The Division Of The Cytoplasm Is Called
Breaking News Today
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
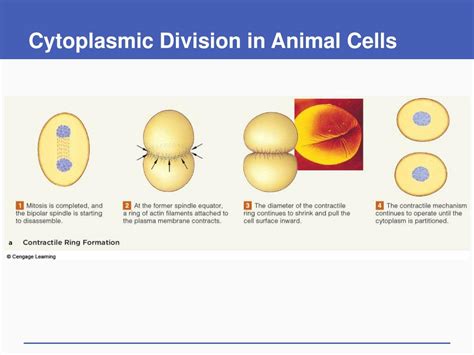
Table of Contents
The Division of the Cytoplasm: A Deep Dive into Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm, a process crucial to successful cell division, is formally known as cytokinesis. This intricate process, tightly coordinated with nuclear division (mitosis or meiosis), ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of organelles and cytoplasmic components. Understanding cytokinesis is fundamental to comprehending cell biology, development, and disease. This article will explore the mechanics of cytokinesis, its variations across different cell types, its regulation, and its significance in various biological contexts.
Understanding the Mechanics of Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is far from a simple splitting of the cell in two. It's a precisely orchestrated event involving a complex interplay of proteins, cytoskeletal elements, and membrane dynamics. The process varies slightly between animal and plant cells due to their differing cell wall structures.
Cytokinesis in Animal Cells: The Role of the Cleavage Furrow
In animal cells, cytokinesis is characterized by the formation of a cleavage furrow. This is a contractile ring of actin filaments and myosin II that assembles beneath the plasma membrane at the cell equator. The actin filaments are organized into parallel bundles, and myosin II acts as a molecular motor, generating the force necessary for constriction.
-
Assembly of the Contractile Ring: The precise mechanism of contractile ring assembly remains an area of active research, but it's understood to involve several key proteins, including RhoA GTPase, which regulates actin polymerization and myosin recruitment. Anillin, a scaffolding protein, plays a critical role in linking the contractile ring to the plasma membrane.
-
Contraction and Furrow Ingression: The actomyosin ring contracts, drawing the plasma membrane inwards. This process, called furrow ingression, progressively deepens the furrow until it eventually bisects the cell. The precise mechanics of ingression are still under investigation, but it likely involves interactions between the contractile ring and membrane-associated proteins.
-
Membrane Fusion and Abscission: As the furrow ingresses, the plasma membrane is pulled inwards, eventually pinching off the two daughter cells. This final stage, called abscission, involves the fusion of the membranes at the furrow's midpoint, followed by the separation of the two daughter cells. Proteins like ESCRT (Endosomal Sorting Complexes Required for Transport) play crucial roles in this final membrane fusion event.
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells: The Construction of the Cell Plate
Plant cells, encased within rigid cell walls, employ a different mechanism for cytokinesis. Instead of a cleavage furrow, they form a cell plate, a new cell wall that divides the cell into two.
-
Phragmoplast Formation: The process begins with the formation of a phragmoplast, a microtubule-based structure that assembles between the two daughter nuclei. The phragmoplast acts as a scaffold for the delivery of cell wall materials to the site of cell plate formation.
-
Cell Plate Growth and Fusion: Vesicles containing cell wall precursors, such as pectin and cellulose, are transported along microtubules to the phragmoplast. These vesicles fuse together to form the cell plate, which grows outwards from the center of the cell, eventually reaching the existing cell wall.
-
Cell Wall Formation: As the cell plate matures, it becomes impregnated with cellulose and other cell wall components, solidifying into a new cell wall that separates the two daughter cells. This new cell wall eventually connects with the pre-existing cell wall, completing the division process.
Regulation of Cytokinesis: A Symphony of Signaling Pathways
Cytokinesis is not an isolated event but rather a tightly regulated process integrated with other phases of the cell cycle. Several signaling pathways ensure proper timing and coordination with nuclear division.
