The Cognitive Behavioral Approach To Therapy Stresses
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
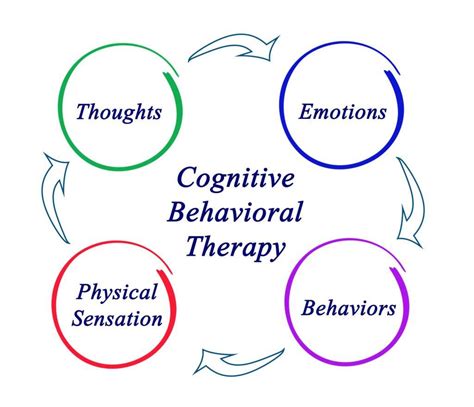
Table of Contents
- The Cognitive Behavioral Approach To Therapy Stresses
- Table of Contents
- The Cognitive Behavioral Approach to Therapy Stresses: Understanding and Managing Anxiety
- Understanding Stress Through a CBT Lens
- The Cognitive Triad: Thoughts, Feelings, and Behaviors
- Identifying Cognitive Distortions
- CBT Techniques for Stress Management
- Cognitive Restructuring
- Behavioral Activation
- Relaxation Techniques
- Exposure Therapy
- Problem-Solving Skills Training
- Assertiveness Training
- The Role of the Therapist in CBT for Stress
- Long-Term Benefits of CBT for Stress Management
- Stress Management Beyond Therapy: Incorporating CBT Principles into Daily Life
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Cognitive Behavioral Approach to Therapy Stresses: Understanding and Managing Anxiety
Stress is an inescapable part of the human experience. From minor daily hassles to major life events, stressors impact our lives, influencing our moods, behaviors, and overall well-being. While some stress is manageable and even beneficial, chronic or overwhelming stress can lead to significant mental health challenges, including anxiety disorders, depression, and even physical ailments. This is where the cognitive behavioral approach to therapy (CBT) proves particularly effective. CBT offers powerful strategies for understanding and managing stress, equipping individuals with the tools to navigate life's challenges with greater resilience.
Understanding Stress Through a CBT Lens
CBT frames stress as a product of the interplay between our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It doesn't necessarily focus on eliminating stressors themselves (although identifying and managing them is part of the process), but rather on how we interpret and react to them. This approach highlights the crucial role of our cognitive appraisal – how we think about a stressful situation – in determining our emotional and behavioral response.
The Cognitive Triad: Thoughts, Feelings, and Behaviors
A core concept in CBT is the cognitive triad, which emphasizes the interconnectedness of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. A stressful event triggers a thought process. This thought process, in turn, influences our emotional response (feeling stressed, anxious, overwhelmed) and subsequent behavior (avoidance, procrastination, unhealthy coping mechanisms). This cycle can become self-perpetuating, reinforcing negative patterns.
Example: Imagine facing a looming work deadline.
- Thought: "I'll never finish this on time. I'm going to fail." (Negative, catastrophic thinking)
- Feeling: Overwhelmed, anxious, panicky.
- Behavior: Procrastination, avoidance of the task, possibly even substance use to cope.
The CBT approach aims to break this cycle by challenging negative thoughts, developing adaptive coping mechanisms, and fostering more positive behaviors.
Identifying Cognitive Distortions
A key aspect of CBT involves recognizing and correcting cognitive distortions. These are systematic errors in thinking that magnify stress and negatively impact our emotional well-being. Some common cognitive distortions include:
- All-or-nothing thinking: Seeing things in black and white terms; everything is either perfect or a complete failure.
- Overgeneralization: Drawing sweeping conclusions based on a single event.
- Mental filter: Focusing only on negative aspects while ignoring positive ones.
- Disqualifying the positive: Dismissing positive experiences as insignificant or flukes.
- Jumping to conclusions: Making assumptions without sufficient evidence (mind reading or fortune telling).
- Magnification (catastrophizing) and minimization: Exaggerating negative aspects while downplaying positive ones.
- Emotional reasoning: Assuming that feelings reflect reality.
- Should statements: Placing excessive pressure on oneself with rigid rules and expectations.
- Labeling: Attaching negative labels to oneself or others.
- Personalization: Assuming responsibility for events outside one's control.
Recognizing these distortions is the first step toward challenging and changing them.
CBT Techniques for Stress Management
CBT utilizes various techniques to help individuals manage stress more effectively. These techniques are tailored to the individual's specific needs and challenges.
