Signs And Symptoms Of A Sympathomimetic Drug Overdose Include
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
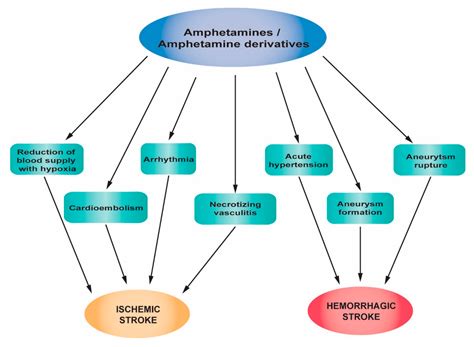
Table of Contents
Signs and Symptoms of a Sympathomimetic Drug Overdose: A Comprehensive Guide
Sympathomimetic drugs, also known as adrenergic agonists, mimic the effects of the sympathetic nervous system. These drugs are widely used in various medical applications, ranging from treating asthma and nasal congestion to managing hypotension and ADHD. However, an overdose of these drugs can lead to serious, even life-threatening, consequences. Understanding the signs and symptoms of a sympathomimetic drug overdose is crucial for prompt medical intervention and improved patient outcomes. This comprehensive guide delves into the various manifestations of such an overdose, categorizing them for clarity and offering insights into their underlying mechanisms.
Understanding Sympathomimetics and Their Mechanisms
Before exploring the signs and symptoms of an overdose, it's essential to briefly understand how sympathomimetics work. These drugs interact primarily with adrenergic receptors—alpha-1, alpha-2, beta-1, and beta-2—located throughout the body. Stimulation of these receptors triggers a cascade of physiological responses, mimicking the "fight-or-flight" response. Different sympathomimetics have varying affinities for these receptors, leading to a diverse range of effects. For instance, some may primarily target beta-2 receptors (causing bronchodilation), while others may predominantly affect alpha-1 receptors (leading to vasoconstriction). This receptor selectivity dictates the specific signs and symptoms observed in an overdose.
Cardiovascular Symptoms: A Primary Manifestation
Cardiovascular symptoms are often the most prominent and potentially life-threatening signs of a sympathomimetic overdose. The excessive stimulation of adrenergic receptors leads to a wide array of cardiovascular complications:
Tachycardia and Palpitations: Increased heart rate (tachycardia) and a racing heart sensation (palpitations) are common early signs. The stimulation of beta-1 receptors in the heart increases the heart's contractility and rate, potentially leading to arrhythmias.
Hypertension: Excessive vasoconstriction, primarily due to alpha-1 receptor stimulation, results in elevated blood pressure (hypertension). This can be a significant concern, potentially leading to stroke, heart attack, or other severe cardiovascular events.
Chest Pain/Angina: The increased cardiac workload and oxygen demand, combined with potential coronary artery spasm, can cause chest pain (angina). This is a serious warning sign requiring immediate medical attention.
Arrhythmias: Severe sympathomimetic overdose can disrupt the heart's normal electrical rhythm, leading to various arrhythmias, such as ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation. These are life-threatening conditions requiring immediate resuscitation.
Neurological and Psychological Symptoms: A Spectrum of Effects
The central nervous system is also significantly affected by sympathomimetic overdose. The resulting neurological and psychological symptoms can be highly variable depending on the specific drug and the dose:
Anxiety and Agitation: Increased sympathetic activity can manifest as feelings of intense anxiety, restlessness, and agitation. Individuals may become highly irritable and difficult to manage.
Tremors and Muscle Rigidity: The excessive stimulation can lead to involuntary muscle tremors and increased muscle tone, resulting in rigidity.
Seizures: In severe cases, sympathomimetic overdose can trigger seizures, particularly in individuals with pre-existing seizure disorders or those who have ingested a high dose.
Psychosis and Hallucinations: Some sympathomimetics can induce psychosis, characterized by altered perception of reality, delusions, and hallucinations. This is particularly common with certain stimulants.
Insomnia: The stimulatory effects of sympathomimetics can severely disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia.
Confusion and Delirium: Cognitive impairment, manifesting as confusion and delirium, is another potential neurological effect.
Gastrointestinal and Metabolic Effects: Often Overlooked
While cardiovascular and neurological symptoms are often the focus, sympathomimetic overdose can also significantly impact the gastrointestinal and metabolic systems:
Nausea and Vomiting: Stimulation of the gastrointestinal tract can lead to nausea and vomiting.
