The Age Of Exploration Paved The Way For...
Breaking News Today
Mar 19, 2025 · 7 min read
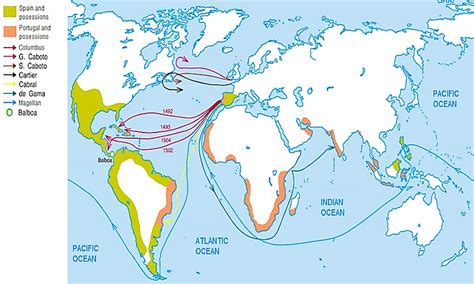
Table of Contents
The Age of Exploration: Paving the Way for a Globalized World
The Age of Exploration, spanning roughly from the 15th to the 17th centuries, was a period of unprecedented maritime exploration and discovery. Driven by a complex interplay of factors—the desire for new trade routes, the pursuit of spices and riches, and a burgeoning spirit of scientific inquiry—this era irrevocably reshaped the world. It wasn't just about charting unknown waters; it paved the way for a multitude of profound and lasting changes that continue to shape our globalized world today.
The Dawn of Globalization: Trade and Economic Transformation
One of the most immediate and impactful legacies of the Age of Exploration was the dawn of globalization. Before the era of extensive seafaring, trade was largely regional and limited. The discovery of new sea routes to Asia, Africa, and the Americas fundamentally altered this. The establishment of vast trade networks connecting distant continents resulted in an unprecedented exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
The Columbian Exchange: A Biological Revolution
The Columbian Exchange, named after Christopher Columbus, represents a pivotal aspect of this transformation. It refers to the widespread transfer of plants, animals, culture, human populations, technology, diseases, and ideas between the Americas, West Africa, and the Old World in the 15th and 16th centuries. This exchange had dramatic consequences, both positive and negative.
-
Positive Impacts: The introduction of New World crops like potatoes, tomatoes, maize, and beans to Europe dramatically increased food production, leading to population growth and economic expansion. Similarly, the introduction of Old World livestock like horses and cattle revolutionized agriculture and transportation in the Americas.
-
Negative Impacts: The Columbian Exchange also brought devastating diseases like smallpox, measles, and influenza to the Americas, decimating indigenous populations who lacked immunity. The transatlantic slave trade, fueled by the demand for labor in the Americas, resulted in the forced migration of millions of Africans, leaving a deep and lasting scar on global history.
The Rise of Mercantilism: Shaping Economic Policies
The Age of Exploration also witnessed the rise of mercantilism, an economic system in which nations sought to maximize their wealth through trade surpluses and the accumulation of precious metals like gold and silver. This system encouraged colonization and the exploitation of resources in newly discovered territories. European powers established vast colonial empires, extracting wealth from their colonies and using them as sources of raw materials and markets for manufactured goods.
The mercantilist system, though ultimately unsustainable and exploitative, laid the foundation for many of the economic structures that persist to this day. It spurred the development of sophisticated financial institutions, merchant networks, and shipping industries, laying the groundwork for modern global capitalism.
The Spread of Knowledge and Cultural Exchange
Beyond economic consequences, the Age of Exploration fostered a significant spread of knowledge and cultural exchange. The encounter between different cultures led to the diffusion of ideas, technologies, and artistic styles across continents.
Scientific Advancements and Cartography: Mapping the World
The need to navigate vast oceans spurred significant advancements in scientific fields, particularly cartography, navigation, and shipbuilding. The development of improved maps, compasses, astrolabes, and more sophisticated sailing techniques allowed for more accurate navigation and exploration. This led to a more detailed understanding of the Earth's geography and spurred further scientific inquiry.
The detailed charting of new lands and sea routes also facilitated further exploration and trade, accelerating the process of globalization. The data gathered fueled further scientific exploration and the creation of new maps and technologies.
The Diffusion of Religion and Ideas: A Complex Interplay
The Age of Exploration also played a crucial role in the spread of religion and ideas. European powers actively sought to convert indigenous populations to Christianity, leading to both peaceful missionary work and violent religious conflicts. However, the exchange wasn't one-sided; indigenous cultures and religions also influenced European thought and practices.
