthesia or anesthesia) in the extremities. These symptoms often worsen at night.
-
Motor Symptoms: Muscle weakness, cramps, and atrophy in the affected extremities. This can lead to difficulties with fine motor skills and gait disturbances.
-
Autonomic Symptoms: Although less common in purely peripheral neuropathy, some autonomic involvement can occur and worsen as the condition progresses.
2. Autonomic Neuropathy: Impacting Internal Organs
Autonomic neuropathy affects the autonomic nervous system, controlling involuntary functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and bladder function. Symptoms include:
-
Cardiovascular Complications: Orthostatic hypotension (a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing), abnormal heart rate, and silent myocardial ischemia.
-
Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, bloating, and gastroparesis (delayed gastric emptying).
-
Urinary Problems: Urinary retention, frequent urination, and incontinence.
-
Sexual Dysfunction: Erectile dysfunction in men and decreased libido in both men and women.
3. Focal Neuropathy: Isolated Nerve Damage
Focal neuropathy involves damage to a single nerve or a small group of nerves. Symptoms vary depending on the affected nerve and can include:
-
Mononeuropathy: Pain, weakness, or numbness in a specific area supplied by the affected nerve. This might include the median nerve, leading to carpal tunnel syndrome-like symptoms.
-
Cranial Neuropathies: Affects the cranial nerves, leading to symptoms like double vision, facial weakness, or swallowing difficulties.
4. Proximal Neuropathy (Diabetic Amyotrophy): Impacting the Legs
Proximal neuropathy primarily affects the nerves supplying the muscles in the thighs, hips, and buttocks. It is characterized by:
- Muscle weakness and pain: primarily in the legs and hips. This can lead to significant mobility issues.
- Weight loss: This can be a significant symptom, often presenting early in the progression.
- Muscle wasting: Atrophy of the muscles in the legs and hips.
Diagnosis of Diabetic Neuropathy: Identifying the Underlying Issue
Diagnosing diabetic neuropathy involves a combination of:
-
Medical History and Physical Examination: Thorough assessment of symptoms, duration, and any associated risk factors (e.g., diabetes duration, blood glucose control). A neurological examination assesses reflexes, muscle strength, sensation, and coordination.
-
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): NCS measures the speed at which electrical signals travel through nerves, identifying nerve damage. Slowed conduction velocity indicates neuropathy.
-
Electromyography (EMG): EMG assesses the electrical activity of muscles, helping differentiate between nerve and muscle disorders.
-
Quantitative Sensory Testing (QST): QST objectively measures sensory perception in various modalities, such as touch, temperature, and pain. This helps quantify the extent of sensory impairment.
-
Blood Glucose Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential to assess diabetes control and its potential impact on nerve function. HbA1c levels provide an average blood glucose over the past 2-3 months.
Management and Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathy: A Multifaceted Approach
Managing diabetic neuropathy aims to alleviate symptoms, prevent further nerve damage, and improve the quality of life. Treatment strategies include:
1. Blood Glucose Control: The Cornerstone of Management
Tight glycemic control is the cornerstone of neuropathy management. Maintaining blood glucose levels within the target range significantly slows disease progression and reduces the risk of further nerve damage. This often involves lifestyle modifications and medication, such as insulin or oral hypoglycemics.
2. Pain Management: Addressing Neuropathic Pain
Managing neuropathic pain is critical for improving patient well-being. Treatment options include:
-
Pharmacological Interventions: Various medications target different pain pathways. Examples include gabapentinoids (gabapentin, pregabalin), tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline, nortriptyline), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs; duloxetine, venlafaxine), and opioids (in carefully selected cases). The selection of medication is tailored to the individual's needs and pain characteristics.
-
Non-Pharmacological Strategies: These include physical therapy, occupational therapy, acupuncture, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). These approaches can help manage pain and improve functional abilities.
3. Lifestyle Modifications: Supporting Overall Health
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing diabetes and its complications. These include:
-
Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity improves blood glucose control, reduces weight, and enhances cardiovascular health. Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling are beneficial.
-
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet low in saturated fats, trans fats, and refined carbohydrates helps manage blood glucose levels and overall health.
-
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the burden on the body and improves blood glucose control.
-
Smoking Cessation: Smoking exacerbates vascular complications, including diabetic neuropathy. Quitting smoking is crucial for overall health and preventing further nerve damage.
4. Foot Care: Preventing Complications
Careful foot care is essential to prevent foot ulcers and infections, common complications of diabetic neuropathy. This involves:
-
Daily Foot Inspections: Checking for any cuts, blisters, redness, or swelling.
-
Proper Footwear: Wearing comfortable, well-fitting shoes that provide adequate support and protection.
-
Skin Hygiene: Keeping feet clean and dry to prevent infections.
-
Regular Podiatry Care: Seeking professional foot care from a podiatrist to address any foot problems promptly.
Conclusion: A Collaborative Approach to Neuropathy Management
Diabetic neuropathy is a complex condition arising from the multifaceted effects of hyperglycemia on the nervous system. Effective management requires a collaborative approach involving the patient, physician, and other healthcare professionals (e.g., podiatrist, physical therapist, pain specialist). Early diagnosis, aggressive blood glucose control, comprehensive pain management, and meticulous foot care are critical for preventing further nerve damage, mitigating symptoms, and enhancing the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes. By understanding the intricate mechanisms and employing a multidisciplinary approach, we can improve outcomes and support those affected by this debilitating complication of diabetes. Regular monitoring, open communication, and proactive management are key to living well with diabetic neuropathy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Simple Sugar
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is Not A Benefit Of Body Scrubs
Mar 25, 2025
-
Recycled Or Repurposed Munitions Are Considered Waste Military Munitions
Mar 25, 2025
-
Understanding The Benefits Of An Activity Can
Mar 25, 2025
-
Use Only A Bandsaw That Has A
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Neuropathy In Patients With Diabetes Is Caused By Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