Abdominal Pain: Abdominal discomfort or pain can also occur.
Hyperthermia: Increased metabolic rate due to the sympathomimetic effects can result in an elevation of body temperature (hyperthermia). This can be particularly dangerous, leading to heat stroke.
Diaphoresis: Excessive sweating (diaphoresis) is a common finding, reflecting the increased sympathetic activity.
Dehydration: Combined with the potential for vomiting and diaphoresis, dehydration can become a significant concern, worsening the overall condition.
Respiratory Symptoms: Bronchodilation and Potential Complications
The effects on the respiratory system are somewhat paradoxical. While some sympathomimetics are used to treat bronchospasm, an overdose can lead to unexpected respiratory consequences:
Tachypnea: Increased respiratory rate (tachypnea) can occur due to the overall stimulation of the nervous system.
Respiratory Alkalosis: Rapid breathing can lead to respiratory alkalosis, a condition where the blood becomes excessively alkaline due to the loss of carbon dioxide.
Pulmonary Edema: In severe cases, pulmonary edema (fluid buildup in the lungs) can develop due to the increased cardiac workload and vascular permeability. This is life-threatening.
Other Possible Symptoms: A Comprehensive Overview
The signs and symptoms of sympathomimetic overdose are not limited to the categories described above. Several other manifestations can occur:
- Dilated Pupils (Mydriasis): The sympathetic nervous system stimulation can lead to the dilation of pupils.
- Increased Blood Glucose: The metabolic effects can cause an elevation in blood glucose levels.
- Headache: The increased blood pressure and vascular changes can contribute to headache development.
- Weakness and Fatigue: Paradoxically, despite the stimulation, individuals may experience weakness and fatigue.
- Visual Disturbances: Blurred vision or other visual disturbances are also possible.
- Renal Effects: The vasoconstriction can potentially affect kidney function.
Specific Sympathomimetics and Their Overdose Profiles
It is crucial to understand that the specific symptoms of a sympathomimetic overdose will vary depending on the particular drug ingested. For example, an overdose of amphetamines might lead to a pronounced psychotic presentation, while an overdose of a beta-agonist might be primarily characterized by cardiac complications. Seeking immediate medical assistance is always the safest course of action.
Treatment and Management of Sympathomimetic Overdose
Treatment of a sympathomimetic overdose is primarily supportive and focuses on managing the symptoms. This often includes:
- Supportive Care: Maintaining adequate oxygenation, ventilation, and circulation are critical.
- Fluid Resuscitation: Intravenous fluids are often administered to manage dehydration.
- Antihypertensive Medications: Medications to lower blood pressure may be necessary.
- Beta-Blockers: In some cases, beta-blockers can help counter the effects of the overdose, but their use requires caution due to the risk of unopposed alpha-adrenergic stimulation.
- Benzodiazepines: Benzodiazepines may be used to control seizures, anxiety, and agitation.
- Cooling Measures: Cooling measures might be necessary to manage hyperthermia.
Prevention and Public Awareness: A Crucial Aspect
Preventing sympathomimetic overdose requires education and awareness. This includes:
- Proper Medication Management: Patients should carefully follow prescribed dosages and store medications securely.
- Drug Abuse Prevention: Education and support programs can help address drug abuse and misuse.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Raising public awareness about the dangers of sympathomimetic overdose is crucial.
- Prompt Medical Attention: Early recognition of the signs and symptoms and seeking immediate medical attention are vital for optimal outcomes.
Conclusion: The Importance of Vigilance
A sympathomimetic drug overdose represents a serious medical emergency that can have life-threatening consequences. Recognizing the diverse range of signs and symptoms, understanding their underlying mechanisms, and promoting public awareness are critical steps in preventing these overdoses and ensuring prompt and effective treatment. The information provided in this guide should not replace professional medical advice. Always seek immediate medical attention if you suspect a sympathomimetic overdose. Early intervention is key to minimizing the potential for severe complications and improving patient outcomes. Remember, vigilance and prompt medical assistance are crucial in managing this potentially life-threatening condition.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Does Simon Doubt The Existence Of The Beast
Mar 27, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Are True Of Teams
Mar 27, 2025
-
A Group Of Biologists Is Studying The Competitive Relationships
Mar 27, 2025
-
The Keyword Tyranny In This Poster Is Primarily Used To
Mar 27, 2025
-
Irene Todavia No 1 Of 2 Lista Para Salir
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Signs And Symptoms Of A Sympathomimetic Drug Overdose Include . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