Cognitive Restructuring
This involves identifying and challenging negative or unhelpful thoughts. It's not about suppressing negative emotions but about replacing unhelpful thinking patterns with more balanced and realistic ones. This process often involves:
- Identifying negative thoughts: Becoming aware of the automatic negative thoughts that arise during stressful situations.
- Evaluating the evidence: Examining the evidence that supports and contradicts the negative thought.
- Generating alternative thoughts: Developing more realistic and balanced interpretations of the situation.
- Experimenting with new thoughts: Putting the new thoughts into practice and observing their effect on feelings and behaviors.
Behavioral Activation
This technique focuses on increasing engagement in enjoyable and rewarding activities. When stressed, individuals often withdraw from activities they once enjoyed. Behavioral activation encourages gradually reintroducing these activities, promoting a sense of accomplishment and improving mood.
Relaxation Techniques
Various relaxation techniques are incorporated into CBT to help manage the physiological symptoms of stress. These can include:
- Deep breathing exercises: Slow, deep breaths help calm the nervous system.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups.
- Mindfulness meditation: Focusing on the present moment without judgment.
Exposure Therapy
For individuals with anxiety disorders exacerbated by stress, exposure therapy may be used. This involves gradually exposing the individual to feared situations or stimuli in a safe and controlled environment, helping them to overcome avoidance behaviors and reduce anxiety.
Problem-Solving Skills Training
This helps individuals develop effective strategies for tackling challenges and managing stressful situations. It involves breaking down problems into smaller, manageable steps and developing action plans.
Assertiveness Training
This teaches individuals how to express their needs and opinions in a clear and respectful manner, reducing stress associated with interpersonal conflicts.
The Role of the Therapist in CBT for Stress
A skilled CBT therapist plays a crucial role in guiding individuals through this process. They provide:
- Psychoeducation: Educating the individual about stress, its effects, and the principles of CBT.
- Collaboration: Working collaboratively with the individual to develop personalized strategies.
- Support: Providing ongoing support and encouragement throughout the process.
- Monitoring progress: Regularly assessing progress and making adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
- Relapse prevention: Developing strategies to help prevent relapse into old patterns of thinking and behavior.
Long-Term Benefits of CBT for Stress Management
The benefits of CBT for stress management extend beyond immediate symptom relief. By equipping individuals with coping skills and changing maladaptive thought patterns, CBT promotes long-term resilience and improved mental well-being. Individuals often report:
- Reduced anxiety and stress levels: More effective management of stressful situations.
- Improved mood and emotional regulation: Greater ability to cope with negative emotions.
- Increased self-efficacy: Greater confidence in their ability to manage challenges.
- Improved relationships: Improved communication and conflict resolution skills.
- Enhanced overall quality of life: Greater sense of well-being and life satisfaction.
Stress Management Beyond Therapy: Incorporating CBT Principles into Daily Life
The principles of CBT can be integrated into daily life to enhance stress management beyond therapy sessions. This includes:
- Practicing mindfulness: Paying attention to the present moment without judgment.
- Challenging negative thoughts: Actively questioning and reframing negative thoughts.
- Engaging in self-care: Prioritizing activities that promote physical and emotional well-being.
- Setting realistic goals: Avoiding perfectionism and setting achievable goals.
- Building a support system: Connecting with supportive friends, family, or support groups.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise, healthy diet, and sufficient sleep.
Conclusion
The cognitive behavioral approach to therapy provides a powerful framework for understanding and managing stress. By targeting the interplay between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, CBT equips individuals with the skills and strategies to navigate life's challenges with greater resilience and achieve lasting improvements in mental well-being. The techniques discussed here are not a replacement for professional help, but rather tools that can be used alongside therapy to cultivate a healthier relationship with stress and build a life characterized by greater calm and fulfillment. If you are struggling with overwhelming stress, seeking professional help from a qualified therapist is recommended.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Potentially Life Threatening Consequences Of Pid Include
Mar 17, 2025
-
And Then They Politely Dusted Themselves Off
Mar 17, 2025
-
Intercultual Communication Study Guide For Chapter 1 And 2
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Did Grant Wood Reject European Abstraction In His Artwork
Mar 17, 2025
-
Este Traje De Bano Nuevo Es Demasiado Grande
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Cognitive Behavioral Approach To Therapy Stresses . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