This period witnessed a complex interplay of religious and philosophical exchanges. The fusion and conflict between different belief systems shaped the cultural landscape of the newly connected world. This intercultural interaction influenced everything from art and architecture to social structures and political systems.
The Legacy of Colonialism: A Complex and Contentious Inheritance
The Age of Exploration's legacy is inextricably linked to colonialism. The establishment of vast European empires in the Americas, Africa, and Asia resulted in the exploitation of resources, the suppression of indigenous cultures, and the establishment of unequal power dynamics that continue to resonate today.
The Transatlantic Slave Trade: A Stain on History
The transatlantic slave trade, a horrific institution deeply intertwined with the Age of Exploration, stands as a stark reminder of the dark side of this era. Millions of Africans were forcibly transported across the Atlantic, subjected to brutal conditions and exploited for their labor. The lasting effects of slavery continue to shape social, economic, and political realities in many parts of the world.
The legacy of slavery has resulted in deep societal inequalities, systemic racism, and persistent economic disparities across different populations. Understanding this legacy is crucial to address present-day challenges and promote social justice.
The Persistence of Colonial Structures: Shaping Geopolitics
The colonial structures established during the Age of Exploration have left a lasting imprint on the geopolitical landscape. Many former colonies still grapple with the effects of colonial rule, including political instability, economic underdevelopment, and ethnic tensions. The legacy of colonialism continues to shape international relations and power dynamics in the world today.
The legacy of colonialism is highly complex and requires careful consideration of its far-reaching effects. This includes examining the political, economic, and cultural consequences to understand its impact on different parts of the world.
The Shaping of Modern Nation-States: Defining Boundaries and Identities
The Age of Exploration significantly contributed to the formation of modern nation-states. The establishment of colonial empires and the subsequent struggles for independence led to the redrawing of political boundaries and the emergence of new national identities.
The Rise of National Identities: Forging a Sense of Belonging
The colonial experience, both positive and negative, played a crucial role in the formation of national identities in both colonizing and colonized nations. In many cases, shared experiences of colonialism, resistance, and the struggle for independence fostered a sense of collective identity and national unity.
Understanding how national identities were formed is crucial in analyzing the geopolitical dynamics of the world today. The impact of colonial rule on the formation of national identities can still be seen in various parts of the world.
The Reshaping of Political Boundaries: Creating and Redistributing Power
The Age of Exploration led to a significant redrawing of political boundaries. European powers carved up vast territories across the globe, often disregarding pre-existing political and cultural divisions. This resulted in arbitrary borders that often caused conflict and instability in the post-colonial era.
The arbitrary nature of these borders continues to have implications on conflicts and geopolitical strategies. Understanding the historical context of these boundaries helps to better comprehend present-day conflicts and power dynamics.
Conclusion: A Lasting Legacy
The Age of Exploration was a pivotal period in human history, with far-reaching consequences that continue to shape our world. It ushered in an era of globalization, spurred scientific and technological advancements, and fostered a complex exchange of cultures and ideas. However, it also left a legacy of colonialism, slavery, and exploitation, the effects of which are still felt today.
By understanding the multifaceted impacts of the Age of Exploration, we can gain valuable insights into the formation of the modern world, appreciate the complexity of global interconnectedness, and address the challenges that remain from this pivotal era in human history. The era served as a catalyst for many of the global systems and dynamics we see today, underscoring its continued relevance in shaping our world. Its complex legacy requires continuous critical examination and understanding to grapple with the enduring consequences of this transformative period.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Know As Multiple Choice Question Known As Sugars
Mar 20, 2025
-
Where May An Aircrafts Operating Limitations Be Found
Mar 20, 2025
-
In The Rain It Is Best To Use Your
Mar 20, 2025
-
One Challenge Faced By The European Union Is The
Mar 20, 2025
-
Letrs Unit 3 Session 2 Check For Understanding
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Age Of Exploration Paved The Way For... . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
