Pepsin Can Break A Polypeptide Chain Into ______.
Breaking News Today
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
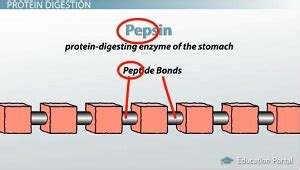
Table of Contents
Pepsin Can Break a Polypeptide Chain into Smaller Polypeptides and Amino Acids
Pepsin, a crucial digestive enzyme, plays a vital role in the initial breakdown of proteins in the stomach. Understanding its function is key to comprehending the complex process of protein digestion. This article delves deep into the intricacies of pepsin's action, exploring its substrate specificity, the products of its enzymatic activity, and its significance in overall human health.
Understanding Pepsin: Structure and Function
Pepsin, an endopeptidase, belongs to the aspartic protease family. This means it cleaves peptide bonds within a polypeptide chain, rather than at the terminal ends like exopeptidases. Its three-dimensional structure, crucial for its catalytic activity, is characterized by two aspartic acid residues in its active site. These residues are essential for the enzyme's ability to hydrolyze peptide bonds. The optimal pH for pepsin activity is highly acidic, perfectly aligning with the stomach's environment.
The Catalytic Mechanism of Pepsin
The mechanism by which pepsin breaks down polypeptide chains involves a complex interplay of its active site residues and the substrate. The two aspartic acid residues in the active site, one protonated and one deprotonated, facilitate the cleavage of the peptide bond. The protonated aspartic acid acts as a proton donor, while the deprotonated aspartic acid acts as a base, facilitating the transfer of a proton from the peptide bond to the attacking water molecule. This intricate mechanism ultimately results in the hydrolysis of the peptide bond, separating the polypeptide chain into smaller fragments.
Pepsin's Specificity: What Peptide Bonds Does it Cleave?
Pepsin isn't indiscriminate in its choice of peptide bonds. It exhibits a certain degree of specificity, preferentially cleaving peptide bonds adjacent to aromatic amino acids such as phenylalanine, tryptophan, and tyrosine. It also has a preference for bonds adjacent to leucine, glutamate, and methionine residues. This specificity, however, is not absolute, and pepsin can cleave other peptide bonds, albeit at a slower rate. This means that the final products of pepsin digestion are not just single amino acids, but rather a mixture of smaller polypeptides and some free amino acids.
The Influence of pH on Pepsin Activity
The highly acidic environment of the stomach (pH 1.5-3.5) is essential for pepsin's optimal activity. At this pH, the enzyme adopts its active conformation, allowing for efficient catalysis. Changes in pH can significantly affect pepsin's activity. A slight increase in pH can lead to a reduction in catalytic efficiency, while a significant increase can lead to complete inactivation due to conformational changes in the enzyme's structure. This pH dependence underscores the importance of the stomach's acidic environment in maintaining optimal protein digestion.
The Products of Pepsin Digestion: Smaller Polypeptides and Amino Acids
Therefore, to answer the question directly: pepsin can break a polypeptide chain into smaller polypeptides and amino acids. It's crucial to emphasize that the result isn't solely a collection of individual amino acids. Instead, pepsin initiates the digestion process by breaking down large proteins into smaller, more manageable polypeptide fragments. These fragments are then further processed by other digestive enzymes in the small intestine. The size and composition of these smaller polypeptides vary greatly depending on the initial protein substrate and the extent of pepsin digestion.
The Role of Other Digestive Enzymes
While pepsin begins the process, the complete digestion of proteins relies heavily on the collaborative efforts of other digestive enzymes. In the small intestine, a series of enzymes like trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidases, and aminopeptidases continue the breakdown of the polypeptides generated by pepsin. These enzymes work in a sequential manner, gradually reducing the polypeptide fragments into their constituent amino acids. These amino acids are then absorbed into the bloodstream and utilized by the body for various metabolic processes.
The Importance of Pepsin in Human Health
Optimal pepsin activity is essential for efficient protein digestion and nutrient absorption. Insufficient pepsin activity, often due to genetic factors, dietary deficiencies, or certain medical conditions, can lead to impaired protein digestion and malabsorption. This can result in a range of symptoms, including bloating, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and nutritional deficiencies.
Pepsin and Related Health Conditions
A deficiency in pepsin production can be indicative of various health issues. Conditions like hypochlorhydria (reduced stomach acid production) and achlorhydria (absence of stomach acid) directly affect pepsin's activity. Furthermore, certain autoimmune disorders can target the stomach lining, affecting the production of pepsin and other digestive enzymes. Understanding the role of pepsin in the digestive process highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy gut environment.
Factors Affecting Pepsin Production and Activity
Several factors can influence pepsin production and activity. Diet plays a significant role; a diet rich in proteins generally stimulates pepsin production, while a deficient diet can hinder it. Stress, medications (particularly proton pump inhibitors), and age can also affect pepsin production and activity. A balanced diet, stress management techniques, and appropriate medical interventions are crucial in maintaining healthy pepsin levels and optimal digestive function.
Pepsin Inhibitors and Their Applications
Pepsin inhibitors are substances that can reduce or completely block the activity of pepsin. These inhibitors have various applications, primarily in the treatment of peptic ulcers and other gastrointestinal conditions. Some naturally occurring compounds, as well as synthetic molecules, have shown pepsin inhibitory activity. Understanding the mechanisms of pepsin inhibition can help in developing more effective treatments for gastrointestinal disorders.
Natural Pepsin Inhibitors
Several natural compounds have demonstrated pepsin inhibitory properties. These include various plant-derived extracts, and specific amino acids. The study of these natural inhibitors continues to offer potential avenues for developing novel therapeutic agents. Further research into their mechanisms of action and potential benefits is ongoing.
Synthetic Pepsin Inhibitors
Synthetic pepsin inhibitors have also been developed, some of which are currently used in clinical settings. These inhibitors often mimic the structure of pepsin substrates, competing with the natural substrates for binding to the enzyme's active site. By blocking the active site, these inhibitors prevent pepsin from cleaving peptide bonds. The development of synthetic inhibitors is driven by the need for more effective and specific treatments for peptic ulcers and related conditions.
Conclusion: The Significance of Pepsin in Protein Digestion
Pepsin, the gastric enzyme, plays a pivotal role in initiating protein digestion. It cleaves polypeptide chains into smaller polypeptides and amino acids, setting the stage for further enzymatic breakdown in the small intestine. Maintaining optimal pepsin activity is crucial for efficient protein digestion and nutrient absorption. Understanding its structure, function, and regulation can help in developing strategies to prevent and treat digestive disorders associated with impaired pepsin function. Further research into pepsin and its inhibitors continues to expand our understanding of this critical enzyme and its role in human health. The interplay between pepsin, the acidic environment of the stomach, and other digestive enzymes demonstrates the intricate and finely-tuned nature of the human digestive system. This complex interaction ensures the efficient breakdown of dietary proteins and the effective absorption of essential amino acids for various bodily functions. Maintaining the health of this system is fundamental to overall well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Statements About Air Is True
Mar 13, 2025
-
Pharmacology Made Easy 5 0 The Gastrointestinal System Test
Mar 13, 2025
-
Life And Health Insurance Exam Cheat Sheet Pdf
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Inference Does The Text Best Support
Mar 13, 2025
-
Paper 2 Option B Comp Sci Definitions
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Pepsin Can Break A Polypeptide Chain Into ______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