-
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs): CDKs, key regulators of the cell cycle, play crucial roles in controlling the timing of cytokinesis. Specific CDK activities are required for the initiation and completion of cytokinesis.
-
Small GTPases: Small GTPases, such as RhoA and Rac1, act as molecular switches, regulating actin cytoskeleton dynamics during cytokinesis. They control the assembly and contraction of the contractile ring in animal cells and the organization of the phragmoplast in plant cells.
-
Checkpoints: Several checkpoints ensure that cytokinesis only occurs after successful completion of chromosome segregation. These checkpoints prevent the formation of daughter cells with incomplete or damaged chromosomes. Failure of these checkpoints can lead to aneuploidy, a condition where cells have an abnormal number of chromosomes, often associated with cancer.
Cytokinesis and its Significance in Biology and Medicine
Cytokinesis plays a crucial role in various biological processes and is intimately linked to several diseases.
Development and Differentiation:
Precise cytokinesis is essential for proper embryonic development and tissue differentiation. Errors in cytokinesis can lead to abnormal cell numbers and tissue organization, potentially resulting in birth defects. The controlled division of stem cells, for instance, relies on precise cytokinesis to maintain the stem cell pool and generate differentiated cell types.
Cancer:
Dysregulation of cytokinesis is frequently observed in cancer cells. Cancer cells often exhibit defects in cytokinesis, leading to abnormal cell division and the formation of multinucleated cells. This contributes to genomic instability and uncontrolled proliferation, hallmarks of cancer. Targeting cytokinesis mechanisms is therefore an active area of cancer research.
Infectious Diseases:
Some pathogens manipulate host cell cytokinesis to their advantage. For example, certain viruses interfere with cytokinesis to promote their own replication or spread. Understanding how these pathogens hijack the host's cytokinesis machinery is crucial for developing effective antiviral strategies.
Tissue Repair and Regeneration:
Cytokinesis is crucial for tissue repair and regeneration. Efficient cytokinesis ensures that damaged tissues can be repaired through the proliferation and differentiation of cells. Understanding the regulation of cytokinesis in these contexts is important for developing therapies to promote tissue regeneration.
Advanced Topics and Future Directions
Research on cytokinesis is ongoing, with many exciting areas of investigation:
-
The precise molecular mechanisms regulating contractile ring assembly and contraction. Further unraveling these mechanisms could lead to new therapeutic targets for diseases associated with cytokinesis defects.
-
The role of membrane dynamics in cytokinesis. Understanding how membrane trafficking and fusion contribute to abscission is crucial for comprehending the completion of cell division.
-
The interaction between cytokinesis and other cellular processes, such as cell migration and apoptosis. Such interactions highlight the intricate regulatory networks governing cell behavior.
-
The development of novel imaging techniques to visualize cytokinesis in living cells with high resolution. These advanced imaging tools will allow researchers to observe the dynamics of cytokinesis in real time.
Conclusion: Cytokinesis - A Cornerstone of Cell Biology
Cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm, is a fundamental process essential for life. Its precise regulation ensures accurate chromosome segregation and the generation of healthy daughter cells. This intricate process, involving a complex interplay of proteins, cytoskeletal elements, and membrane dynamics, is crucial for various biological functions, from development and differentiation to tissue repair and regeneration. Understanding the mechanisms and regulation of cytokinesis remains a vital area of research, offering significant insights into fundamental biological principles and potential therapeutic avenues for various diseases. Further exploration into this fascinating field promises to reveal even more about the intricacies of cell biology and its impact on health and disease.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Correct Match
Apr 01, 2025
-
The End Of Big Trees Commonlit Answers
Apr 01, 2025
-
All Of The Following People Should Receive W 2 Forms Except
Apr 01, 2025
-
Nurse Logic Knowledge And Clinical Judgment Beginner
Apr 01, 2025
-
First 36 Elements On The Periodic Table
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Division Of The Cytoplasm Is Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
