Scheduled Maintenance Should Be Performed In Accordance With The
Breaking News Today
Mar 29, 2025 · 5 min read
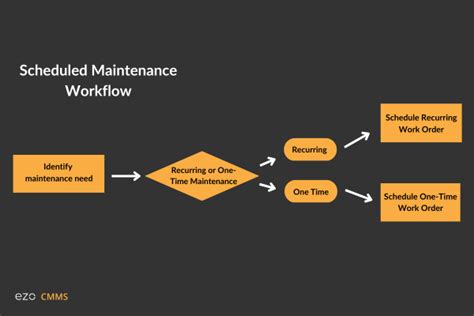
Table of Contents
Scheduled Maintenance: A Comprehensive Guide to Compliance and Best Practices
Scheduled maintenance is the cornerstone of reliable operations across diverse industries. From manufacturing plants and IT infrastructure to transportation networks and healthcare facilities, adhering to a rigorous maintenance schedule is crucial for preventing equipment failures, minimizing downtime, and ensuring operational efficiency. This comprehensive guide explores the critical aspects of scheduled maintenance, emphasizing compliance with industry standards, best practices, and the significant benefits of a proactive approach.
Understanding the Importance of Scheduled Maintenance
Ignoring scheduled maintenance is a gamble with potentially disastrous consequences. The consequences of neglecting preventative measures can manifest in several ways:
1. Catastrophic Equipment Failure: The most immediate risk is the unexpected breakdown of critical machinery or systems. This can lead to production halts, service disruptions, and significant financial losses. In industries like healthcare, failure of medical equipment can have life-threatening implications.
2. Increased Repair Costs: Reactive repairs, undertaken after a failure, are often significantly more expensive than preventative maintenance. Repairing damaged components frequently involves higher labor costs, the need for specialized parts, and extended downtime.
3. Safety Hazards: Malfunctioning equipment presents a serious safety hazard to employees and the public. Regular maintenance helps identify and rectify potential safety risks before they escalate into accidents.
4. Reduced Efficiency and Productivity: Even minor equipment malfunctions can disrupt workflows and reduce overall productivity. Regular maintenance ensures equipment operates at peak performance, maximizing output and minimizing wasted resources.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Many industries are subject to strict regulations requiring regular maintenance and documentation. Failure to comply can lead to hefty fines, legal repercussions, and damage to reputation.
Defining the Scope of Scheduled Maintenance
Scheduled maintenance encompasses a broad spectrum of activities aimed at preserving equipment functionality and prolonging its lifespan. These activities can be broadly categorized as:
1. Preventative Maintenance: This involves regular inspections, cleaning, lubrication, and minor repairs to prevent potential problems before they occur. This is the cornerstone of a proactive maintenance strategy. Examples include:
- Lubricating moving parts: Reducing friction and wear.
- Cleaning filters and air vents: Preventing blockages and ensuring efficient operation.
- Inspecting electrical connections: Identifying loose wires or corrosion.
- Testing safety devices: Ensuring proper functioning of emergency shut-off systems.
2. Predictive Maintenance: This utilizes advanced technologies, such as vibration analysis and thermal imaging, to identify potential problems before they manifest as failures. Predictive maintenance allows for more targeted interventions, optimizing maintenance schedules and resource allocation. Examples include:
- Vibration analysis: Detecting imbalances or bearing wear in rotating machinery.
- Oil analysis: Monitoring lubricant condition for signs of contamination or degradation.
- Thermal imaging: Identifying overheating components that might indicate impending failure.
3. Corrective Maintenance: This involves repairing equipment after it has failed. While essential, corrective maintenance is reactive and inherently more costly and disruptive than preventative or predictive measures. It is best viewed as a last resort, indicating a gap in the preventative maintenance strategy.
Developing a Comprehensive Scheduled Maintenance Plan
A successful scheduled maintenance plan requires careful planning and execution. Key elements of a robust plan include:
1. Equipment Inventory: A complete inventory of all equipment, including details such as model numbers, serial numbers, and manufacturer specifications, is crucial. This allows for accurate scheduling of maintenance activities.
2. Maintenance Procedures: Detailed procedures for each maintenance task should be developed and documented. These procedures should include step-by-step instructions, safety precautions, and required tools and parts.
3. Scheduling and Tracking: A systematic scheduling system is essential to ensure that all maintenance tasks are performed on time. Software solutions are often used to track maintenance activities, generate work orders, and monitor equipment performance.
4. Spare Parts Inventory: Maintaining an adequate inventory of spare parts is crucial to minimize downtime during repairs. This requires accurate forecasting of part usage and efficient inventory management.
5. Training and Competence: Maintenance personnel must be properly trained and competent to perform the required tasks safely and effectively. Regular training updates are essential to ensure personnel are up-to-date with the latest techniques and safety procedures.
6. Documentation and Record Keeping: Meticulous record-keeping is essential for compliance and for identifying trends and patterns in equipment performance. This documentation should include maintenance logs, repair records, and inspection reports.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements is paramount. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, including fines, legal action, and reputational damage. Specific requirements vary significantly across industries, and it's crucial to understand the applicable regulations in your specific sector.
1. Industry-Specific Standards: Many industries have their own standards for maintenance practices. These standards often outline best practices, recommended procedures, and documentation requirements. Adherence to these standards is often a key component of compliance.
2. Regulatory Compliance: Government agencies frequently impose regulations on maintenance practices, particularly in safety-critical industries. These regulations may dictate specific maintenance intervals, inspection procedures, and record-keeping requirements. Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties.
3. Insurance Requirements: Insurance policies often include requirements for regular maintenance as a condition of coverage. Failure to meet these requirements could jeopardize insurance coverage in the event of an accident or equipment failure.
Benefits of a Proactive Maintenance Approach
A well-executed scheduled maintenance program offers substantial advantages, including:
1. Reduced Downtime: Preventative maintenance significantly reduces the likelihood of unexpected equipment failures, minimizing costly downtime.
2. Extended Equipment Lifespan: Regular maintenance prolongs the operational life of equipment, delaying the need for costly replacements.
3. Improved Safety: Regular inspections and maintenance help identify and mitigate safety hazards, protecting employees and the public.
4. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Well-maintained equipment operates at peak performance, maximizing output and reducing waste.
5. Cost Savings: While preventative maintenance involves upfront costs, it ultimately leads to significant cost savings by preventing expensive repairs and replacements.
6. Improved Compliance: A well-documented maintenance program simplifies compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
7. Enhanced Reputation: A commitment to regular maintenance demonstrates professionalism and reliability, enhancing the company's reputation with customers and stakeholders.
Conclusion
Scheduled maintenance is not simply a cost; it's a strategic investment in operational reliability, safety, and profitability. By implementing a comprehensive maintenance plan that incorporates preventative, predictive, and corrective measures, organizations can minimize downtime, reduce costs, enhance safety, and improve their overall operational efficiency. Adherence to industry standards and regulatory requirements is crucial, emphasizing the importance of meticulous documentation and adherence to best practices. Ultimately, a proactive approach to scheduled maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term success and sustainability of any operation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
End Of Semester Test Us History Semester B
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Could A Skier Benefit From A Sports Specific Training Program
Apr 01, 2025
-
Where Did Ajs Dad Find His Phone
Apr 01, 2025
-
Apes Unit 6 Progress Check Mcq Part A
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Project Network Provides The Basis For
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Scheduled Maintenance Should Be Performed In Accordance With The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
