Product Lines Are A Part Of A Product Blank______.
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 7 min read
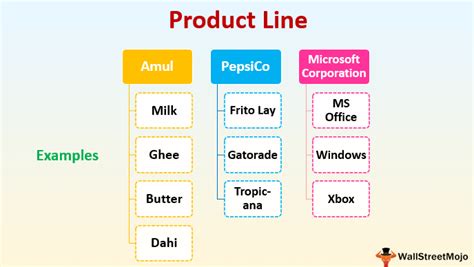
Table of Contents
Product Lines Are a Part of a Product Mix
A strong product strategy is the backbone of any successful business. Understanding the different components of that strategy is crucial for growth and market dominance. One key element often overlooked is the concept of the product mix, and within that, the vital role of product lines. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the definition of a product mix, its components, the importance of product lines within that mix, and how effectively managing your product lines can lead to increased profitability and market share.
What is a Product Mix?
A product mix, also known as a product portfolio or product assortment, represents the complete range of products a company offers to its customers. It's a holistic view of all the goods and services a business provides, encompassing the breadth and depth of its offerings. Think of it as the complete picture of your company's product landscape. This isn't just about individual products; it's about the overall strategy behind the variety and organization of those products.
A well-defined product mix is critical for several reasons:
- Meeting diverse customer needs: A broad product mix allows businesses to cater to a wider range of customer preferences and requirements, increasing market reach and potential customer base.
- Optimizing resource allocation: By strategically managing the product mix, businesses can efficiently allocate resources to the most profitable and promising products.
- Mitigating risk: Diversification across various product categories reduces reliance on any single product, minimizing the impact of market fluctuations or unforeseen circumstances.
- Building brand image: A consistent and well-defined product mix helps to build a strong brand identity and recognition, enhancing customer loyalty.
- Achieving competitive advantage: A unique and well-curated product mix can differentiate a business from competitors, offering a compelling value proposition to customers.
Key Dimensions of a Product Mix
The product mix can be analyzed across four key dimensions:
- Width: This refers to the number of different product lines offered by a company. A company with a wide product mix offers many different product lines, while a company with a narrow product mix focuses on fewer product lines. Think of a large conglomerate versus a niche boutique.
- Length: This refers to the total number of items within all product lines. A company with a long product mix offers a vast number of individual products, while a company with a short product mix offers a smaller number of products. This relates to the depth of offerings within each line.
- Depth: This refers to the number of variations offered within each product line. This could include different sizes, colors, models, or features. A deep product mix offers many variations of each product, while a shallow product mix offers fewer variations.
- Consistency: This refers to how closely related the various product lines are in terms of end-use, production requirements, distribution channels, or customer target groups. A consistent product mix features products that share similar characteristics, while an inconsistent product mix features products that are quite different.
Understanding these dimensions is crucial for effective product mix management. A company can adjust its product mix by adding new product lines (increasing width), extending existing lines (increasing length), adding variations to existing products (increasing depth), or streamlining its offerings to focus on a more consistent range of products.
Product Lines: The Building Blocks of the Product Mix
Product lines are groups of closely related products offered by a company. They share similar characteristics, target a similar customer base, are sold through similar channels, and often use similar production processes. These lines form the essential building blocks of the overall product mix.
Consider a clothing retailer: they might have several product lines, including men's wear, women's wear, children's wear, and accessories. Each line contains a range of individual products (e.g., shirts, pants, dresses, shoes) but shares the common thread of being clothing items.
Why are product lines important?
- Targeted marketing: Product lines allow for more focused marketing efforts. You can tailor your messaging and promotions specifically to the needs and preferences of the target customer for each line.
- Efficient resource allocation: Producing and distributing products within a line often shares economies of scale, leading to lower costs.
- Brand building: Strong product lines contribute to a cohesive brand identity, fostering customer loyalty and recognition.
- Market expansion: Adding new product lines allows for expansion into new markets and customer segments.
- Competitive advantage: A well-developed product line can differentiate your offerings from those of competitors, providing a unique selling proposition.
Managing Your Product Lines for Success
Effective product line management involves several key strategies:
- Analyzing market trends: Regularly assess market demand, competitor activity, and emerging trends to identify opportunities for growth and innovation within each product line.
- Product lifecycle management: Understand the stages (introduction, growth, maturity, decline) of each product within a line. Adapt your marketing, pricing, and distribution strategies accordingly. For example, you might aggressively promote a product in its growth stage and focus on cost reduction in its maturity stage.
- Product differentiation: Clearly define the unique selling points of each product within a line to differentiate it from competitors and appeal to specific customer segments. This could involve focusing on quality, features, design, branding, or price.
- Pricing strategies: Develop appropriate pricing strategies for each product based on its cost, market positioning, and competitor pricing. This could involve cost-plus pricing, value-based pricing, or competitive pricing.
- Distribution strategies: Choose suitable distribution channels for each product line to ensure efficient reach to target customers. This could involve direct sales, wholesale distribution, retail partnerships, or e-commerce.
- Branding and packaging: Develop strong branding and packaging strategies for each product line to create a distinct identity and enhance customer appeal.
Expanding and Contracting Product Lines: Strategic Decisions
Companies are constantly evaluating the performance of their product lines and making decisions about expansion or contraction.
Expanding Product Lines: This can involve:
- Line extension: Adding new products within an existing product line. For example, a coffee company might add a new flavor to its existing line of instant coffees. This leverages existing brand recognition and customer loyalty.
- Line filling: Adding new products to fill gaps in an existing product line. For example, a clothing brand might add a new size range to its existing line of jeans. This caters to unmet customer needs within the existing market segment.
- Brand extension: Using an existing brand name to launch products in a new product category. For example, a successful shoe brand might launch a new line of sportswear. This capitalizes on brand equity and recognition to enter new markets.
Contracting Product Lines: This might involve:
- Product deletion: Removing unprofitable or outdated products from a product line. This is a necessary step to optimize resource allocation and improve profitability. Careful analysis of sales data and market trends is crucial here.
- Line simplification: Reducing the number of products within a product line to focus on the most successful and profitable items. This streamlines operations and improves efficiency.
Case Studies: Product Line Success and Failure
Analyzing successful and unsuccessful product lines provides valuable insights for strategic decision-making. Consider companies that have successfully expanded their product lines by identifying unmet customer needs or capitalizing on market trends. Contrast this with companies that have struggled due to poor product line management or a failure to adapt to changing market conditions. Study the strategies employed, the challenges encountered, and the ultimate outcomes to extract valuable lessons applicable to your own business.
Conclusion: Mastering Your Product Mix Through Effective Product Line Management
The product mix is a crucial element of any successful business strategy. Understanding the components of your product mix, particularly the role and importance of individual product lines, is essential for achieving sustainable growth and competitive advantage. By applying effective product line management strategies, you can optimize your offerings, increase profitability, build strong brands, and expand your market reach. Regular monitoring, adaptation, and strategic decision-making regarding your product lines are critical for navigating the ever-changing market landscape and ensuring long-term success. Remember, the key is to create a product mix that perfectly aligns with your business goals, customer needs, and competitive environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Potential Risk Factor For Breast Cancer Includes Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Corporate Taxes Are A Type Of Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Rn Targeted Medical Surgical Perioperative Online Practice 2023 Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Shadow Health Tina Jones Health History Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Cause May Produce Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Product Lines Are A Part Of A Product Blank______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
